Zeyu Wang, Sen Xiang, Huiping Deng, Jin Wu. Panoramic Three-Dimensional Reconstruction Method Based on Multi-View Encoded Light Field[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(12): 1210009
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 60, Issue 12, 1210009 (2023)

Fig. 1. Framework of proposed method
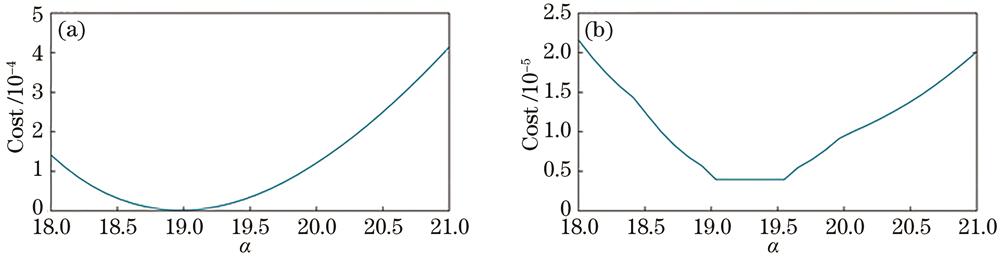
Fig. 2. Cost curves. (a) Cost curve of proposed method; (b) cost curve of conventional light field
Fig. 3. Schematic diagrams of subpixel resampling. (a) Subpixels at different shear values; (b) subpixel sampling method
Fig. 4. Multi-angle fusion. (a) Sampling schematic; (b) point cloud fusion
Fig. 5. Schematic diagrams of point cloud processing for overlapping parts.(a) Overlapping point clouds; (b) point cloud octree for voxelization; (c) overlapping points; (d) overlapping point processing effect
Fig. 6. Schematics of flying pixel. (a) Generation principle of flying pixels; (b) errors brought by flying pixels; (c) effect after removing flying pixels
Fig. 7. Experimental images. (a) Conventional light field single viewpoint light path; (b) phase-encoded light field single viewpoint light path; (c) 720° multi-view light path, both applicable to conventional light field and phase-encoded light field; (d) 360° horizontal circular light field light path
Fig. 8. Experimental data comparison of dog dataset. (a) MVS; (b) CMVS; (c) conventional light field method[10]; (d) proposed method; (e) ground truth
Fig. 9. Experimental data comparison of head dataset. (a) MVS; (b) CMVS; (c) conventional light field method[10]; (d) proposed method; (e) ground truth
Fig. 10. Experimental data comparison of stone dataset. (a) MVS; (b) CMVS; (c) conventional light field method[10]; (d) proposed method; (e) ground truth
Fig. 11. Results from different angles of proposed method. (a) conventional light field method[10]; (b) proposed method; (c) ground truth
Fig. 12. Comparison of reconstruction effect of dog dataset. (a) 7×7 phase-encoded light field; (b) 5×5 phase-encoded light field; (c) 3×3 phase-encoded light field; (d) 7×7 conventional light field; (e) 5×5 conventional light field; (f) 3×3 conventional light field
Fig. 13. Comparison of reconstruction effect of head dataset. (a) 7×7 phase-encoded light field; (b) 5×5 phase-encoded light field; (c) 3×3 phase-encoded light field; (d) 7×7 conventional light field; (e) 5×5 conventional light field; (f) 3×3 conventional light field
Fig. 14. Comparison of reconstruction effect of stone dataset. (a) 7×7 phase-encoded light field; (b) 5×5 phase-encoded light field; (c) 3×3 phase-encoded light field; (d) 7×7 conventional light field; (e) 5×5 conventional light field; (f) 3×3 conventional light field
Fig. 15. Reconstruction effect of dog dataset under different influencing factors
|
Table 1. Comparison of different datasets
|
Table 2. RMSE on different datasets with different angular resolutions
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 3. RMSE on dog datasets with different influencing factors

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



