Kunliang Xie, Renjiao Yi, Haifang Zhou, Chenyang Zhu, Yuwan Liu, Kai Xu. Efficient Material Editing of Single Image Based on Inverse Rendering[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(14): 1415014
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 59, Issue 14, 1415014 (2022)
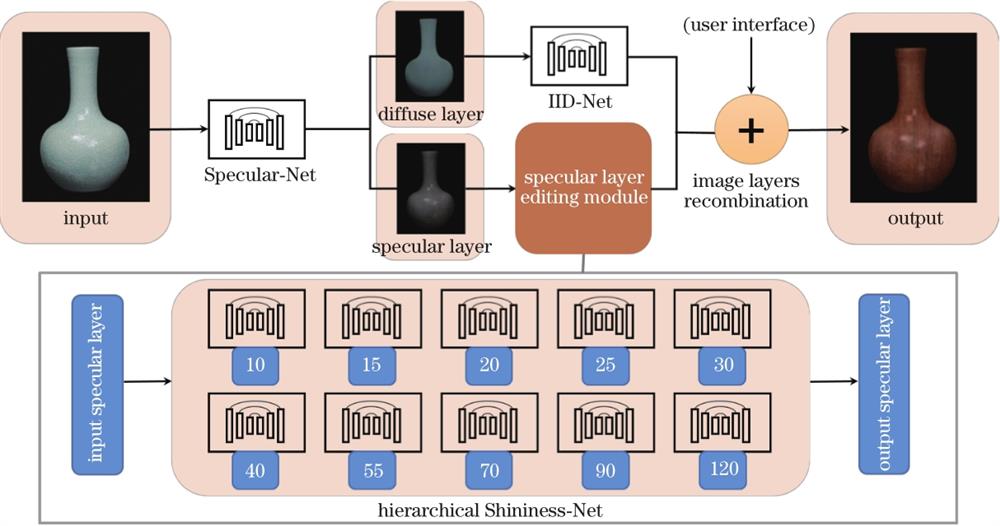
Fig. 1. Architecture of proposed neural network
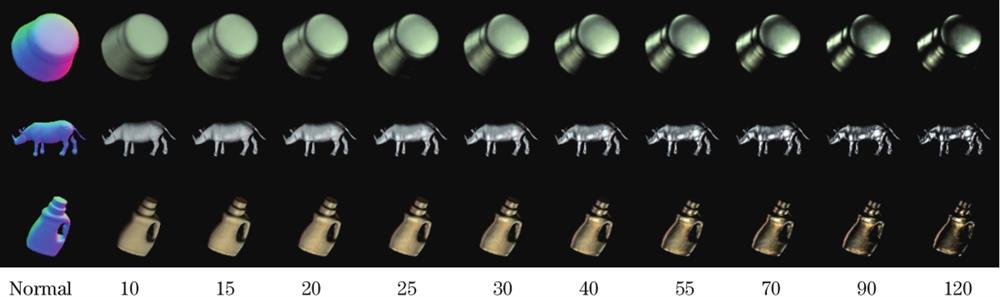
Fig. 2. Picture display in the Hierarchical Shininess dataset
Fig. 3. Visual comparisons of highlight separation on real pictures
Fig. 4. Visual comparisons on the MIT intrinsics dataset
Fig. 5. Visual comparisons on specular layer between GT images and network output images
Fig. 6. Visual comparisons between the synthetic images (GT) after the combination of specular layer and diffuse layer with different material shininess parameters and the output results of the proposed method
Fig. 7. Material editing of real pictures
|
Table 1. Hyperparameter settings in network training
|
Table 2. Datasets used by proposed networks
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 3. Quantitative comparisons on the SHIQ dataset, ShapeNet Intrinsics dataset, and some real pictures
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 4. Quantitative comparisons on the MIT intrinsics dataset

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



