Bin Zhong, Zhiyun Liu, Xiangxin Li, Jiaying LÜ. Ascending and Descending Time Series Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Monitoring and Analysis of Landslide Deformation[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(24): 2428002
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 59, Issue 24, 2428002 (2022)
![Geographic location map of study area [base map uses global 30 m resolution AW3D30 digital elevation model (DEM) issued by Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency]](/richHtml/lop/2022/59/24/2428002/img_01.jpg)
Fig. 1. Geographic location map of study area [base map uses global 30 m resolution AW3D30 digital elevation model (DEM) issued by Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency]
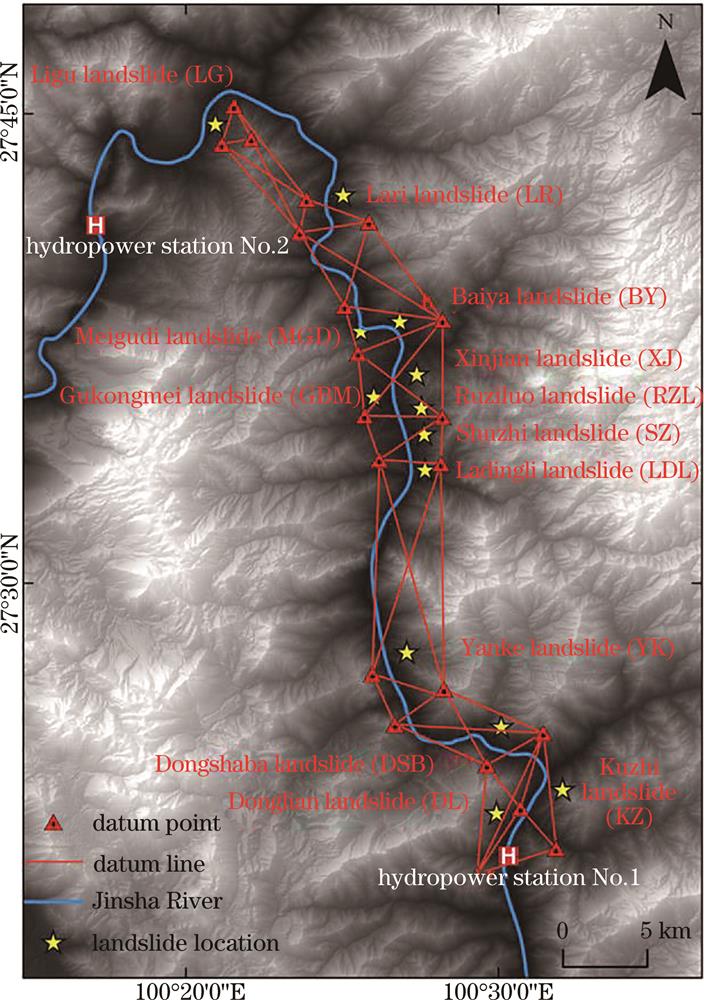
Fig. 2. GPS reference point location and approximate distribution of landslide areas
Fig. 3. Annual average line-of-sight (LOS) deformation rate in study area (aescending)
Fig. 4. Annual average LOS deformation rate in study area (descending)
Fig. 5. Annual average deformation rate of newly built (base map from Google Earth)
Fig. 6. GPS reference points and monitoring points distribution of Xinjian landslide (base map from Google Earth)
Fig. 7. Comparison of LOS cumulative displacements of InSAR and GPS data
Fig. 8. Relationship between water level change of Fengke Reservoir and daily rainfall in Lijiang City and cumulative displacement of characteristic points of Xinjian landslide
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 1. Basic parameters of SAR data
|
Table 2. Comparison of LOS cumulative deformations of GPS and InSAR

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



