Journals >Chinese Journal of Ship Research
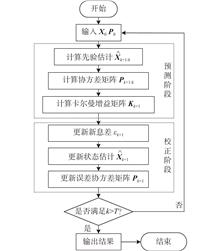
To construct an accurate MMG (mathematical model group) model for a water-jet propulsion unmanned surface vehicle, the traditional extended Kalman filter algorithm and improved extended Kalman filter algorithm are combined with the real-world boat data for parameter identification.
First, based on the traditional EKF algorithm, in order to fully utilize the valuable information hidden in the historical data, an improved EKF algorithm integrating multi-innovation theory and dynamic forgetting factor is proposed. Then, using the real-world unmanned surface vehicle data, the unknown parameters in the MMG model are identified. Finally, the identified parameter values are substituted into the established MMG model, and the rudder angle and main engine speed consistent with the real boat data are input. The heading angle, longitudinal velocity, transverse velocity, heading angle rate and position information data are obtained through simulation, and the comparative analysis is carried out.
The results indicate that compared with the traditional EKF algorithm, the root mean squared error index and the symmetric mean absolute percentage error index of the improved EKF algorithm are closer to 0. Specifically, the root mean squared error index is reduced by up to 20.02% at the highest, and the symmetric mean absolute percentage error index is reduced by 26.84% at the highest.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 38 (2025)
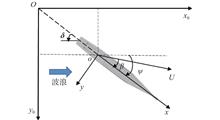
Aiming at the requirements of the real-time and accurate prediction of ship maneuvering motion, this paper investigates the prediction of ship maneuvering motion in regular waves using gray-box modelling to improve the accuracy.
A maneuvering motion equation is proposed to reveal the known movement mechanism. The hydrodynamic forces in calm water are approximated using the Taylor series expansion, and the second-order steady wave drift forces are estimated using empirical formulas, thereby obtaining the mathematical model for predicting ship maneuvering motion in regular waves. To promote the precision of the hydrodynamic expression, the Fourier transform method is adopted to separate the data of the maneuvering and seakeeping motions. A model for hydrodynamic correction and second-order steady wave drift forces is developed on the basis of the maneuvering motion and deep neural network (DNN) data, then submitted into the mechanistic equation of maneuvering motion. Finally, an gray-box modelling incorporation mechanism and data for predicting ship maneuvering motion in regular waves is established.
Taking the Office of Naval Research Tumblehome (ONRT) as an example, the maneuvering motion is predicted with the adoption of the mathematical model and gray-box model respectively. For all simulated cases, the simulation of the unit time step costs 2–3 ms on average, and the average error between the results of the gray-box model and experiments is 94.83%, with the accuracy promoted by an average of 4.50% compared with the mathematical model.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 47 (2025)
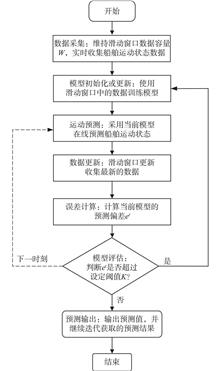
Aiming to address the problem of model inaccuracy caused by ship dynamic changes during actual navigation, this study proposes an adaptive online modeling method for ship maneuvering motion based on an error monitoring mechanism.
The method determines model update timing through a model prediction error monitoring mechanism and realizes the adaptive retraining update of the model based on voyage data by combining the sliding window technique and support vector machine. Taking a KCS container ship as the research object, the method is tested and validated under zigzag maneuvering and turning circle motion scenarios with variable speed, and the influence of the error monitoring mechanism’s hyperparameter selection on the online modeling is analyzed.
The simulation results show that the error detection mechanism can effectively reduce the frequency of online model updating and save computational resources. Compared with the offline method, this method can update the model in time when the dynamic characteristics of the ship change, thereby guaranteeing prediction accuracy.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 58 (2025)
To address the issue of multicollinearity and parameter drift in the identification of hydrodynamic coefficients in ship separated-type models, this paper proposes a method for modeling simplified three-degree-of-freedom modular models based on support vector regression (SVR).
Initially, a processing strategy is introduced to enhance the effectiveness of the sample data. Further, Lasso regression is introduced to select the most influential hydrodynamic coefficients and alleviate multicollinearity. Subsequently, a regression model for the identification of hydrodynamic derivatives is derived for the MMG model. A data centralization and differencing method is then employed to reconstruct the regression model, mitigating the impact of parameter drift on hydrodynamic derivative identification errors.
