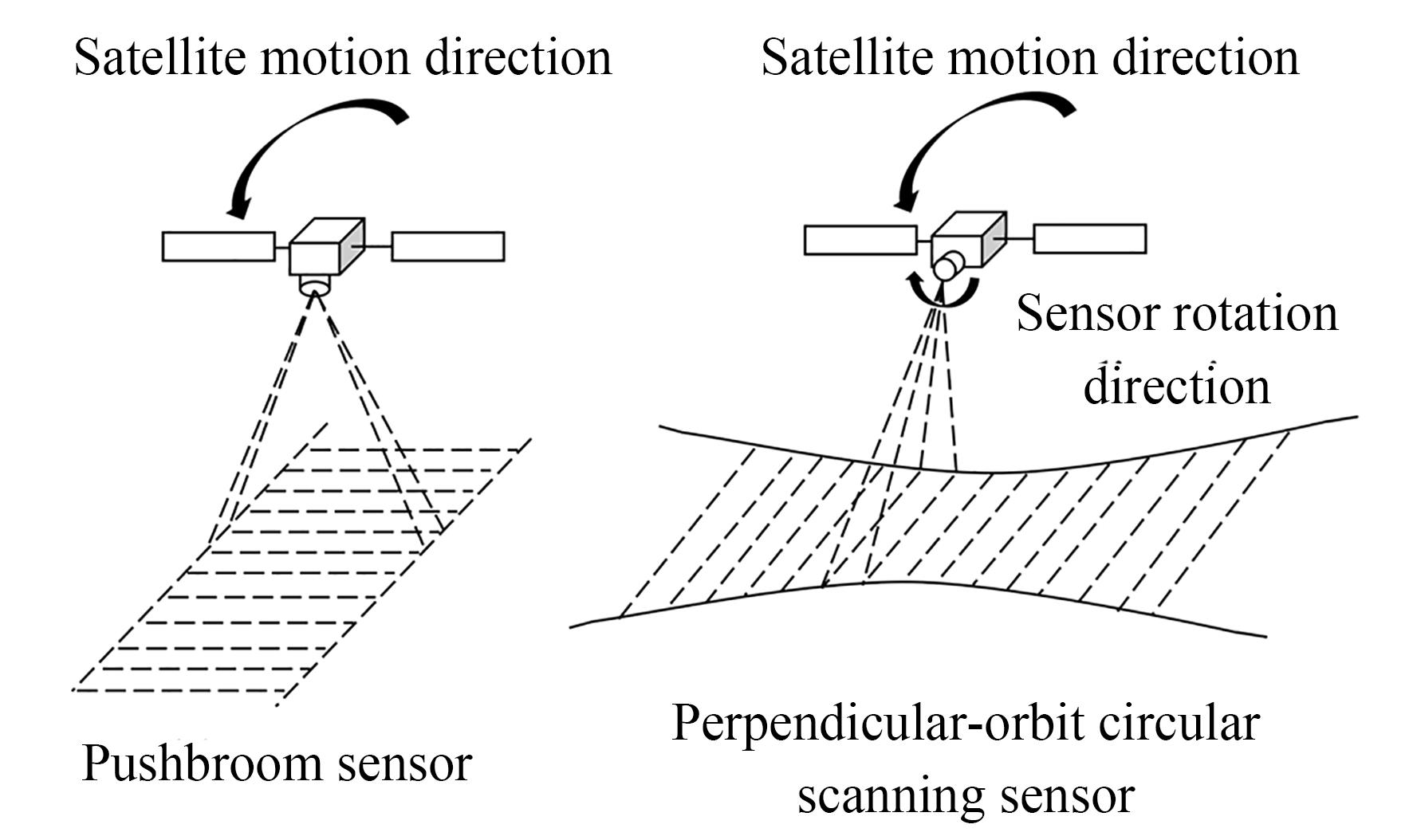
Xian LIU, Wu XUE, Peng WANG. Construction and accuracy assessment of rational function model for perpendicular-orbit circular scanning satellite images[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2023, 31(19): 2898
Search by keywords or author
- Optics and Precision Engineering
- Vol. 31, Issue 19, 2898 (2023)
Abstract
Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



