Chen Liang, Junwei Wu, Hangbing Peng, Lijun Deng, Yiqin Lin, Zhongwen Cheng, Lüming Zeng, Xuanrong Ji, "In vivo whole brain photoacoustic microscopy through a transparent ultrasound transducer," Chin. Opt. Lett. 23, 021102 (2025)
Search by keywords or author
- Chinese Optics Letters
- Vol. 23, Issue 2, 021102 (2025)
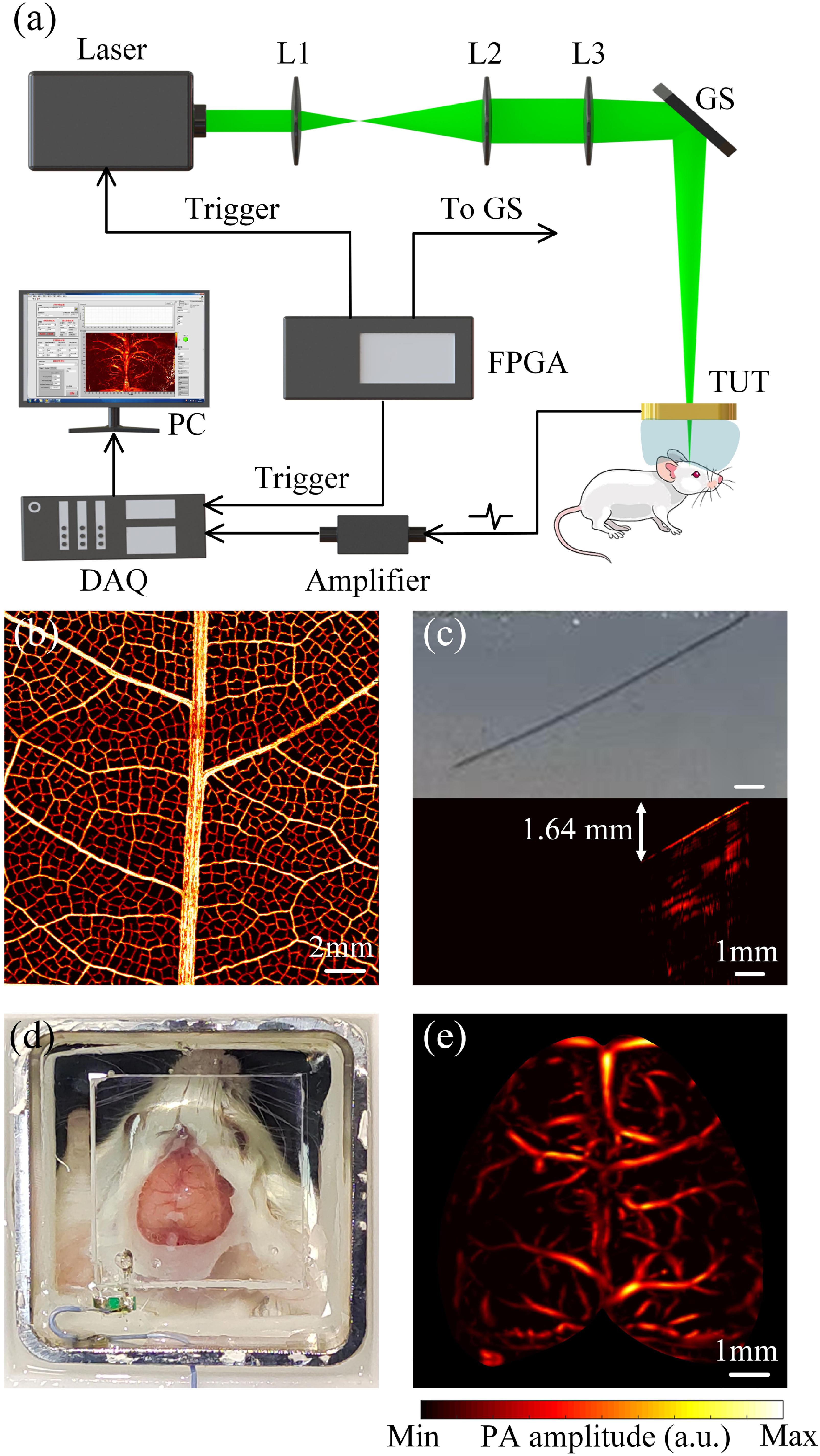
Fig. 1. (a) Schematics of the TUT-based PAM system. L1, L2, and L3, lenses; GS, galvanometer scanner; TUT, transparent ultrasonic transducer; DAQ, data acquisition system; PC, personal computer; FPGA, field programmable gate array. (b) The PA image of the leaf venation skeleton. (c) Optical photo and PA image of a tilted tungsten filament inserted into an agar phantom. (d) The optical photo of the TUT. (e) The PA image of the whole mouse cortex vasculature.
