Guangle Wang, Yatong Zhou, Zhao Wang. Lightweight Model for Irregular Wear Detection in Power Operations[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2025, 62(6): 0615007
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 62, Issue 6, 0615007 (2025)
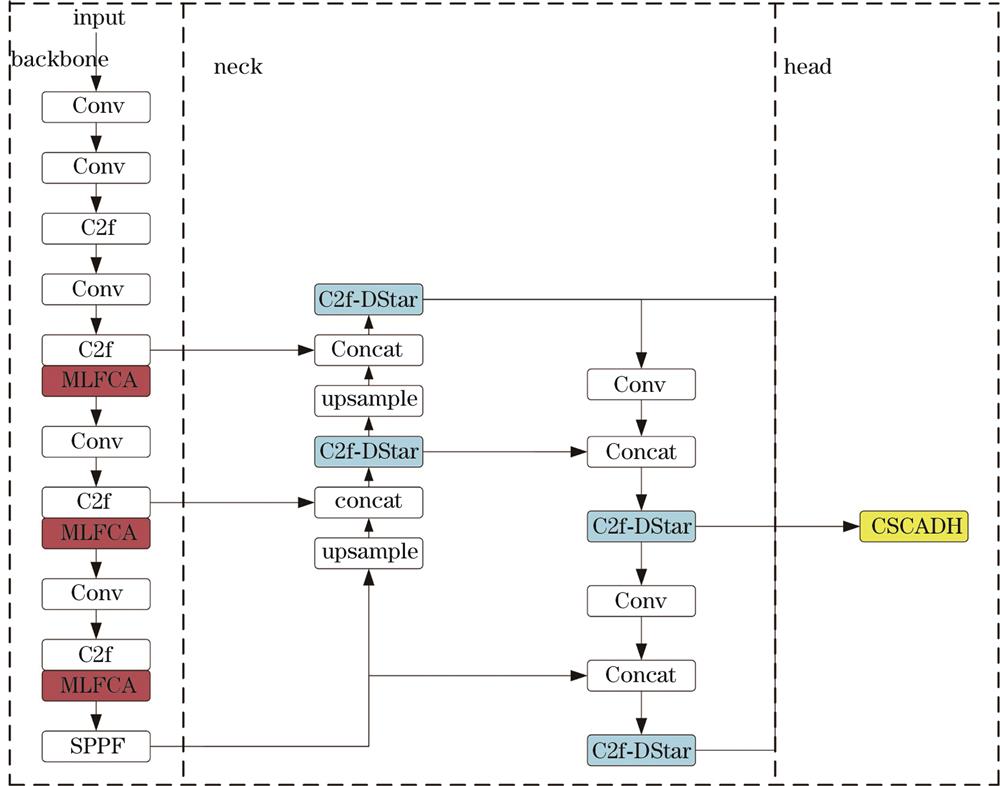
Fig. 1. YOLO-WWS structure diagram

Fig. 2. YOLOv8n detection head
Fig. 3. Structure of SCTADH
Fig. 4. bottleneck and DStar structures. (a) bottleneck structure;(b) DStar structure
Fig. 5. MLFCA attention module
Fig. 6. Model parameter quantity distribution before and after improvement. (a) YOLOv8n parameter quantity distribution; (b) YOLO-WWSP parameter quantity distribution
Fig. 7. Comparison of YOLOv8n (left) and YOLO-WWSP (right) test results
|
Table 1. Experimental model parameters
|
Table 2. Results of the ablation experiments
|
Table 3. Comparison of the five attention mechanisms
|
Table 4. Comparison of the experimental results

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



