Jie Li, Yi Zhang, Zhichao Liang, Cong Chen. Process Characteristics of Laser Powder Filling Welding of B340LA High-Strength Steel[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(17): 1714010
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 60, Issue 17, 1714010 (2023)
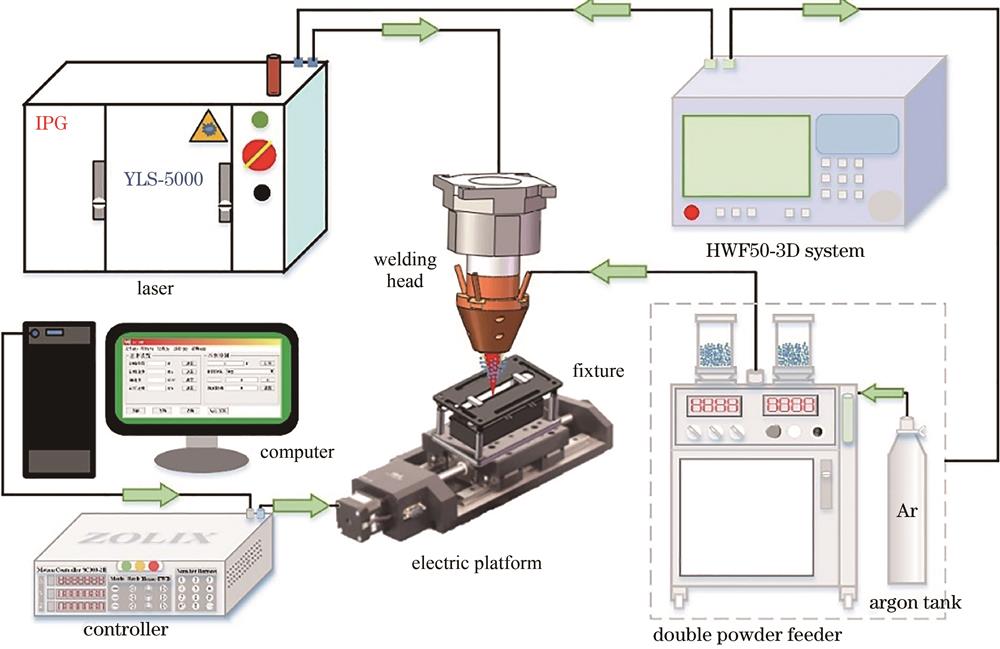
Fig. 1. Experimental setup for laser powder feeding welding
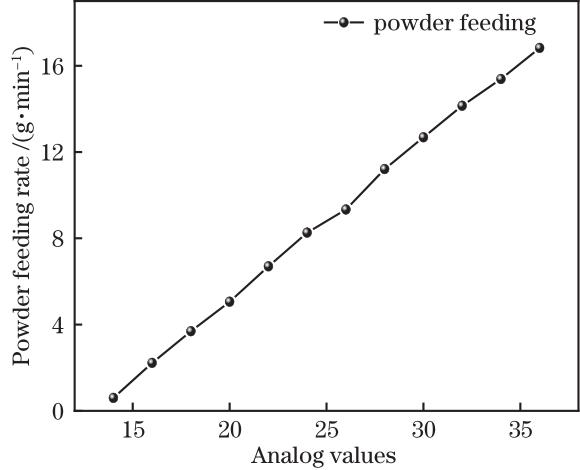
Fig. 2. Relationship between powder feeding rate and analog quantity
Fig. 3. Schematic diagram of the test method of cross-sectional topography
Fig. 4. Typical weld surface and section morphology. (a) P=1.2 kW, v=20 mm/s, M=8.27 g/min, D=0.05 mm; (b) P=1.2 kW, v=16 mm/s, M=12.69 g/min, D=0.05 mm
Fig. 5. Influence of butt gap on weld morphology. (a) Weld width; (b) bump/collapse depth of upper surface
Fig. 6. Evolution of molten pool with different butt gaps. (a) 0.05 mm; (b) 0.25 mm; (c) 0.30 mm
Fig. 7. Influence of powder feeding rate on weld morphology. (a) Weld width; (b) bump/collapse depth of upper surface
Fig. 8. Evolution of molten pool flow with different powder feeding rates. (a) Little powder; (b) bulk powder
Fig. 9. Evolution of molten pool flow with different welding speeds. (a) Weld width; (b) bump/collapse depth of upper surface
Fig. 10. Influence of process parameters on weld morphology
Fig. 11. Effect of process parameters on tensile strength. (a) Butt gap; (b) welding speed; (c) powder feeding rate
Fig. 12. Microstructure of weld with different powder feeding rates. (a) 0.75 g/min; (b) 5.06 g/min; (c) 8.27 g/min
|
Table 1. Chemical composition of B340LA high-strength steel
|
Table 2. Single factor test parameter table

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



