Tao Jiang, Haihua Cui, Xiaosheng Cheng, Wei Tian. Combined Optical Scanning Transposition Pose Calibration Method Integrating Scale Factor[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(23): 2312005
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 59, Issue 23, 2312005 (2022)
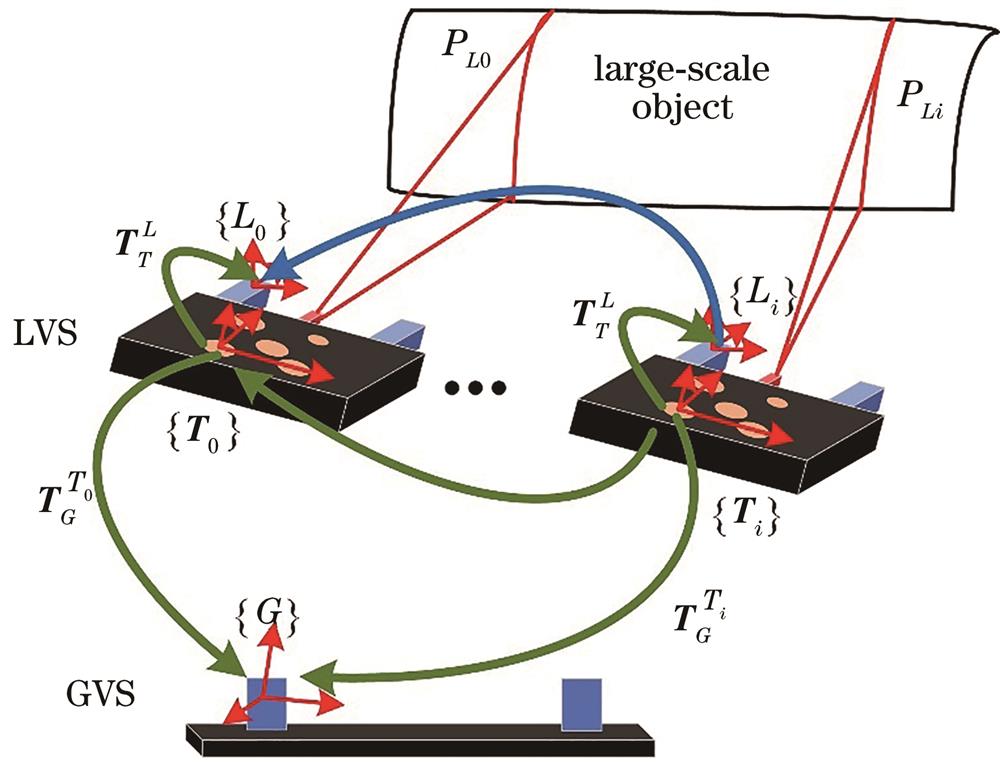
Fig. 1. Geometrical model of combined optical tracking and scanning
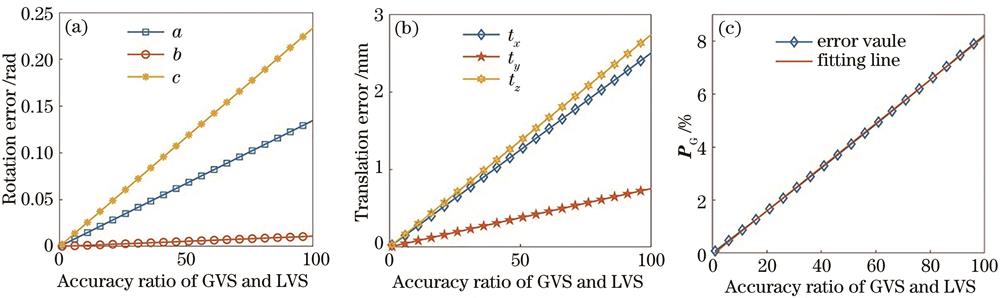
Fig. 2. Variation curves of
Fig. 3. Simulation of transposition pose calibration. (a) Visualization platform; (b) data transmission route
Fig. 4. Experiment of transposition pose calibration. (a) Experimental setup; (b) calibration board; (c), (d) target detection results of GVS view; (e), (f) target detection results of LVS view
Fig. 5. Evaluation of scanning accuracy using standard plane
Fig. 6. Scanning accuracy comparison of proposed method with commercial device. (a) Blade 1 without scale factor; (b) blade 1 with scale factor; (c) blade 2 without scale factor; (d) blade 2 with scale factor
|
Table 1. Calibration result error with scale change
|
Table 2. Combined calibration error

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



