Zhijian Wu, Xuefeng Peng. Research Progress of Mid-Infrared Supercontinuum and Its Coherence Based on Chalcogenide Fibers[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(17): 1700003
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 60, Issue 17, 1700003 (2023)
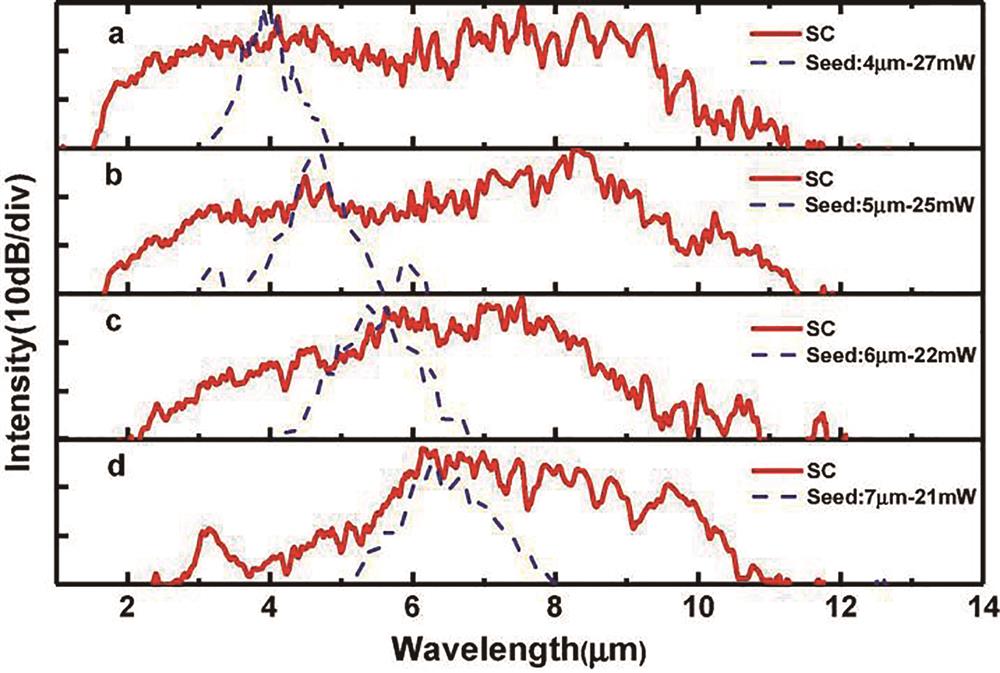
![SC generation in 13 cm-long Ge-As-Se fiber pumped with different wavelength[20]](/richHtml/lop/2023/60/17/1700003/img_01.jpg)
Fig. 1. SC generation in 13 cm-long Ge-As-Se fiber pumped with different wavelength[20]
![Transmission loss characteristic of Ge-Sb-S fiber[24]. (a) Loss diagram of Ge-Sb-S fiber (inset: output spot at 1.55 μm); (b) transmission efficiency of Ge-Sb-S fiber (inset: cross section of Ge-Sb-S fiber)](/richHtml/lop/2023/60/17/1700003/img_02.jpg)
Fig. 2. Transmission loss characteristic of Ge-Sb-S fiber[24]. (a) Loss diagram of Ge-Sb-S fiber (inset: output spot at 1.55 μm); (b) transmission efficiency of Ge-Sb-S fiber (inset: cross section of Ge-Sb-S fiber)
Fig. 3. The SC of Ge-Se-Te fiber[9]. (a) Optical fiber preform and cross section of fiber under electron microscope; (b) loss and dispersion of fiber; (c) experimental setup for enerating SC; (d) SC generated under experiment; (e) SC generated under simulation
Fig. 4. Structure and optical properties of all-solid hybrid MOF[30]. (a) Structure of As2Se3-AsSe2-As2S5 fiber; (b) transmittance for three glasses; (c) dispersion curves of As2Se3-AsSe2-As2S5 fiber with different core diameters
Fig. 5. Optical properties and structure of Ge-Sb-Se MOF[31]. (a) Cross-section of fiber; (b) output of SC
Fig. 6. Structure and optical properties of four-hole chalcohalide suspended core fiber[35]. (a) Cross section of four hole chalcohalide suspended core fiber; (b) transmittance for two glasses; (c) represents the SC produced by the experiment and simulation of four hole chalcohalide suspended core fiber at different wavelengths
Fig. 7. Optical properties of Ge-As-Se-Te tapered fiber[38]. (a) Structure diagram of tapered fiber (inset: represent untapered, taper waist, and transition region respectively); (b) loss diagram of fiber (inset: transmittance of core glass); (c) dispersion curves of Ge-As-Se-Te fiber with different fiber core diameters; (d) output of SC
Fig. 8. Structure diagram of cascade pump[43]
Fig. 9. Output SC of SiO2-ZBLAN-As2Se3 PCF[51]. (a) Cascade system structure for generating SC; (b) SC generated in ZBLAN fiber; (c) SC generated in As2Se3 fiber
Fig. 10. Double-cladding Ge-As-Se-Te fiber[55]. (a) SC output under different pump conditions; (b) first-order coherence
Fig. 11. GeS2-GaS3-CsI chalcohalide microstructure fiber[56]. (a) Cross section of optical fiber; (b) dispersion curves at different apertures; (c) SC output and coherence curve
Fig. 12. Double-cladding Ge-As-Se-Te tapered fiber[11]. (a) Structure and refractive index profile; (b) dispersion curve; (c) SC output; (d) coherence curve
|
Table 1. Physical parameters of low loss chalcogenide fiber matrix materials
|
Table 2. Main research results of SC spectrum generation with three different types in recent year
|
Table 3. Main achievements of output power of chalcogenide fibers in recent years
|
Table 4. Main achievements of SC coherence of chalcogenide fibers with different types in recent years
Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



