Zhiwei TAO, Congming DAI, Pengfei WU, Yichong REN, Haiping MEI, Wenqing XU, Gang XU, Jie TONG, Yunsong FENG, Ruizhong RAO, Heli WEI. Atmospheric Effects of Star Imaging(I ):Sky Polarization[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2023, 52(5): 0552209
Search by keywords or author
- Acta Photonica Sinica
- Vol. 52, Issue 5, 0552209 (2023)
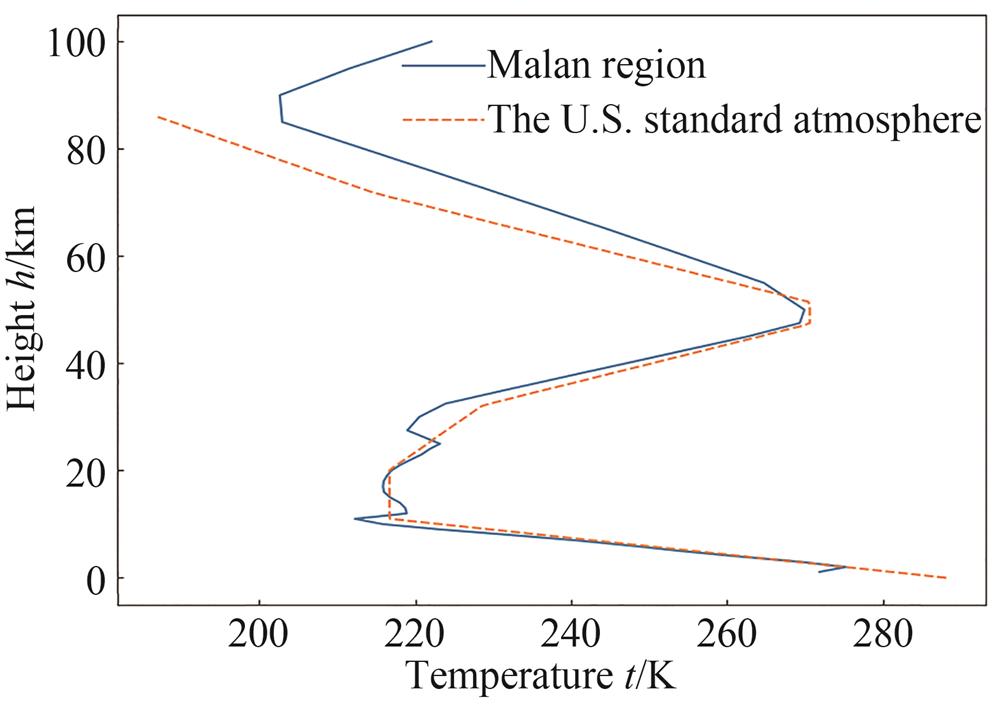
Fig. 1. Temperature profile of Malan region and the U.S. standard atmosphere

Fig. 2. Aerosol extinction profile in Malan region on November 27,2015(measured by lidar)
Fig. 3. Variation of the elements of the scattering phase matrix with scattering angle under different wavelengths in the lowest atmospheric layer
Fig. 4. Flow chart for solving sky polarization distribution characteristics based on the doubling and adding method
Fig. 5. Variation of spectral radiant flux density with wavelength under AM1.5 standard
Fig. 6. Observation geometry of star sensor
Fig. 7. Distribution of sky irradiance(I component)at a solar zenith angle of
Fig. 8. Distribution of sky Q component at a solar zenith angle of
Fig. 9. Distribution of sky U component at a solar zenith angle of
Fig. 10. Distribution of sky polarization at solar zenith angle of
Fig. 11. Distribution of sky polarization at solar zenith angle of
Fig. 12. Distribution of sky polarization at solar zenith angle of
Fig. 13. Distribution of sky polarization at solar zenith angle of
Fig. 14. Distribution of sky polarization at solar zenith angle of
Fig. 15. Distribution of sky polarization at solar zenith angle of
Fig. 16. Variation of polarization with observation angle for different observation altitudes at 0.55 μm
Fig. 17. Variation of polarization with observation angle for different observation altitudes at 0.9 μm
Fig. 18. Variation of polarization with observation angle for different observation altitudes at 1.65 μm
Fig. 19. Variation of polarization with observation angle for different solar zenith angles at a wavelength of 1.65 μm and an azimuth of
Fig. 20. Variation of polarization with observation angle for different solar zenith angles at a wavelength of 1.65 μm and an azimuth of
Fig. 21. Variation of polarization with observation angle at different wavelengths for a solar zenith angle of
Fig. 22. Variation of polarization with observation angle at different wavelengths for a solar zenith angle of
Fig. 23. Variation of polarization with observation angle at different wavelengths for a solar zenith angle of
|
Table 1. The relationship between the wavelength and the spectral radiant flux density used in this calculation
|
Table 2. Fixed parameters used in this calculation

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