Simulation experiments demonstrate good agreement between the hydrodynamic coefficient forecast values and numerical simulation results. The calculated values of root mean square error (RMSE) and correlation coefficient (CC) fall within a favorable range.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 65 (2025)
Aiming at the low prediction precision and poor adaptability of ship models based on the data-driven modeling strategy, an enhanced bi-directional long short-term memory (Bi-LSTM) model is proposed for the high-precision non-parametric modeling of ships.
First, the feature extraction of the bi-directional time dimension is realized using bi-directional long short-term memory (Bi-LSTM) neural networks. On this basis, the spatial dimension features of the one-dimensional convolutional neural network (1D-CNN) extraction sequence are designed. Then, a multi-head self-attention (MHSA) mechanism is used to deal with the sequence from multiple angles. Finally, using the navigation data of KLVCC2 ships, the prediction effects of the enhanced Bi-LSTM model are compared with those of the Support Vector Machine (SVM), Gate Recurrent Unit (GRU), and long short-term memory (LSTM) models.
The Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and Mean Absolute Error (MAE) performance indicators of the enhanced Bi-LSTM model in the test set are lower than 0.015 and 0.011 respectively, and the coefficient of determination(R2)is higher than
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 76 (2025)
To address the challenges of path planning for unmanned surface vehicles in complex waters, this paper proposes an improved ant colony optimization(ACO)algorithm based on uneven distributed pheromone and multi-objective optimization.
First, a probabilistic roadmap method (PRM) is used to generate an initial path. Based on the orientation information of the initial path and the endpoint, the ACO algorithm is guided to unevenly distribute the initial pheromone, resulting in higher pheromone concentration of the initial path and endpoint while decreasing the pheromone concentration of other grids in mapping according to the initial path-endpoint distance. Therefore, the problem of the ants' blindness in the preliminary path search improved, the calculation time is shortened thereof. Next, an objective function is constructed for solving the multi-objective path planning problem, and the weights are set to balance the relationship among the safety index, the energy consumption, the tortuosity, so as to providing diversified path to meet the requirement for different scenarios, moreover adaptively adjust the increment of pheromone to strengthen the influence of high-quality path in the whole ants colony based on the pros and cons of the planed paths. Meanwhile, to optimize efficiency improvement, an adaptive adjustment strategy of heuristic matrix coefficient is established, incorporating cosine modulation factors pertaining to iteration numbers. To obtain the global optimal path, quadratic optimization is carried out to reduce turns and turning amplitudes. Finally, on the basis of the maps of two real lakes—Lake Xiangdao (Huangshi ) and Lake Qiandao ( Hangzhou), the experiments are conducted to compare the effects of path planning using the proposed algorithm with that of other algorithms, i.e. traditional ACO, A* algorithm and improved ACO algorithm.
The results indicate that the proposed algorithm has the shortest planning paths, which is 61.71% shorter than that of the traditional ACO algorithm, the farthest distance from obstacles, and the smallest tortuosity. The running time of the algorithm is also improved.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 115 (2025)
Maintaining consistent tracking of surface ships using unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) is particularly challenging due to the target's high maneuverability and complex motion trajectories. Additionally, environmental interferences in marine environments further complicate the task by reducing positioning accuracy. These issues often lead to tracking vibrations and delays, significantly impacting stability and precision. To address these challenges, this study proposes innovative solutions to improve the performance of USVs in maintaining effective target tracking.
This study presents an advanced bidirectional fitting algorithm integrating polynomial fitting and particle swarm optimization (PSO) to address radar sampling errors. By systematically analyzing the correlation between target motion amplitude and radar observation errors, the sampling period is optimized to accurately capture the target's motion patterns. Additionally, the optimal number of sampling points is carefully determined. Polynomial fitting is initially applied to minimize longitudinal errors, followed by secondary horizontal error reduction using PSO. A penalty function is incorporated to impose strict constraints on the fitting range, ensuring that corrected coordinates align with the actual motion capabilities of the target ship. Furthermore, real-time motion data from the USV and the target ship, including target speed, separation distance, and USV performance parameters, are used to develop a robust speed strategy. Geometric methods combined with USV turning dynamics are used to formulate a precise course strategy, enabling optimal speed and trajectory planning.
