Fang-Kun TIAN, Li-Kun AI, Guo-Yu SUN, An-Huai XU, Hua HUANG, Qian GONG, Ming QI. Influence of InyAl1-yAs graded buffer layer on properties of InP-HEMT materials[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2022, 41(4): 726
Search by keywords or author
- Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves
- Vol. 41, Issue 4, 726 (2022)

Fig. 1. Hall mobility and electron concentrations in different channel indium contents
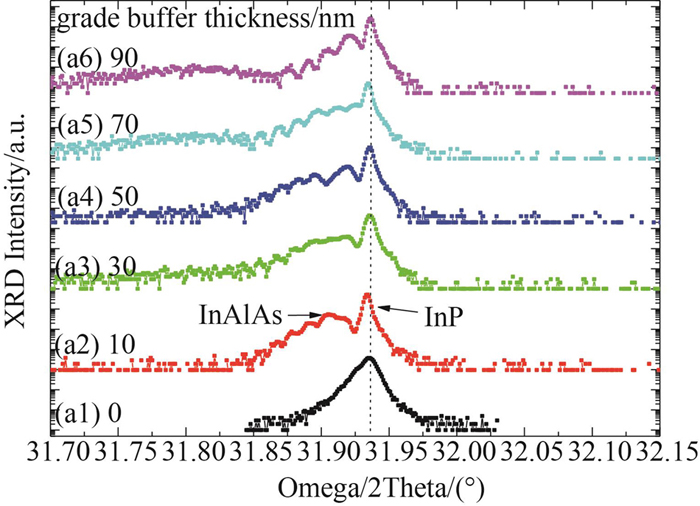
Fig. 2. HRXRD(004)ω-2θ scans for InAlAs graded buffer layer with different thickness
Fig. 3. The surface morphology of the InAlAs graded buffer layer with different thickness
Fig. 4. The surface morphology of the InGaAs channel with different InAlAs graded buffer layer thickness
Fig. 5. Hall mobility and electron concentrations in different InAlAs graded buffer layer thickness
Fig. 6. The surface morphology of the InAlAs graded buffer layer with different aluminum contents
Fig. 7. The surface morphology of the InGaAs channel with different aluminum contents
Fig. 8. TEM energy spectrum image of InP-HEMT with InAlAs graded buffer layer
Fig. 9. TEM Cross-sectional image of InP-HEMT with InAlAs graded buffer layer
Fig. 10. Hall mobility and electron concentrations in different InAlAs graded buffer layer aluminum contents
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 1. InP-HEMT structure
|
Table 2. Properties of InAlAs graded buffer layer with different thickness
|
Table 3. Properties of InAlAs graded buffer layer with different aluminum contents

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



