Shaoye Wang, Jianbo Zhang, Ziwen Zhao, Yifan Du, Shuangqi Zhong. COMSOL Simulation of Temperature Field of CO2 Laser Annealing Ge Core Fiber[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(15): 1506005
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 60, Issue 15, 1506005 (2023)
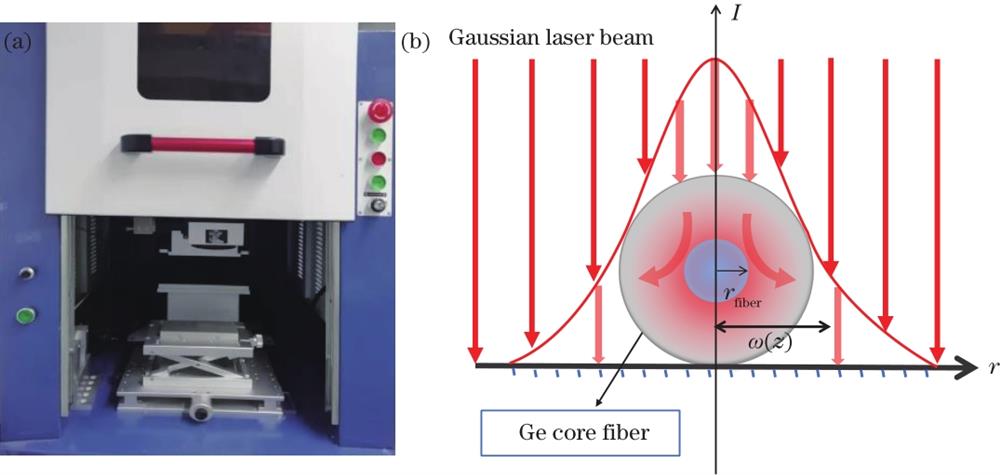
Fig. 1. Annealing device. (a) CO2 laser device diagram; (b) laser beam
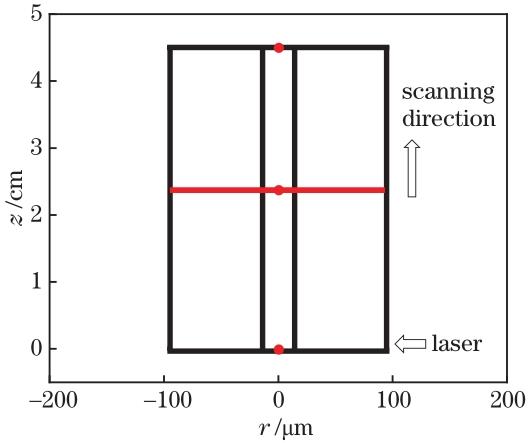
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of laser annealing Ge core fiber
Fig. 3. Ge core fiber. (a) Cross-section of Ge core fiber; (b) side view of Ge core fiber
Fig. 4. Temperature change curve of axial center point. (a) v = 6 mm/s; (b) v = 9 mm/s; (c) v = 12 mm/s; (d) v = 15 mm/s; (e) v = 18 mm/s; (f) v = 21 mm/s
Fig. 5. Radial temperature field distribution of the Ge core fiber at z = 2.25 cm
Fig. 6. Temperature field distribution at the center point of the two ends of the fiber axis. (a) v = 15 mm/s, P = 4.305 W; (b) v = 18 mm/s, P =5.381 W
Fig. 7. Fitting diagram of fiber axial and radial temperature difference
Fig. 8. Raman spectrum. (a) Comparison of Raman peak frequency; (b) line chart of Raman peak
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 1. Statistics of the maximum temperature at the center point
|
Table 2. Radial temperature difference at different annealing conditions
|
Table 3. Statistics of maximum temperature at the center point of both ends of the fiber axis
|
Table 4. Normalized axial and radial temperature difference

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



