Zhiming Tian, Teng Cai, Ruozhou Li, Yuming Fang, Ying Yu. Wavelength-Controlled Photothermal Microactuator Based on Suspension Printing and its Characterization[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(1): 0114005
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 60, Issue 1, 0114005 (2023)

Fig. 1. Structure of U-shaped photothermal microactuator
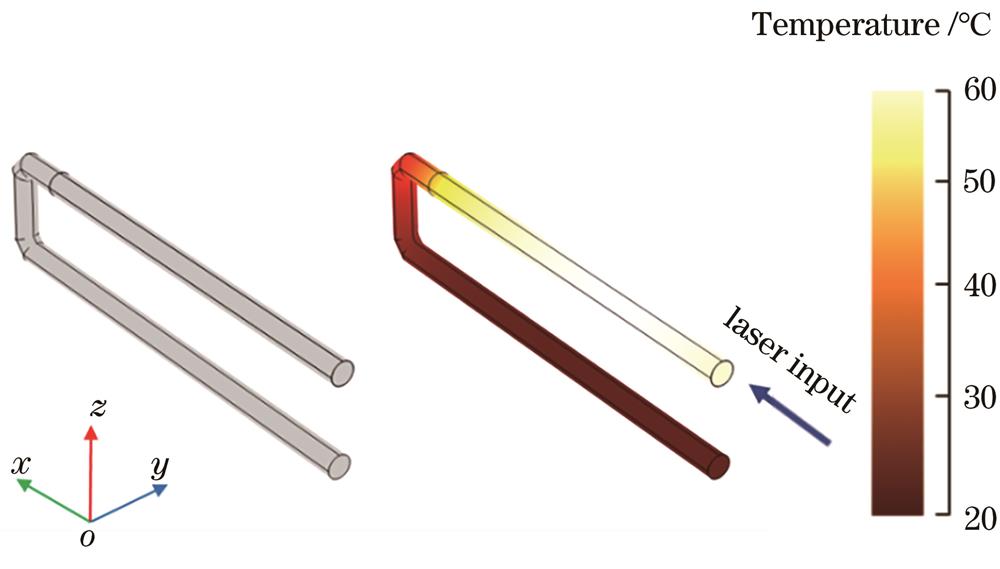
Fig. 2. Simulation structure of U-shaped photothermal microactuator
Fig. 3. Absorption spectra of functional dye solutions
Fig. 4. Fabrication process for the square-spiral actuating arm. (a) Hydrogel printing; (b) UV beam curing; (c) coating of functional dye solutions
Fig. 5. Photothermal microactuator printed by hydrogel support. (a) Photothermal microactuator; (b) photothermal microactuator fixed on a cured resin support plate; (c) microscopic image of the actuation drive arm; (d) output from the free end of the cantilever beam
Fig. 6. Initial state of the photothermal microactuator under the thermal imaging camera. (a) Type I photothermal microactuator; (b) type II photothermal microactuator
Fig. 7. Variation curve of actuator temperature with time. (a) 638 nm laser; (b) 405 nm laser
Fig. 8. State of the actuator driven by the laser. (a) Initial state of type Ⅰ actuator (0 mW); (b) strain state of type Ⅰ actuator (100 mW); (c) initial state of type Ⅱ actuator (0 mW); (d) strain state of type Ⅱ actuator (100 mW)
Fig. 9. Variation curve of actuator displacement with time. (a) 408 nm laser; (b) 638 nm laser
|
Table 1. Material parameters and structural dimensions of photothermal microactuator

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



