Yinuo Fang, Qianqian Huang, Kaiquan Yan, Zishuo Xu, Mingjiao Wang, Kai Wang, Yuehui Ma, Weixi Li, Yunqi Liu, Chengbo Mou. High-Capacity, High-Speed Demodulation System for Fiber Bragg Grating Sensor Arrays Using Dispersion Fourier Transform Technology[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2025, 62(5): 0506004
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 62, Issue 5, 0506004 (2025)
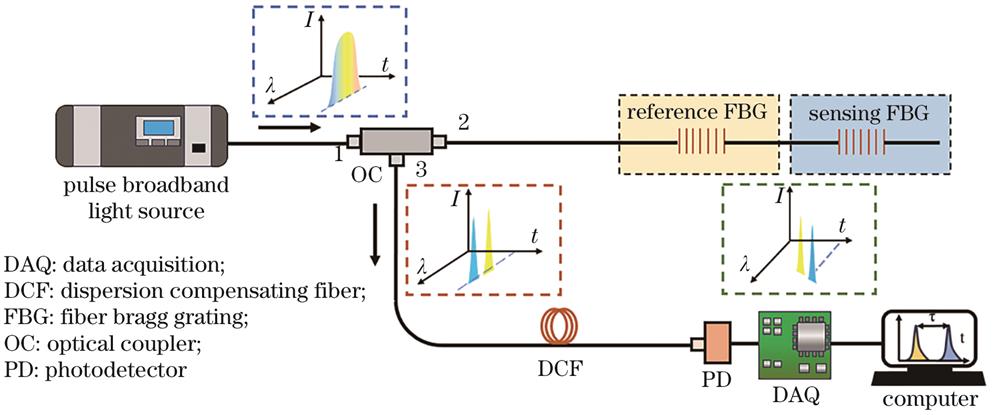
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of a typical DFT-based FBG demodulation system
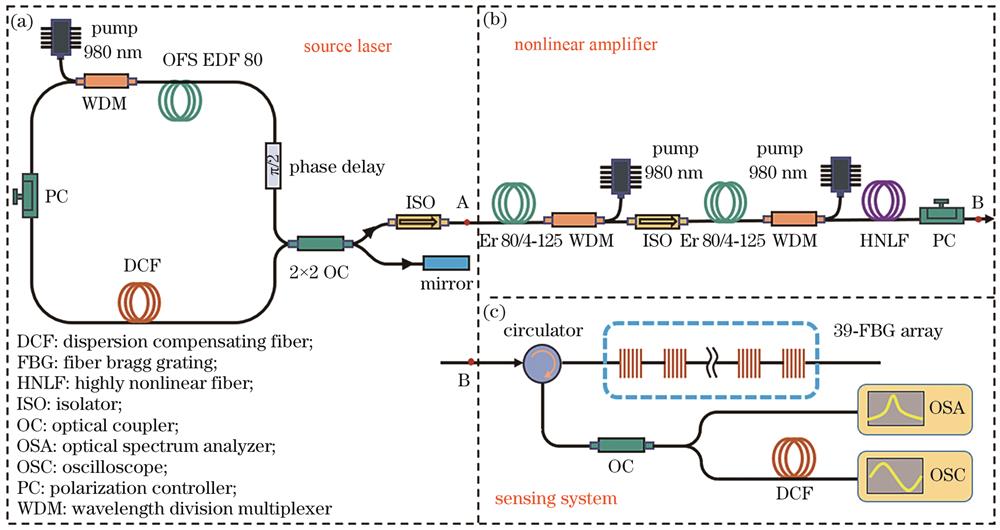
Fig. 2. Experimental setup. (a) Source laser; (b) nonlinear amplifier; (c) sensing system
Fig. 3. Characteristics of the incident optical pulses. (a) Time-domain waveform of the mode-locked pulses from figure-9 fiber laser; (b) RF spectrum of the mode-locked pulses from figure-9 fiber laser with a scan range of 1 MHz and a resolution bandwidth of 1 kHz, the scanning range of the illustration is 1.0 GHz, with a resolution bandwidth of 10 kHz ; (c) optical spectrum, with the blue solid line representing the source laser spectrum and the red dashed line representing the spectrum after nonlinear amplification; (d) autocorrelation waveform after nonlinear amplification
Fig. 4. Reflected signal from the FBG array. (a) Reflection spectrum; (b) reflected pulse sequence; (c) reflected pulse sequence before and after DFT; (d) zoomed-in view of the reflected pulse sequence before and after DFT
Fig. 5. Temperature-to-center wavelength calibration results for FBG 1 to FBG 5
Fig. 6. Demodulation results of FBG 1 during heating. (a) Reflection spectrum variation; (b) zoomed-in view of the reflection spectrum variation; (c) evolution of the reflected pulse sequence; (d) zoomed-in view of the reflected pulse sequence evolution; (e) comparison of the wavelength demodulation results with the direct wavelength measurement results; (f) temperature demodulation results
Fig. 7. Zoom-in views of the spectral and time-domain waveform variations caused by heating during sensor multiplexing. (a) Reflection spectrum variation of FBG 2 and FBG 3; (b) time-domain waveform variation of FBG 2 and FBG 3; (c) reflection spectrum variation of FBG 4 and FBG 5; (d) time-domain waveform variation of FBG 4 and FBG 5
Fig. 8. Comparison between the wavelength demodulation results and the direct wavelength measurement results during sensor multiplexing. (a) FBG 2 and FBG 3; (b) FBG 4 and FBG 5
Fig. 9. Temperature demodulation results during sensor multiplexing
|
Table 1. Error and correlation analysis of the temperature demodulation results

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