Rigorous validation through real-vessel experiments shows that the radar data processed with the bidirectional fitting algorithm achieves significantly enhanced smoothness, closely aligning with the ship's actual motion patterns.Moreover, the USV consistently and accurately tracks the target ship by following the optimized speed and course strategies. Vibrations and delays are effectively mitigated, ensuring stable tracking performance throughout the operation process.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 125 (2025)
To make local path planning algorithms more consistent with the maneuvering characteristics of ships, thereby generating safer and more reliable reference paths, this paper proposes a three-dimensional potential field modeling method.
By converting the Cartesian coordinate system to the ellipsoidal coordinate system, it addresses the anisotropy problem of the potential field distribution function. The ship’s potential energy distribution function is calculated by solving the Laplace equation. A control framework combining the potential field model and model predictive control (MPC) algorithm is designed to enhance the adaptability of dynamic real-time local path planning for ships in different scenarios. Simulations are conducted with actual navigation vessels in the waters of the Sutong Yangtze River Highway Bridge area. The three-dimensional potential field model is used to obtain local reference paths, and the MPC algorithm is employed for ship path tracking control simulation experiments.
As the results show, compared to reference paths generated by traditional and improved artificial potential field methods, the three-dimensional potential field model’s local reference paths are superior in terms of length, curve smoothness, maximum steering angle, and average absolute heading error. This model can generate shorter and smoother local paths which are more consistent with the actual maneuvering habits of ships and exhibit less jitter in traffic-intensive scenarios.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 135 (2025)
To enhance the safety and efficiency of maritime traffic, this paper proposes an autonomous collision avoidance decision-making method for unmanned ships based on an enhanced Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) algorithm.
In order to address the issues of low data utilization and poor convergence in traditional DDPG algorithms, we employ Priority Experience Replay (PER) to dynamically adjust experience priority, reduce sample correlation, and utilize the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network to improve the algorithm convergence. Based on the domain knowledge of ships and adhering to the International Regulations for Preventing Collisions at Sea (COLREGs), a model for determining meeting situations and a novel set of reward functions that consider urgent scenarios when other ships fail to comply with the COLREGs are introduced. Generalization experiments are conducted involving two-ship and multi-ship encounters to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
As the experimental results demonstrate, compared to traditional DDPG algorithms, our improved approach enhances the convergence speed by approximately 28.8%.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 172 (2025)
Considering that existing research on autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) obstacle avoidance mainly focuses on low-speed obstacle avoidance for small and medium-sized AUVs and overly simplifies the diverse constraints within and outside the system, a real-time three-dimensional high-speed obstacle avoidance method for large AUVs is proposed.
The method integrates perception, planning, and control modules, enabling large-scale, high-speed, underactuated AUVs to navigate safely and efficiently through the unknown and unstructured ocean floor. First, a robocentric dual-resolution seafloor map is constructed to balance perception accuracy with computational efficiency. Next, a dynamic perception framework incorporating filters and feature extraction and matching is designed to achieve the motion prediction of unknown moving obstacles. Subsequently, global risk-aware path searching and local spatial-temporal trajectory optimization are introduced to generate an aggressive trajectory that satisfies multiple constraints. Finally, a spherical-coordinate feedback controller is employed for trajectory tracking.
In high-fidelity experiments involving long-range seabed traversal, a 13.96-meter-long AUV flexibly avoids dynamic and static obstacles while adhering to the constraints, maintaining a predefined speed of 6.0 m/s.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 181 (2025)
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 15 (2025)
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 25 (2025)
The traditional model predictive control method employs a repeated online optimization approach, resulting in a high computational burden for underactuated ship path-following predictive controller. To address this issue, this paper presents an efficient predictive controller for underactuated ship path following based on the neurodynamic optimization system.
First, the line-of-sight (LOS) guidance principle is employed to mitigate the underactuated problem herein; for kinematic model uncertainty in traditional LOS guidance law, a robust LOS guidance method based on the sliding mode concept is proposed. Furthermore, the sideslip angle induced by external disturbances negatively affects path following. To compensate for this effect, a robust adaptive LOS guidance method is proposed, enhancing robustness against model uncertainty and external disturbances. Second, in order to address the input saturation problem, the model predictive control is adopted herein to transform ship path following problem into the quadratic optimization problem with input constraints. Finally, the neurodynamic optimization solver is proposed based on the projection recurrent neural network herein to solve the quadratic optimization problem with input constraints, enhancing the computational efficiency.
