Yuexin LIU, Wei LIU, Hongyan JIA, Jizhou CHEN, Yajin WANG, Jin SHEN. Optimal Selection of Correlation Function Fitting Window in Bimodal Particle Size Inversion by Dynamic Light Scattering[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2023, 52(6): 0629001
Search by keywords or author
- Acta Photonica Sinica
- Vol. 52, Issue 6, 0629001 (2023)
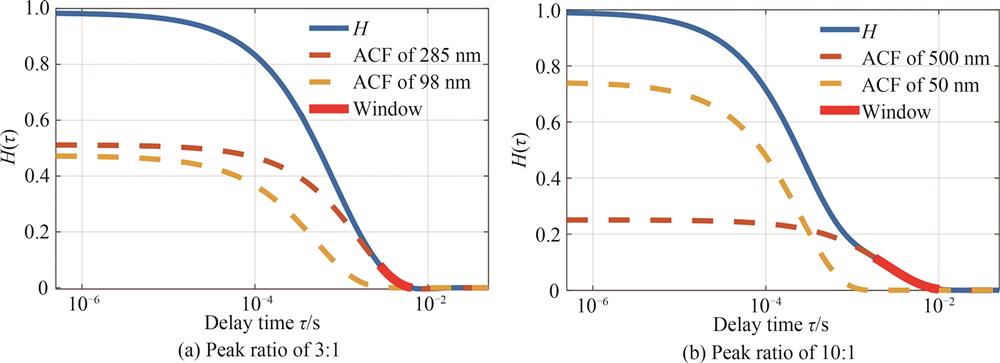
Fig. 1. Example of sequential extraction of late exponentials method corresponding to bimodal particle systems

Fig. 2. Attenuation characteristics of the correlation function derived from the electric field correlation function
Fig. 3. Electric field correlation function and attenuation rate of correlation function for 140.9 nm equivalent mean particle size
Fig. 4. Electric field correlation function and attenuation rate of correlation function for 70.6 nm equivalent mean particle size
Fig. 5. Bimodal particle correlation function relative attenuation characteristics plots
Fig. 6. Extraction results of 95 nm/285 nm bimodal correlation function by SELE method under the first fitting window
Fig. 7. Extraction results of 95 nm/285 nm bimodal particle correlation function by SELE method under the second fitting window
Fig. 8. H-RAC plots and reference points of bimodal particles for different equivalent mean particle sizes
Fig. 9. Extraction results of 95 nm/285 nm bimodal correlation function by ACSELE method
Fig. 10. Extraction results of 100 nm/400 nm bimodal correlation function by ACSELE method
Fig. 11. ACSELE method for 60 nm/220 nm measured bimodal particle correlation function extraction results
Fig. 12. ACSELE method for 65 nm/450 nm measured bimodal particle correlation function extraction results
|
Table 1. Results of the simulated bimodal correlation function calculation using SELE method
|
Table 2. Calculation of start and end point of fitting window of simulated bimodal correlation function
|
Table 3. Results of the simulated bimodal correlation function calculation using the ACSELE method
|
Table 4. Results of correlation function calculation for two groups of real bimodal particles using different methods

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



