Shiguang Liu, Shufeng Sun, Pingping Wang, Xingbo Zhang, Jin Wang, Haitao Wang, Jixin Liu. Effect of Laser Incident Angle on Paint Removal of 2024 Aluminum Alloy Surface[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(17): 1714009
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 59, Issue 17, 1714009 (2022)
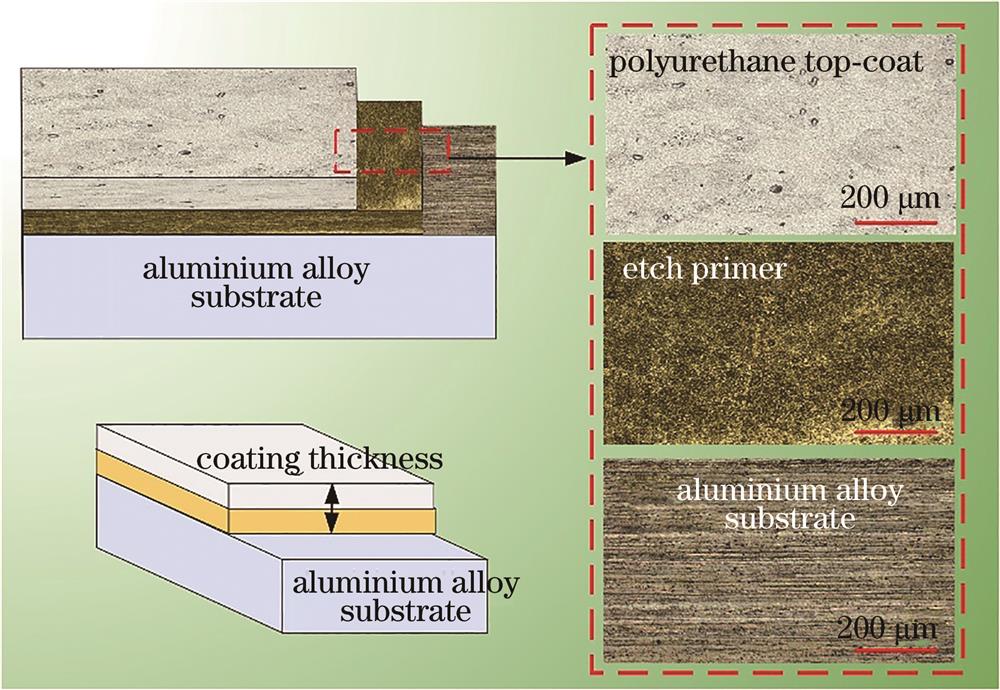
Fig. 1. 2024 aluminum alloy surface paint diagram
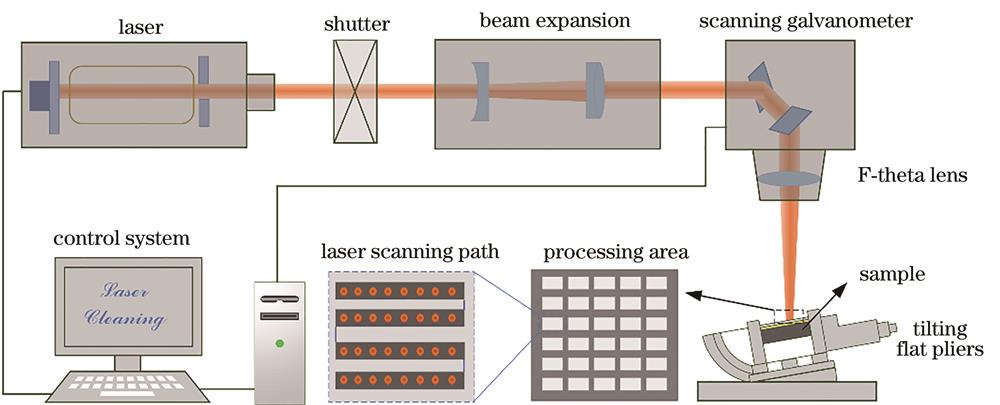
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of experimental equipment
Fig. 3. Schematic diagram of laser angle incidence. (a) Schematic diagram of different laser incidence angles; (b) processing area division diagram
Fig. 4. Schematic of relationship between ablation rate and laser flux[30]
Fig. 5. Change law of paint removal depth. (a) Paint removal depth at different laser incidence angles; (b) comparison of paint removal depth at various angles and at normal incidence
Fig. 6. Three-dimensional morphology of the sample at different laser incidence angles,when energy density is 4.5 J/cm2. (a) 90°; (b) 80°; (c) 70°; (d) 60°; (e) 50°; (f) 40°
Fig. 7. Energy spectrum analysis and micromorphology of sample surface,when laser energy density is 5 J/cm2 and 6 J/cm2, respectively. (a) Energy spectrum analysis diagram at 5 J/cm2; (b) microtopography at 5 J/cm2; (c) carbon distribution map at 5 J/cm2; (d) energy spectrum analysis diagram at 6 J/cm2; (e) microtopography at 6 J/cm2; (f) aluminum distribution diagram at 6 J/cm2
Fig. 8. Surface topography of samples at different laser incidence angles
Fig. 9. Surface roughness of samples at different laser incidence angles
Fig. 10. Phenomenon of plume combustion at different laser incidence angles in the experiment. (a) Laser incidence angle is 90°; (b) laser incidence angle is 70°
Fig. 11. Scanning electron microscope images of paint particles collected by monocrystalline silicon sheets, when energy density is 4.5 J/cm2

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