In this study, both simulations for straight line path following and curved line path following are conducted. Overall, the simulation results show that the presented efficient predictive controller can achieve arbitrary path following. Additionally, the comparative simulations are performed, revealing that the presented method exhibits advantage in computational efficiency compared to the Fmincon optimization solver. Specifically, the neurodynamic optimization solver achieves approximately a 90-fold improvement in computational efficiency compared to the Fmincon optimization solver.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 203 (2025)
A dynamic event-triggered collaborative path-following control method for multiple unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) is proposed, considering the constraints of network bandwidth resources, model uncertainties, and external environmental disturbances.
Specifically, a dynamic variable is introduced to design a dynamic event-triggered mechanism at the cooperation layer, and a dynamic event-triggered path parameter update law is developed to reduce network traffic. Additionally, a path-parameter predictor is designed to estimate the path parameters of neighboring USVs during the communication interval. In the guidance layer, a line-of-sight-based guidance law is proposed. Finally, in the control layer, a super-twisting observer is used to estimate the total disturbances, and a super-twisting dynamic control law is developed based on the estimated disturbances.
Stability and Zeno behavior analyses demonstrate that the closed-loop system is input-to-state stable, and the proposed approach does not exhibit Zeno behavior. Comparative simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed dynamic event-triggered cooperative path-following control method for USVs.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 213 (2025)
A data-driven trajectory tracking control scheme is proposed for unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) with uncertain parameters.
First, the USV kinematics subsystem is processed by the backstepping, and we can obtain the virtual control signal of the kinematics subsystem which ensure the accuracy of the system trajectory tracking. Secondly, the data-driven is used to deal with the USV dynamics subsystem to get the controller which reduces the impact of uncertainties such as unknown disturbances and reduce the complexity of controller design.
The stability of the system is proved by analyzing the pseudo Jacobian matrix and the convergence of the tracking error of dynamics and kinematics.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 223 (2025)
Aiming at the problems of unknown ship model parameters and external disturbance and servo constraints, this paper proposes a method for the data-driven online identification of ship parameters and iterative analytical calculation of the optimal control quantity of track tracking control.
A three degrees of freedom dynamics equation of a double propeller ship is constructed, and the extended state observer-multiple innovation recursive least squares interactive algorithm is designed by collecting the motion data of the ship. By approximating the identified ship motion model to a time-invariant linear model in the sampling period, the ship trajectory tracking problem can be transformed into a linear quadratic optimization control problem with constraints and disturbances. The weighted matrix and penalty function are introduced to construct the quadratic performance index including trajectory error, external disturbance, and control constraint inequality. The precise integration method is then used to obtain the analytical solution of the matrix Riccati differential equation and the iterative calculation formula of the finite time state regulator.
Th online identification of the ship motion model parameters and estimation of unknown disturbances are achieved, and a trajectory tracking control algorithm with "no need to worry after startup" is designed, reducing the strict requirements of parameter identification and control algorithms for experimental design.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 232 (2025)
This paper presents a novel approach to the precise control of variable mass unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) during payload deployment tasks, addressing the control challenges caused by unpredictable variations in both mass and draught. The primary objective is to propose an adaptive control method that can effectively adapt to these unknown variations in mass and draught, thereby ensuring the stable and reliable operation of the USV under complex and dynamic mass conditions.
First, regarding to the motion modeling of variable-mass USVs, this study analyzes the impact mechanism of mass variations on the hydrodynamic characteristics of the vehicle. It also analyzes how these variations, through changes in the parameters of the dynamic model, affect the vehicle's motion state. To address the issue that current controller design models are insufficient in analytically and intuitively representing this coupling influencing process, we use the draught term as the reference variable. The progressive coupling relationships among draught and the mass term, added mass term, added moment of inertia term, and various hydrodynamic derivatives are systematically analyzed. Based on this analysis, the mathematical model for the maneuvering motion of the variable-mass USV is then constructed. Secondly, to design an effective estimation method, a super-twisting sliding mode observer is proposed for estimating the unknown draught and mass of the variable-mass USV. This method is based on an analysis of the coupling relationships between mass variations and the vehicle's motion state and control inputs, as described in the maneuvering model of the USV. Subsequently, addressing the motion control problem of variable-mass USVs under unknown mass variations, we propose an adaptive speed control strategy based on the sliding mode observer. Specifically, leveraging the maneuvering motion mathematical model of the variable-mass USV and the draught observations from the sliding mode observer, a feedback linearization method is used to design the adaptive speed control algorithm. The asymptotic stability of the proposed control algorithm is proved using the Lyapunov theory.
