Hao Hu, Qibing Wang, Jiawei Lu, Hongye Su, Jiankun Lai, Gang Xiao. MSPoint: Point Cloud Denoising Network Based on Multiscale Distribution Score[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(16): 1615002
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 60, Issue 16, 1615002 (2023)
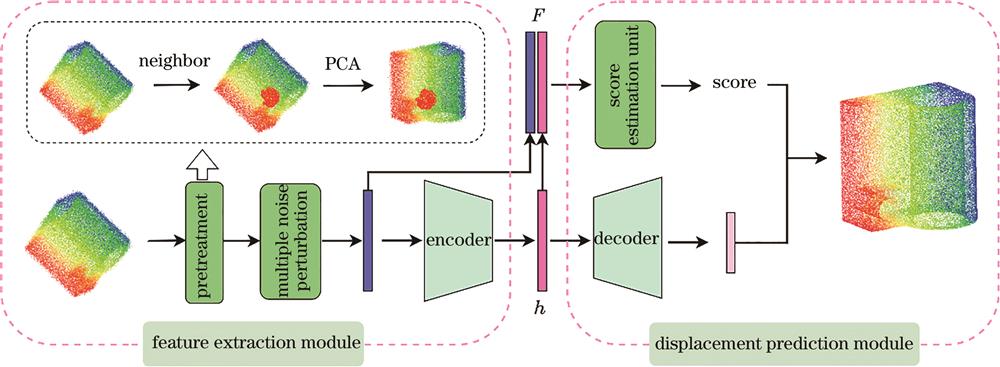
Fig. 1. Overall network structure
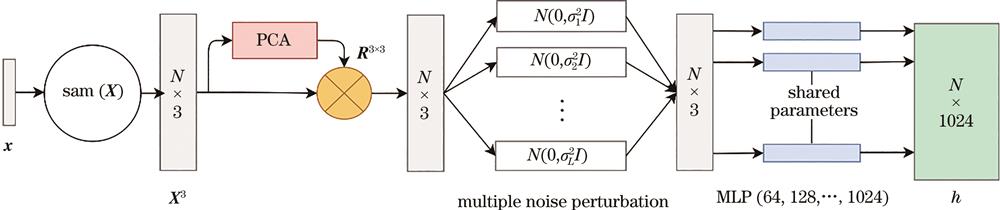
Fig. 2. Feature extraction module
Fig. 3. Displacement prediction module
Fig. 4. Relation between score and denoising effect
Fig. 5. Score estimation unit
Fig. 6. Effect of different loss functions on point cloud denoising results. (a)
Fig. 7. Point cloud dataset. (a) block; (b) blade; (c) column; (d) joint; (e) casting; (f) cube; (g) fandisk
Fig. 8. Schematic diagrams of point cloud neighborhood extraction. (a) joint; (b) blade; (c) block; (d) column
Fig. 9. Comparison of 0.5% noise casting point cloud model denoising results
Fig. 10. Comparison of 0.5% noise cube point cloud model denoising results
Fig. 11. Comparison of 0.5% noise fandisk point cloud model denoising results
Fig. 12. Point Cloud data of a university library
Fig. 13. Comparison of gate steps before and after noise removal. (a) Before noise removal; (b) after noise removal
Fig. 14. Comparison of back corridor before and after noise removal. (a) Before noise removal; (b) after noise removal
Fig. 15. Comparison of corner before and after noise removal. (a) Before noise removal; (b) after noise removal
Fig. 16. Loss convergence of disturbances of different degrees. (a)
|
Table 1. Comparison of denoising effects of different neighborhood radii using DCD error as the evaluation standard
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 2. Comparison of denoising effects of different algorithms using DCD error as evaluation standard
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 3. Comparison of denoising effects of different algorithms using P2F error as the evaluation standard
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 4. Comparison of denoising effects using different loss functions

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



