Bo Chen, Baojie Zhu, Yifan Wu, Pengpeng Sang, Jixuan Wu, Xuepeng Zhan, Jiezhi Chen. Laser processing induced nonvolatile memory in chaotic graphene oxide films for flexible reservoir computing applications[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2024, 45(12): 122403
Search by keywords or author
- Journal of Semiconductors
- Vol. 45, Issue 12, 122403 (2024)
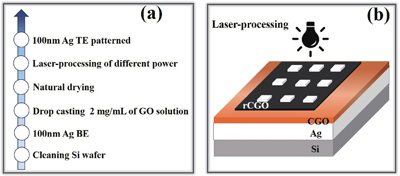
Fig. 1. (Color online) (a) The fabrication process for the rCGO memristor. (b) The schematic images of the rCGO memristor structure.
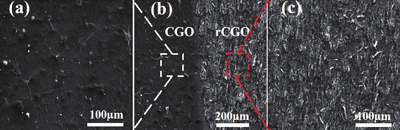
Fig. 2. (Color online) SEM images of the rCGO memristor. (a) Non-laser-processed region. (b) Comparison of non-laser-treated and laser-treated regions. (c) Laser-processed region.
Fig. 3. (Color online) The electrical performance of rCGO memristor. (a)−(c) Resistive switching behaviors under laser processing with 0, 18, and 22 mW power. (d) The summary of resistance values with different laser power.
Fig. 4. (Color online) (a) Schematic image of RC network based on the rCGO memristor. (b) The read current and the pulse train for reservoir computing of rCGO memristor.
Fig. 5. (Color online) (a) The diagram of the rCGO memristor with a tunable control terminal. (b) The corresponding current of the rCGO memristor with the control terminal at locations 1, 2, and 3 (applying voltages of 3 V). (c) The corresponding current of the rCGO memristor with different electric field directions when the control probe is at location 1. (d) The NRMSE results obtained by Hénon map.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 1. The elemental analysis of laser-processed region and non-laser-processed region.

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



