Li Dong, Maohai Hu, Zhirong Yang. Object Attitude Perception Method Based on Depth Camera[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(14): 1415028
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 59, Issue 14, 1415028 (2022)
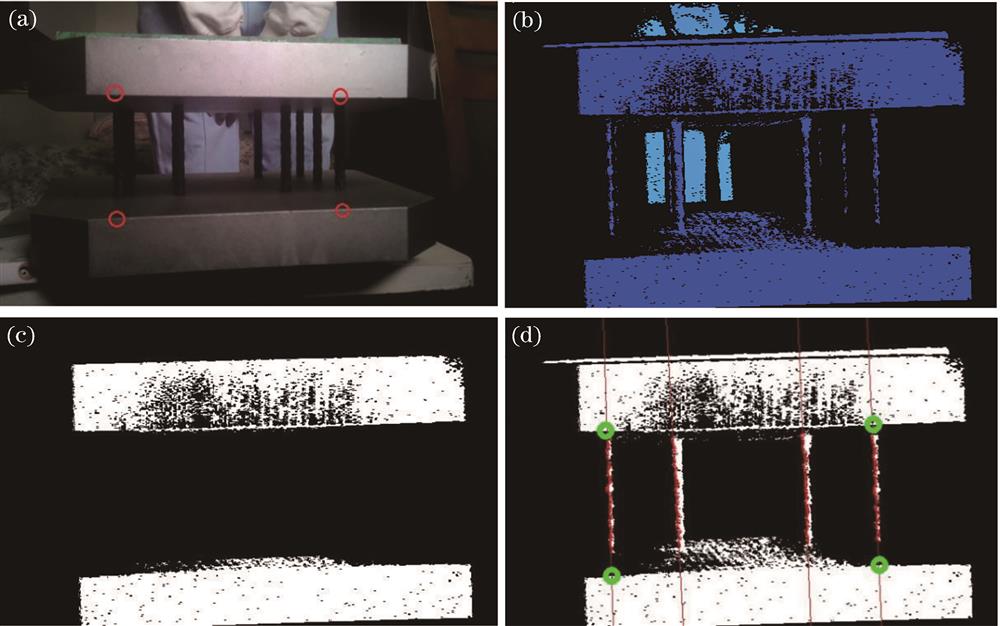
Fig. 1. Example diagram of sleeper cutting image processing. (a) RGB diagram; (b) depth map; (c) end face binarization diagram; (d) diagram of image processing result
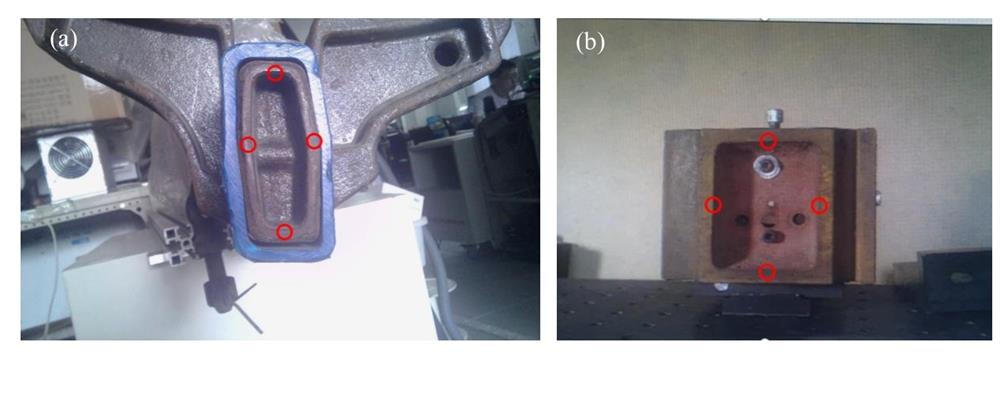
Fig. 2. RGB diagrams of workpiece with successful image processing. (a) RGB drawing of workpiece 1; (b) RGB drawing of workpiece 2
Fig. 3. Robot hand holding depth camera and laser
Fig. 4. Software operation interface
Fig. 5. Repetitive line graph of Euler angle and translation of object in the first attitude
Fig. 6. Repetitive line graph of Euler angle and translation of object in the second attitude
Fig. 7. Repetitive line graph of Euler angle and translation of object in the third attitude
|
Table 1. Three postures of the object relative to the camera in the experiment

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



