Yan Yin, Xiao Zhang, Mengzhi Xiao, Yan Gong, Wei Zhou, Ruihua Zhang. Effect of Dual-Beam Energy Ratio on Microstructure and Properties of Q355ND Steel Laser-MAG Hybrid Welding Joint[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(17): 1714003
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 59, Issue 17, 1714003 (2022)
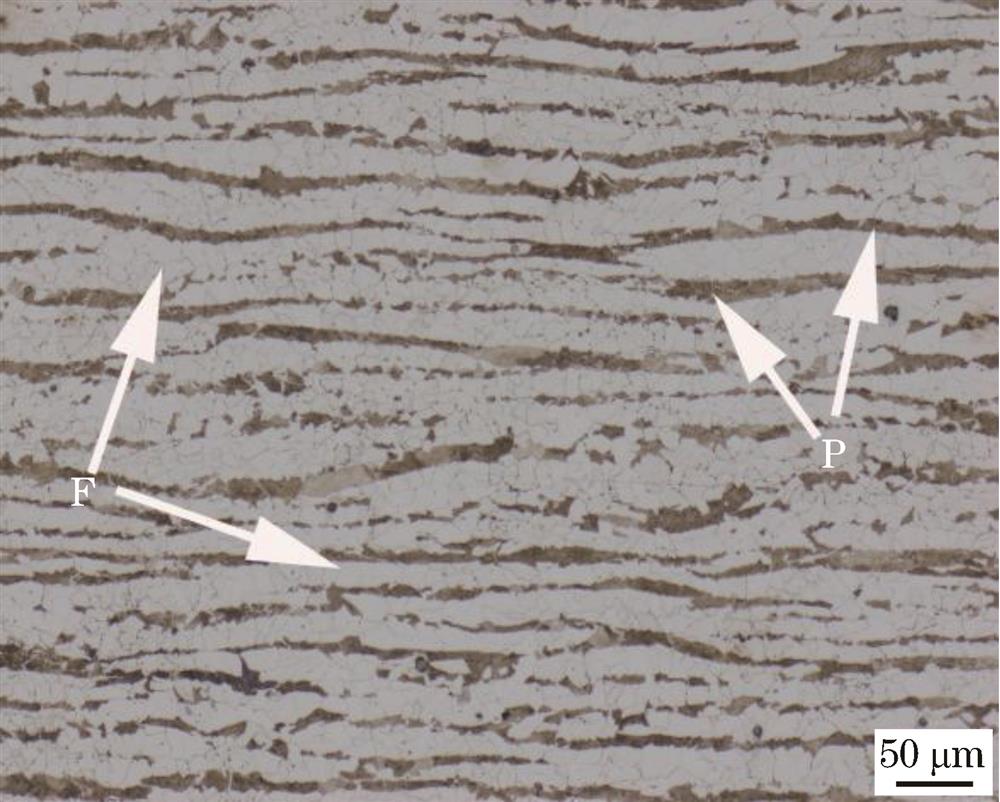

Fig. 1. Microstructure of base metal
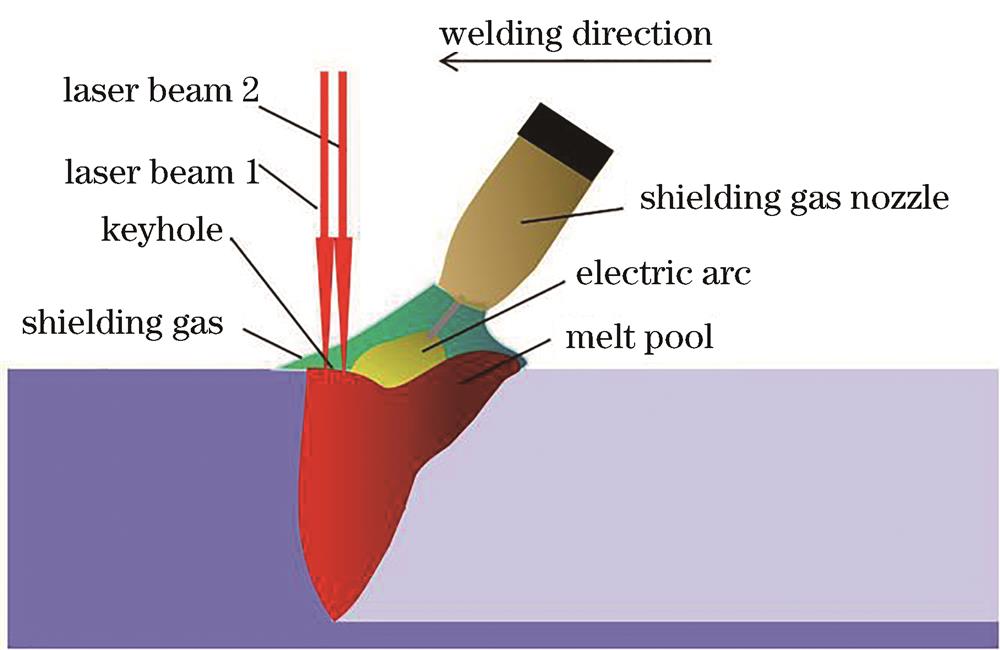
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of dual-beam laser-MAG hybrid welding
Fig. 3. Energy ratio of dual-beam laser
Fig. 4. Schematic of the groove
Fig. 5. Schematic diagram of microhardness test position of weld cross section
Fig. 6. Relationship between equilibrium phase and temperature of welding materials. (a) Q355ND; (b) ER50-6
Fig. 7. XRD patterns of different regions of welded joints
Fig. 8. Relationship between weld penetration depth, weld width, and hybrid welding energy ratio
Fig. 9. Macro morphology of weld and cross section. (a) Front morphology; (b) back morphology; (c) cross section of joint
Fig. 10. Microstructure of weld zone and heat affected zone. Main arc action zone (a) weld center, (b) coarse grain zone, (c) fine grain zone, and (d) incomplete recrystallization zone; main laser action zone (e) weld center, (f) coarse-grained zone, (g) fine-grained zone, and (h) incomplete recrystallization zone
Fig. 11. Element distributions in the region near the fusion line. (a) Photo of the fusion line near the main arc action zone; (b) element distribution of Fig. (a); (c) photo of the fusion line near the main laser action zone; (d) element distribution of Fig. (c)
Fig. 12. Relationship between microhardness of welded joint and distance from weld center
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 1. Chemical composition of Q355ND steel and ER50-6 welding wires
|
Table 2. Parameters of dual-beam laser-MAG hybrid welding
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 3. Macro morphology and related data of weld cross section under different energy ratios

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address








