Chunmei Hu, Huajie Fei, Guofang Xia, Xi Liu, Xinjian Ma. High-Precision Registration of Non-Homologous Point Clouds in Laser Scanning and Photogrammetry[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(24): 2415007
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 59, Issue 24, 2415007 (2022)
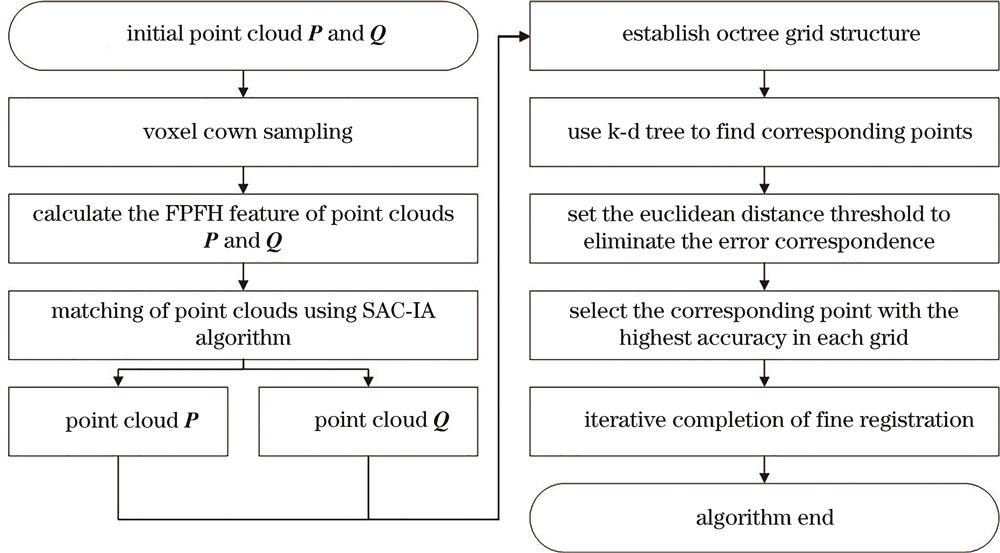
Fig. 1. Algorithm flow
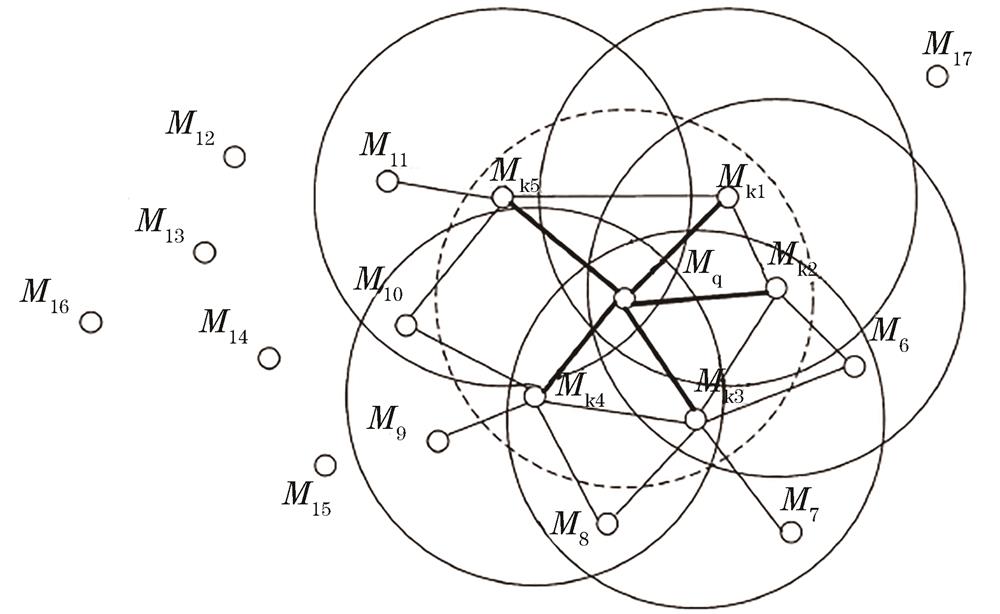
Fig. 2. FPFH calculation principle
Fig. 3. Schematic diagram of octree structure
Fig. 4. Point cloud visualization. (a) Face point cloud; (b) ear point cloud; (c) buddha head point cloud
Fig. 5. Rough registration results of different algorithms. (a) Overall point cloud after down sampling; (b) 4PCS algorithm; (c) RANSAC algorithm; (d) proposed algorithm
Fig. 6. Iterative estimation of grid size
Fig. 7. Octree grid rendering. (a) Face point cloud; (b) ear point cloud; (c) buddha head point cloud
Fig. 8. Corresponding point matching diagrams. (a) Before removing false matching; (b) after removing false matching; (c) the number of point pairs corresponding to the removal of errors varying with the number of iterations
Fig. 9. Registration results of different methods. (a) Grid centroid; (b) nearest point of grid centroid ; (c) point with the smallest Euclidean distance in the grid
Fig. 10. Registration results of different algorithms. (a) ICP algorithm; (b) proposed algorithm
|
Table 1. Rough matching result of model point cloud
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 2. Comparison of registration results of different coarse registration algorithms
|
Table 3. Comparison of registration errors of different corresponding point pair selection methods
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 4. Comparison of registration performance between proposed algorithm and classical algorithm

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