A series of simulation experiments are conducted to validate the proposed method. In the mass step-change observation experiment, the super-twisting sliding mode observer demonstrates satisfactory performance. Compared to the traditional sliding mode observer, the average observation errors of the draught and mass are significantly reduced by 43.75% and 43.76%, respectively. Furthermore, it shows rapid convergence when mass changes occur suddenly. In the continuous mass change observation experiment, the observer also performs excellently, exhibiting fast convergence and high accuracy, thus demonstrating significant advantages compared to the traditional observer. The speed control experiments reveal that the designed adaptive speed control algorithm can stably track the target speed under both mass step-change and continuous-change conditions. Although it may require slightly more adjustment time compared to the traditional Backstepping controller, it offers significant advantages in handling variations in mass and draught, achieving superior control performance. In the environmental disturbance experiment, while the adaptive control algorithm maintains stable speed control, demonstrating a certain degree of robustness, it also highlights the need for further improvement in the draught observation method to enhance its disturbance rejection capabilities.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 247 (2025)
This study investigates how to effectively address path-dependent constraints during the path-following of unmanned surface vessels in complex waterways while ensuring navigation safety and stability.
First, performance and feasibility constraints are established for the vessel's navigation based on the precision and safety requirements of autonomous ships in shallow waters. Next, to address the issues of the path parameter representation and convergence requirements of the controller, a barrier Lyapunov function (BLF) combined with a fixed-time convergence strategy is applied. A path-dependent controller capable of converging within a fixed time is then designed, and radial basis function neural networks (RBFNN) and adaptive robust terms are used to handle nonlinearities and environmental disturbances. Finally, the intelligent unmanned surface vehicle model "Dazhi" is used to simulate shallow water effects, and the controller's performance is analyzed through simulations.
The simulation results show that the path tracking error converges rapidly to the desired region without violating the constraints. Compared to the unconstrained case, the controller demonstrates clear advantages in convergence speed and precision, verifying its effectiveness and robustness.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 263 (2025)
In order to solve the track-keeping problem of a fishing vessel under rough sea conditions, a separated track-keeping controller is proposed.
The nonlinear feedback method is used to improve the closed-loop gain shaping algorithm, and an arctan function is introduced to effectively solve the problem of the system's excessive control energy. At the same time, an integral separation design is used to solve the integral term influence of conventional PID (proportion integration differentiation) controllers on the transient performance of the system.
Based on the results of simulation experiments on a common 32.98 m fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP) trawler (model SDB8102) sailing under force 7 of the Beaufort wind scale, the steady state trajectory error is less than 3 m, which verifies that the method is safe, feasible, concise and effective.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 272 (2025)
Intelligent ships at sea are influenced by environmental interference, and the influence of the uncertainty of model parameters leads to the problem of low ship motion control accuracy, so it is necessary to improve the resistance of the ship's control algorithm to such interference.
Based on an L1 adaptive control algorithm and Gaussian process regression (GPR) model, an L1 adaptive controller combined with a GPR model controller for underactuated ship path tracking control is proposed, and the control law is derived using the Lyapunov control function. The L1 adaptive controller is a new technique that considers both robustness and fast adaptivity. The closed-loop control system has proven to be consistently globally asymptotically stable, while the GPR model is used to model sudden disturbances and environmental disturbances during ship navigation, and achieve the rapid elimination of the effects of such disturbances in combination with the adaptive law.
The simulation results show that adding the GPR model reduces the average rudder amplitude by 14.9%, average absolute heading error by 23.2%, and maximum absolute heading error by 12.1%. The effects of environmental disturbances can be cancelled out faster and a stable state reached more rapidly than in cases without added disturbances.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 278 (2025)
In the process of marine resource development, some thrusters of over-actuated ships are prone to failures during operation, resulting in a decrease in propulsion power. This paper aims to propose a fault-tolerant control method based on improved adaptive control allocation to enhance the fault tolerance and the safety reliability of ship operations.
Firstly, an adaptive control allocation algorithm is designed to online reconstruct the configuration matrix of the faulty propulsion system based on the current propulsion capacity, reducing the thrust deviation. Additionally, a differential term is added to the adaptive update law to suppress the thrust jitter. Then, the unprocessed control allocation error is regarded as a lumped disturbance, which is estimated and compensated by a modified extended state observer. Finally, the boundedness of the error in the closed-loop control system is proved using Lyapunov theory, ensuring the theoretical feasibility of the method.
