Yanrong Yang, Junlei Zhao, Haoxin Zhao, Fei Xiao, Jiaxin Xie, Tiejun Liu, Yun Dai, "Objective visual performance evaluation with visual evoked potential measurements based on an adaptive optics system," Chin. Opt. Lett. 16, 053301 (2018)
Search by keywords or author
- Chinese Optics Letters
- Vol. 16, Issue 5, 053301 (2018)
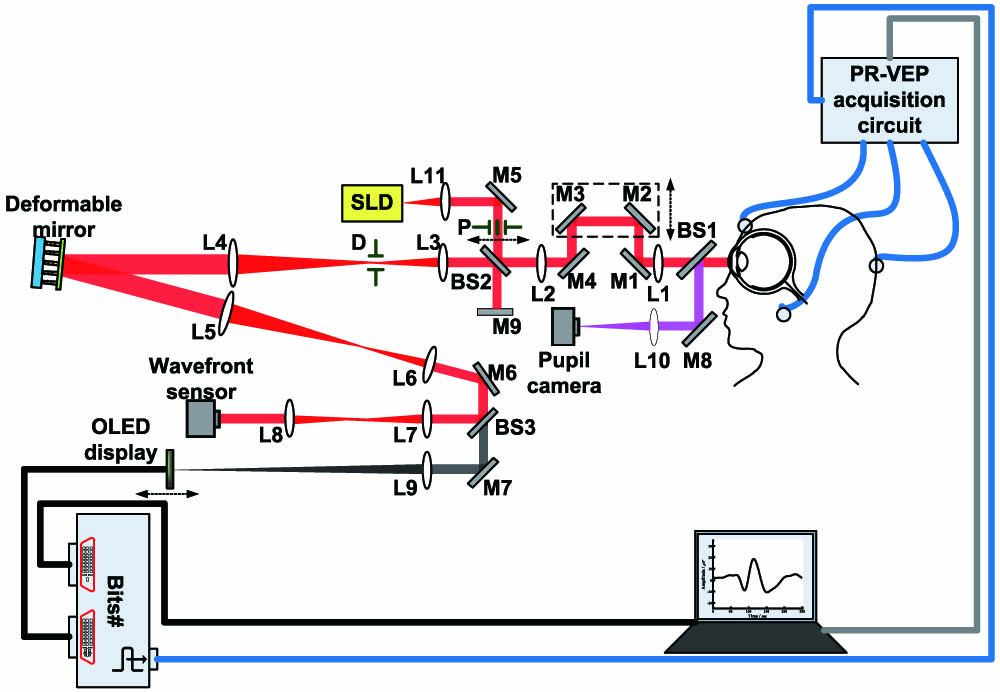
Fig. 1. AO system integrated with pattern reversal VEP (PR-VEP) measurements. SLD, superluminescent diode; BS, beam splitter; M, mirror; L, lens; P, artificial entrance pupil; D, diaphragm.

Fig. 2. Wavefront aberrations sensing and aberrations manipulation. R x y − A ′ N th orders of Zernike aberrations; A d G ′ A ′ G d A d
Fig. 3. Schematic of the miniaturized AO system. L, lens; BS, beam splitter; TL, trial lens holder; Ls, LED source; Pxyz, three-dimensional traveling platform.
Fig. 4. (a), (b) Zernike coefficient values , and (c), (d) PSF of subject CKY without and with AO correction. (a), (c) without AO correction. (b), (d) with AO correction.
Fig. 5. PR-VEP waveform comparison of three subjects without and with AO correction. (a) and (b) are the right and left eye of DP, respectively. (c), (d) and (e), (f) correspond to ZZ and CKY, respectively.
Fig. 6. Average NPN magnitude and latency of all eyes from three subjects. The first column (a), (c), (e) are the amplitudes at 4, 8, 16 cpd, respectively. The second column (b), (d), (f) are the latencies at 4, 8, 16 cpd, respectively.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 1. Detailed Information for All Subjects

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



