Tanbin Shao, Kecheng Yang, Min Xia, Wenping Guo. Techniques and Applications of Chromatic Confocal Microscopy[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(12): 1200001
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 60, Issue 12, 1200001 (2023)
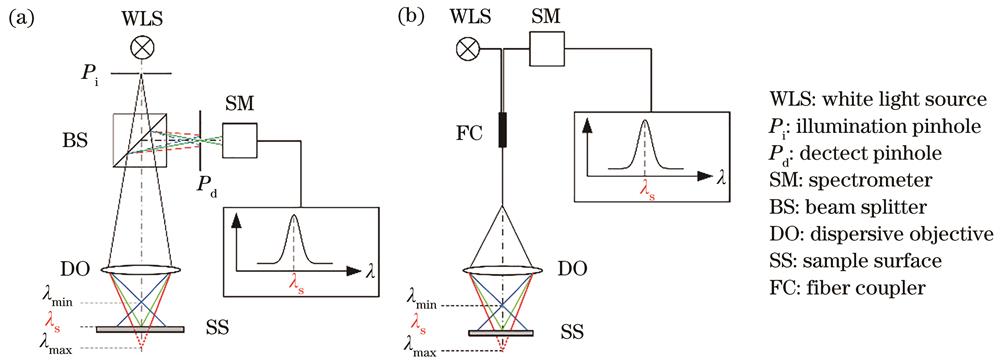
Fig. 1. Schematics of chromatic confocal microscopy. (a) Based on beam splitter; (b) based on fiber coupler
![Schematic diagram of a beam scanning chromatic confocal microscope[7]](/richHtml/lop/2023/60/12/1200001/img_02.jpg)
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of a beam scanning chromatic confocal microscope[7]
Fig. 3. Schematic diagrams of the line-scanning chromatic confocal sensor[20]
Fig. 4. Drawing of a chromatic confocal θ-microscope[24]
Fig. 5. Schematic of the snapshot chromatic confocal matrix sensor[19]
Fig. 6. Experimental setup and scanning pattern for the microLED-based chromatic confocal microscope[37]. (a) Experimental setup; (b) schematic pattern of the scanning microLED array
Fig. 7. Schematic diagrams of dispersion focusing and experimental prototype of CCM[61]. (a) Schematic diagram of the negative dispersion phenomenon of FZP; (b) experimental prototype
Fig. 8. Schematic of a chromatic confocal measurement system[4]
Fig. 9. Prior self-reference strategy by pre-scanning progress[44]
Fig. 10. Measurement flowchart with the prior self-reference strategy[44]
Fig. 11. Fluctuation of peak finding results of different algorithms[40]. (a) Centroid method; (b) modified centroid method by the interpolation density of 5; (c) modified centroid method by the interpolation density of 9
Fig. 12. Flowchart of mean-shift iterative algorithm
Fig. 13. Schematic of physical slit and virtual slit detection[81]. (a) Physical slit; (b) virtual slit
Fig. 14. Cross-sectional surface profile of the 8 μm step sample[37]
Fig. 15. Reconstructed 3D image of an onion epidermis and its volume image[37]. (a) 3D image; (b) volume image
Fig. 16. Schematic diagrams of line-scanned chromatic confocal microscope[84]. (a) Optical configuration; (b) prototype system
Fig. 17. Schematic diagrams of the spatially matching image fiber pairs[84]. (a) Optical configuration of fiber pairs; (b) optimal design of the fiber core diameter and fiber pitch
Fig. 18. Optical system configuration[33]: (a) DMD-based chromatic confocal microscopic system; (b) DMD projection mode; (c) corresponding CCD sensors
Fig. 19. Light intensity distribution obtained using four different projecting spot sizes[33]
Fig. 20. Experimental results[18]. (a) Comparison between the original spectrum signal and the processed signal after one-time deconvolution (the above is the original one while the bottom is the processed one); (b) depth response curves obtained by different number of iterations; (c) relationship between iteration number and FWHM of depth response curve
Fig. 21. Media 1[92]. (a) CCM image of porcine buccal mucosa; (b) an image of the same tissue from the Lucid Vivascope confocal microscope
Fig. 22. Media 2[92]. (a) CCM image of porcine buccal mucosa; (b) an image of the same tissue from the Lucid Vivascope confocal microscope
Fig. 23. Schematic of chromatic confocal endoscope[27]
Fig. 24. Comparison of confocal images in human fingers[27]. (a) Confocal images of human fingers obtained by CCE; (b)(c) cross-sectional and frontal confocal images of human fingers obtained with a portable confocal microscope
Fig. 25. Cross-section confocal images of human lower lip[27]. (a) Confocal image of human lower lip internal section obtained by CCE; (b) Frontal confocal image of human lower lip obtained by portable confocal microscope
Fig. 26. System structure and dispersion probe schematic diagram[94].(a) Schematic of the chromatic confocal system; (b) schematic of the dispersion probe; (c) structure of the annular aperture; (d) the beam of approximately fixed angle of incidence
Fig. 27. Three-dimensional thickness topography of film 3[94]
Fig. 28. Confocal images acquired with the experimental system[99]. (a) Standard resolution target; (b) optical section of a microprocessor chip; (c) optical section of the same chip acquired at a different level; (d)-(f) identical to those directly above, however, the optical sectioning strength of the images has been enhanced
Fig. 29. Structural configuration of the on-machine measurement system[101]
Fig. 30. Schematic presentation of the principle of operation of the optical system[104]
Fig. 31. The spectral data acquired by the detector in two states[104].(a) The offline regime; (b) the online regime
|
Table 1. Performance comparison of different peak extraction algorithms[42]
| |||||||||||||||||||
Table 2. Thickness measurements of different instruments[94]
|
Table 3. Form error parameters of the on-machine and offline measurements[101]

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