Simulation and modeling experiments are carried out using a self-developed over-actuated ship experimental prototype. In terms of the upper limit of positioning error, the IACA method demonstrates a significantly lower upper limit of positioning error across all directions when compared to the ACA and QPCA methods. Furthermore, regarding system dynamic performance, the IACA method facilitates rapid stabilization of the system to a steady state following thruster failure. In the simulation experiments, the abrupt changes in disturbance estimation values, actual force, and thrust deviation associated with the IACA method were minimal post-failure, indicating a rapid recovery. Additionally, the adaptive parameter updates were both faster and more stable, exhibiting minimal jitter, effectively enhancing the system's performance in terms of jitter reduction.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 289 (2025)
The heave and pitch motions of a catamaran under severe sea states vary drastically, and the amplitudes of the motions are too large, which seriously affects seaworthiness. To address this problem, this paper proposes a form of vertical stabilization control that combines low-high gain feedback control with high order extended state observer (HOESO) feed-forward compensation.
First, the coupled catamaran vertical motion model is approximately decoupled, and the coupling of the heave and pitch motions, wave disturbances, etc. are regarded as lumped disturbances which are extended into three virtual state quantities. HOESO is designed to improve the accuracy of disturbance estimation, and the estimated values are used for feed-forward compensation. Second, a low-high gain feedback controller is proposed to achieve vertical stabilization and reduce the conservatism of the low gain feedback control while ensuring that the attachment inputs of the T-foil and flaps satisfy the constraints. Finally, MATLAB is used to build the vertical stabilization control system of the catamaran for simulation.
The results show that the proposed control strategy can effectively suppress the amplitudes of the heave and pitch motions and improve the stability of the vertical motion. The heave displacement is reduced by about 49.47%, while the pitch angle is reduced by about 53.83%.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 300 (2025)
An adaptive neural control (ANC) scheme with specified performance is proposed for the tracking control of marine autonomous surface ships (MASS) subject to uncertain model parameters and unknown external environmental disturbances in cross-water scenarios.
Under the back-stepping design framework, a neural network is utilized to approximate the uncertain model parameters and unknown external environmental disturbances. A novel specified performance function is constructed and combined with the barrier Lyapunov function (BLF) to transform the cross-water design, while the dynamic surface control technique is employed to reduce the system's computational complexity. Stability analysis is then performed by means of Lyapunov theory to demonstrate that all signals within the control system are bounded.
The simulation results show that the designed control scheme is not only capable of solving the cross-water tracking control of MASS, but that the tracking error can satisfy the convergence to a given bounded range within a predefined time offline.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 309 (2025)
This study aims to solve the problem of path-following control under environmental disturbances and model uncertainties, especially the effects of external wind and wave environments.
Based on a model predictive control (MPC) controller, improved model-free adaptive control (IMFAC) is introduced as the path following control compensator. The error between the ship's actual state and predicted state is corrected to solve the problem of the insufficient accuracy of the model under environmental disturbances such as sudden crosswinds and external wind waves, thereby improving the precision of path-following control.
Ship path-following control simulation experiments are conducted with a scaled-down KVLCC2 ship model. As the results show, compared with traditional MPC control, the MPC-IMFAC method reduces the maximum absolute heading error of the ship by 25.4% under sudden disturbances, and the average absolute heading error decreases by 2.6% under time-varying environmental disturbances.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 317 (2025)
This paper seeks to provide a solution for the formation control issue that arises when autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) are subjected to interference from obstacles and complex ocean currents.
To tackle the issue of AUV hysteresis resulting from an overly rapid predicted convergence speed during dynamic obstacle avoidance, a multi-AUV formation adaptive control method (NDP-ABS) based on brain dynamics model prediction is created. Active and inhibitory sources are created to solve the local optimization problem of potential field methods. When paired with optimal control, dynamic obstacle avoidance, formation control, and predicted tracking are accomplished. Second, a nonlinear adaptive backstepping method is used to design the AUV expected tracking controller, which resolves the interference of shallow ocean current disturbances and nonlinear factors on the AUV expected tracking control in consideration of unknown nonlinear factors and ocean current disturbances introduced in the control law of the NDP process. Finally, Lyapunov theory is used to demonstrate the system's stability.
The anti-interference and obstacle avoidance performance of the NDP-ABS system are tested in six sets of comparative simulation tests, and the results confirm its efficacy.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 326 (2025)
To address the covert communication requirements of autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), this study proposes a near-surface communication mode equipped with a foldable antenna.
Utilizing strip theory to predict the wave forces of regular waves, a five-degree-of-freedom motion equation for the AUV near the water surface is established. Simulation studies on wave-following control of the AUV are conducted using the line-of-sight (LOS) method and PID controllers.
