Wenbin Ji, Chuncheng Liu, Shijie Dai, Riqing Deng. Effect of Substrate Material and Powder Feeding Speed on M2 High-Speed Steel Using Selective Laser Melting[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(1): 0116004
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 60, Issue 1, 0116004 (2023)

Fig. 1. Morphology of M2 HSS powder
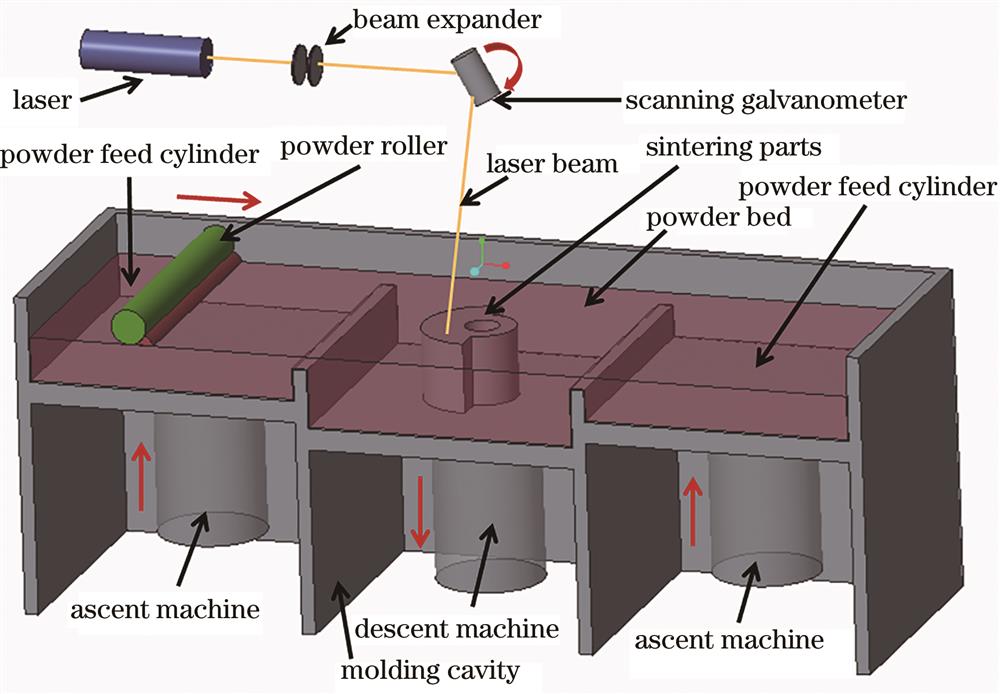
Fig. 2. Forming principle diagram
Fig. 3. Metal printing process in laser selective melting
Fig. 4. Cubic specimen formed by SLM and size of tensile specimen. (a) Cubic specimen; (b) tensile specimen
Fig. 5. Effect of substrate materials on Rockwell hardness and tensile strength of M2 HSS formed by SLM
Fig. 6. Simulation results of residual stress of M2 HSS formed by SLM with different substrate materials
Fig. 7. Comparison of microstructure of M2 HSS formed by SLM with different substrate materials. (a) Stainless steel substrate; (b) high-speed steel substrate
Fig. 8. Effect of powder feeding speed on Rockwell hardness and tensile strength of M2 HSS formed by SLM
Fig. 9. Comparison of microstructure of M2 HSS formed by SLM at different powder feeding speeds. (a) 150 mm/s; (b) 20 mm/s
Fig. 10. Microstructure of M2 HSS under different magnifications. (a) Rotation angle between layers is 90°; (b) network structure; (c) a large number of columnar crystals; (d) (e) spheroidization and micro-porosity; (f) micro-cracks
Fig. 11. XRD patterns of M2 HSS samples by selective laser melting
|
Table 1. Chemical composition of M2 HSS (W6Mo5Cr4V2) powder
|
Table 2. Single factor experimental design of M2 HSS formed by SLM
|
Table 3. Thermal physical properties of high-speed steel and stainless steel

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



