Xuehui Yang, Zhengyan Zhang, shun Wang. Simulation of Thermal Behavior of Selective Laser Melting High Strength Aluminum Alloy[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(23): 2314003
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 59, Issue 23, 2314003 (2022)
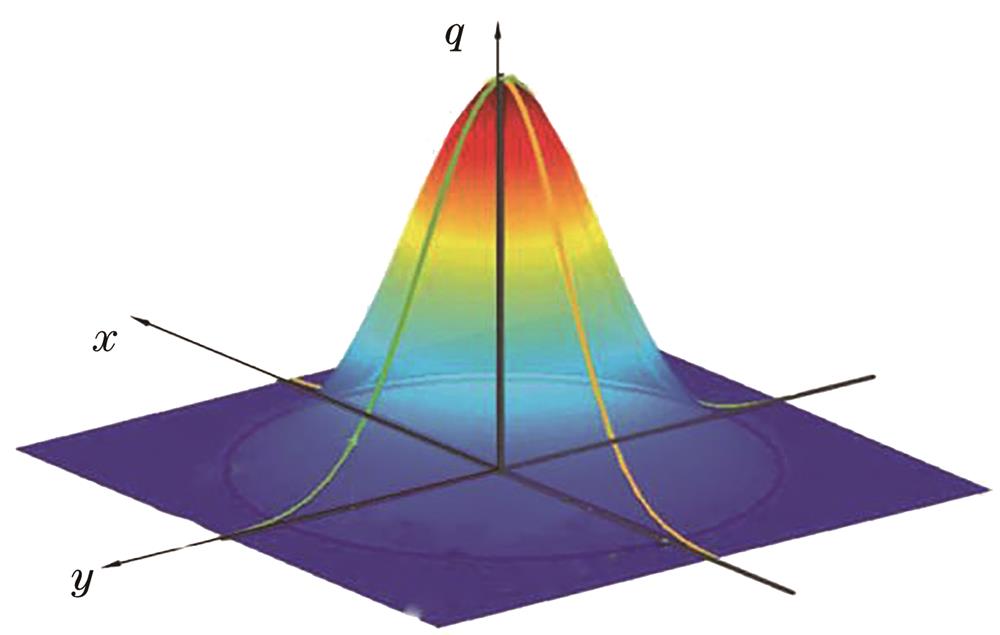
Fig. 1. Gaussian heat source model
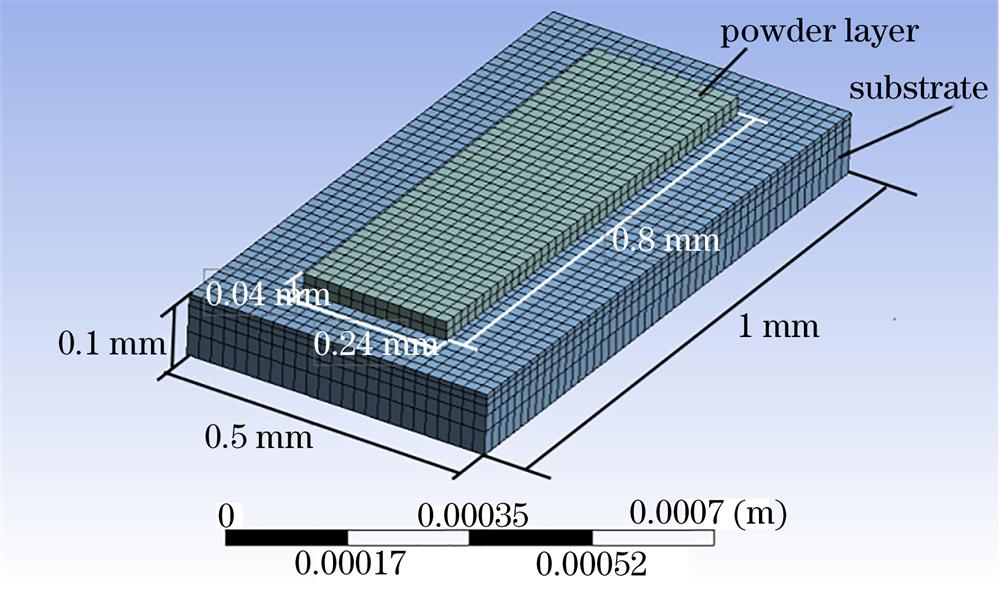
Fig. 2. Finite-element model
Fig. 3. Cloud map of temperature distribution of selective laser melting of aluminum alloy
Fig. 4. Temperature field distributions at the midpoint of the scan line. (a) Thermal cycle curve; (b) temperature gradient curve
Fig. 5. Molten pool at the midpoint of the scan line. (a) Molten pool surface; (b) cross section of molten pool
Fig. 6. Molten pool surface at different scanning speeds. (a) 100 mm/s; (b) 500 mm/s
Fig. 7. Temperature evolution under different process parameters. (a) Different scanning speeds; (b) different laser powers
Fig. 8. Length, width, and depth of the molten pool under the different parameters. (a) Different scanning speeds; (b) different laser powers
Fig. 9. Block print test piece
Fig. 10. Cross section of molten pool at scaning speed of 100 mm/s
Fig. 11. Melt width comparison at different scanning speeds
|
Table 1. Physical performance parameters of 2024 aluminum alloy

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