Simulation results demonstrate that the normal tracking stability accuracy of the spatial trajectory is 0.247 6 m, and the vertical tracking stability precision of wave-following motion is 0.232 6 m, indicating satisfactory control performance. Statistical analysis reveals that wave height and frequency significantly impact control effectiveness; larger wave height and frequency result in poorer control outcomes.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 340 (2025)
In order to improve the robustness of autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) controllers to environment modeling errors, this paper proposes a reinforcement learning control strategy that introduces contextual information and a course-learning training mechanism.
First, the contextual information is embedded into the policy network using the interaction history data as part of the policy network input; second, the course-learning training mechanism is designed to gradually increase the interference strength during the training process to avoid training instability and early stopping phenomenon caused by too much interference. Fixed-depth control experiments are conducted in a simulation environment, and the effectiveness of the algorithm is further verified using a real AUV in a tank.
The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can improve the convergence speed by 25.00% and the reward steady state value by 10.81%, effectively improving the training process. The proposed algorithm can realize static-free tracking in the simulation environment. In the tank experiment, compared with the domain randomization algorithm and baseline algorithm, the average depth position tracking error of our method was reduced by 45.81% and 63.00% respectively, and the standard deviation was reduced by 36.17% and 52.76% respectively, effectively improving tracking accuracy and stability.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 350 (2025)
To improve the ability of autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) formations to perform tasks in complex obstacle scenarios, a distributed three-dimensional affine formation shape maneuver control method is proposed for multi-AUV formations.
Based on the affine transformation theory and stress matrix, AUV formation shape can achieve rotation, scaling, shear, coplanarity, collineation, or their combination. Meanwhile, the yaw consistency of the multi-AUV formation is achieved based on the Laplacian matrix. Furthermore, a non-singular integral terminal sliding mode controller is employed to ensure that the multi-AUV formation can track the desired trajectory fast and with high accuracy.
Through high-fidelity simulation experiments, the proposed AUV formation maneuver control method can drive the multi-AUV formation to realize the high-precision maneuvering transformation of a three-dimensional formation with high maneuverability and strong robustness.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 360 (2025)
The rapid integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into maritime technology has driven unprecedented advancements in unmanned surface vehicles (USVs), positioning them as a crucial force in future maritime operations and military transformations. The intelligent navigation system is the core of USVs, responsible for environmental perception, decision-making, and motion control, which collectively enable autonomous mission execution and integration into systematic operations. This study provides a comprehensive review of the fundamental technologies underpinning USV intelligent navigation, critically evaluates existing challenges, and proposes future research directions to advance and expand the application of intelligent navigation technologies for USVs. The research aims to bridge existing knowledge gaps, providing a foundation for the further development of autonomous maritime systems.
This research provides a comprehensive review of the current state of intelligent navigation technologies for USVs, focusing on three critical areas: environmental perception, decision-making and planning, and motion control. (a) In the domain of environmental perception, the primary sensing modalities include visible light, infrared, sonar, electromagnetic signals, navigation radar, and LiDAR. With advancements in multi-source information fusion technology, perception techniques have evolved from relying on single sensors to utilizing multi-sensor fusion, transitioning from object-level fusion to feature-level fusion. Despite these advancements, achieving accurate and efficient environmental perception remains a key challenge. The ability to provide real-time, comprehensive environmental awareness is essential for USVs to navigate autonomously in complex maritime conditions. (b) For decision-making and planning, a variety of methodologies, including operations research, optimization algorithms, and AI-based approaches, have been employed to generate optimal decisions under multiple constraints, such as mission parameters, payload configurations, and environmental factors. Existing technologies facilitate global path optimization, target tracking, and emergency collision avoidance under predefined conditions. However, challenges remain in multi-objective adversarial decision-making and path planning in highly dynamic and adversarial environments, especially under strong external interferences. The ability to enhance decision-making robustness in these scenarios is crucial for advancing autonomous USV capabilities. (c) In motion control, various algorithms such as proportional-integral-derivative (PID) control, model predictive control (MPC), model-free adaptive control (MFAC), linear quadratic regulators (LQR), robust control, and sliding mode control have been applied to achieve accurate trajectory tracking, course keeping, and speed regulation. Current advancements allow for precise control under design conditions; however, adaptive control remains a challenge in scenarios with extreme environmental variations. Moreover, effective control of roll and pitch motions remains underdeveloped, limiting USV stability in high sea states. Motion control techniques serve as the foundation of USV intelligent navigation, ensuring the successful implementation of autonomous navigation systems.