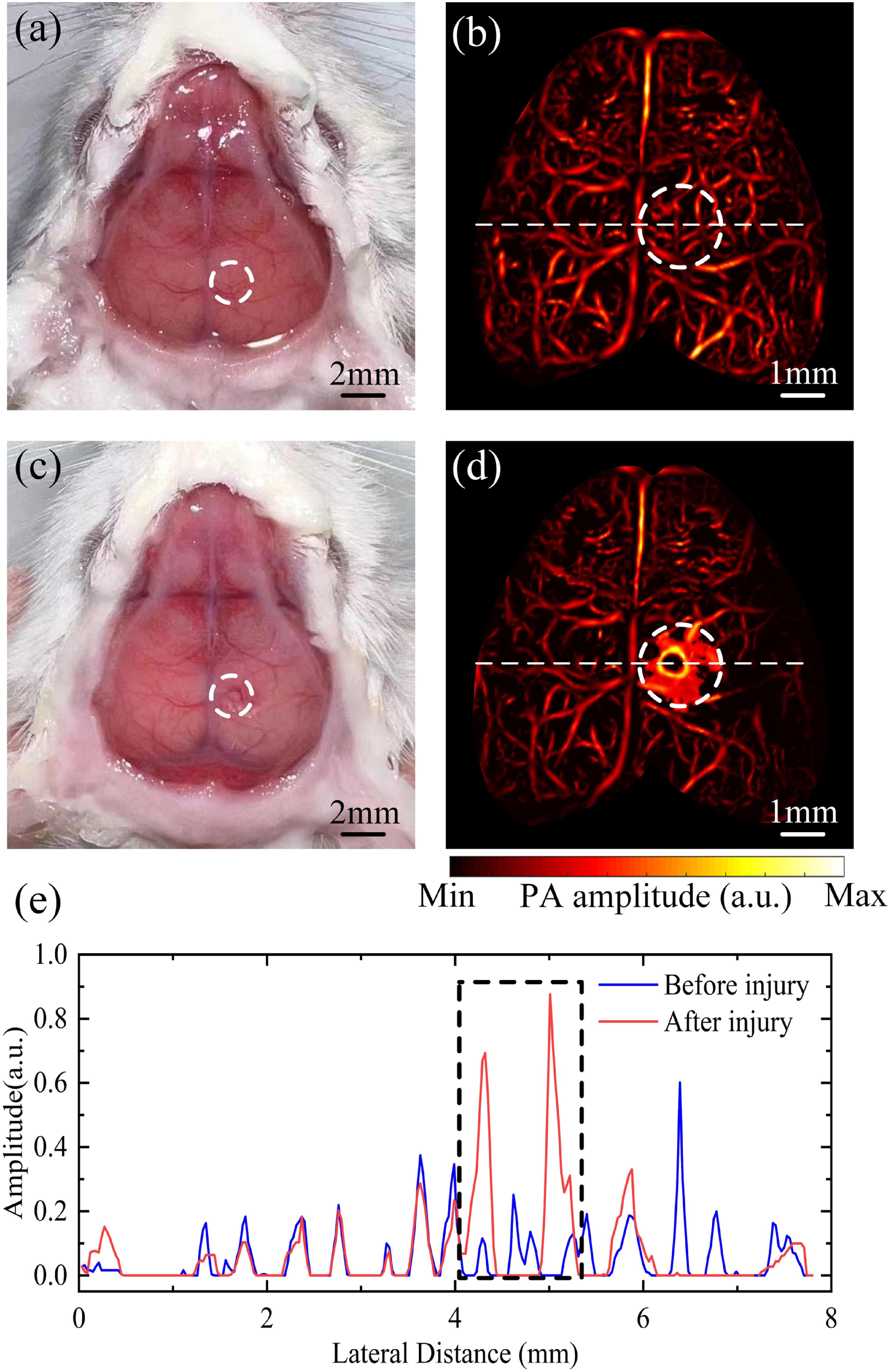
Fig. 2. (a) The optical photo of a mouse before brain injury. (b) The PA image of the mouse before brain injury. (c) The optical photo of a mouse after brain injury. (d) The PA image of the mouse after brain injury. (e) Profiles of blood vessels traced along the white dashed lines in (b) and (d).
Fig. 3. (a) The optical photo of glioma in a nude mouse. (b) The PA image of the glioma. (c) The MRI imaging result of the glioma. (d) The HE staining result of the glioma.
Fig. 4. (a) Plot of changes in the cerebral cortex of a mouse 6 min and 40 s after hemorrhage. The location of the hemorrhage is circled by dotted lines. (b) Pixels and amplitudes in the white dashed circle over time.

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



