Yi Yu, Jiayu Yi, Liu Xu, Jianli Shang, Jing Wu, Lixin Tong, Qingsong Gao, Chun Tang, Wei Zhang, Lei Chen, "Large aperture disk standing-wave unstable resonator with intra-cavity adaptive correction," Chin. Opt. Lett. 22, 051401 (2024)
Search by keywords or author
- Chinese Optics Letters
- Vol. 22, Issue 5, 051401 (2024)
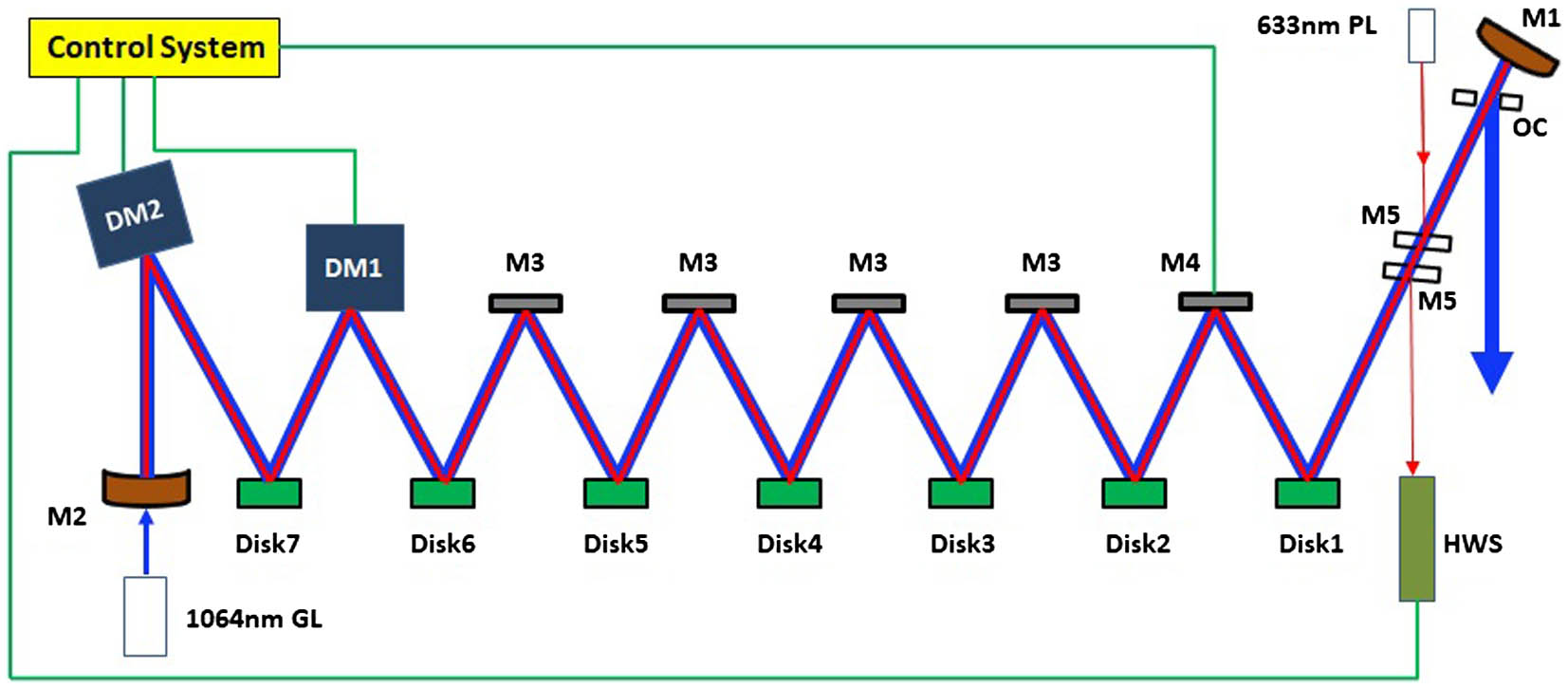
Fig. 1. Experimental setup of the disk standing-wave unstable resonator.

Fig. 2. Schematic of the disk gain module.
Fig. 3. Photo of the composite ceramic disk.
Fig. 4. Small signal gain coefficient versus pulse peak pumping power.
Fig. 5. Logical diagram of synergic controlling process.
Fig. 6. Average output power versus time.
Fig. 7. (a) The RTWF after tilt and defocus correction (the corresponding profiles of the near field and far field are shown in the insets). (b) The RTWF after tilt, defocus, and high order aberrations correction (the corresponding profiles of the near field and far field are shown in the insets).
Fig. 8. The RMS value of the RTWF versus iterations.
Fig. 9. (a) The output power versus total input power. The inset (b) shows the oscilloscope trace of a single pulse.
|
Table 1. Compensating Capabilities of Correcting

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