The study identifies key limitations. In environmental perception, while current technologies allow for target detection and identification in open seas, their accuracy significantly decreases under adverse weather conditions, such as fog, heavy rain, and high sea states. Real-time wave field perception remains inadequate, further compromising navigation safety in dynamic operational conditions. Decision-making and planning algorithms, though effective in structured mission scenarios, struggle with the complexity of dynamic constraints, adversarial interactions, and unexpected environmental disturbances in real operations. Motion control strategies, while efficient under nominal operating conditions, require enhanced adaptability to handle sudden environmental shifts and complex vessel dynamics. The inability to manage roll and pitch movements effectively limits the operational capability of USVs in high sea states.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 3 (2025)
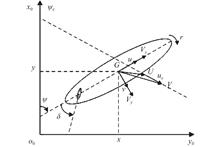
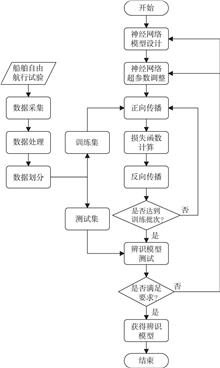
It is difficult to achieve comprehensive parameter identification in multiple dimensions and degrees of freedom using traditional parameter identification methods. In order to obtain the real-time complex parameters and attitude information of ships, and ensure the stability and safety of ships during navigation, an improved wild horse optimizer (IWHO) is introduced into the ship parameter identification method. It is then combined with traditional ship identification methods to improve the accuracy of ship parameter identification.
On the basis of establishing a longitudinal motion model of the ship, a dynamic inertia weight design is introduced to further optimize the wild horse optimizer and complete the design of the longitudinal parameter identification method.
By comparing and analyzing the tracking performance of ship identification models using different algorithms, as well as the identification results of ship parameters under different wave encounter angles, it is found that IWHO has an identification error of about 1%, which is lower than those of other algorithms. Therefore, the identification model of this algorithm has a more accurate tracking effect on the ship's attitude during navigation.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 85 (2025)
Due to mixed-frequency multi-source disturbances, unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) encounter challenges in accurately capturing state information and ensuring path-tracking precision. To address this issue, a composite anti-disturbance control method based on an extended state observer combined with Kalman filter (KFESO) is proposed for distributed cooperative path following of multiple USVs.
Firstly, an extended state observer combined with Kalman filter is constructed to estimate the state variables and lumped disturbances of USVs. Secondly, a distributed state observer is designed to obtain the speed information of the virtual leader. Based on the consistency theory and the line-of-sight guidance law, a kinematic cooperative controller is designed by combining the output of the KFESO and the estimated reference speed. Furthermore, a kinetic anti-disturbance controller is designed using the backstepping method and the dynamic surface control technique. The Lyapunov stability theory is employed to prove that all error signals in the control system are uniformly ultimately bounded.
Simulation experiments show that the proposed method can accurately obtain the states of USVs. Under mixed-frequency multi-source disturbances, compared with the standard ESO-based control method, it has higher tracking precision and stronger anti-disturbance ability. Regarding path tracking trajectories, the proposed method achieves reduced lateral deviations and more stable trajectories. For position errors, the convergence times are comparable, but the proposed method effectively eliminates oscillations. In terms of path parameter coordination error, the proposed method can stabilize the formation, whereas the comparison method suffers from high-frequency oscillations. In terms of state estimation accuracy, the proposed method significantly improves the estimation accuracy of various state variables, enables the distributed state observer to effectively estimate the speed of the virtual leader, and achieves smaller errors in speed and control force (moment), effectively mitigating the frequent actuator response to noise.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 191 (2025)
In order to improve the economy and safety of ship navigation path in actual sea environment, this paper proposes a ship global path planning method with an improved Deep Q-Network (DQN) algorithm.
First, a prioritized experience replay (PER) mechanism is introduced to the DQN to give higher weights to important samples and improve learning efficiency. Next, its network structure is improved through a duel network and noise network, enabling it to evaluate the values of specific states and actions more accurately and generalization capabilities.
An experiment is carried out in the marine environment near Manila, and the results show that compared with the A* algorithm and DQN algorithm, the improved algorithm reduces the path length by 1.9% and 1.0% respectively, and the number of turning points by 62.5% and 25% respectively.
- Publication Date: Feb. 28, 2025
- Vol. 20, Issue 1, 107 (2025)