Yanfang Ju, Guochao Gu, Bo Li, Guanyu Lin, Zhengzheng Ma, Bin Xu. Stray-Light Suppression of Far Ultraviolet Ionization Layer Hyperspectral Imager[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(10): 1030001
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 60, Issue 10, 1030001 (2023)
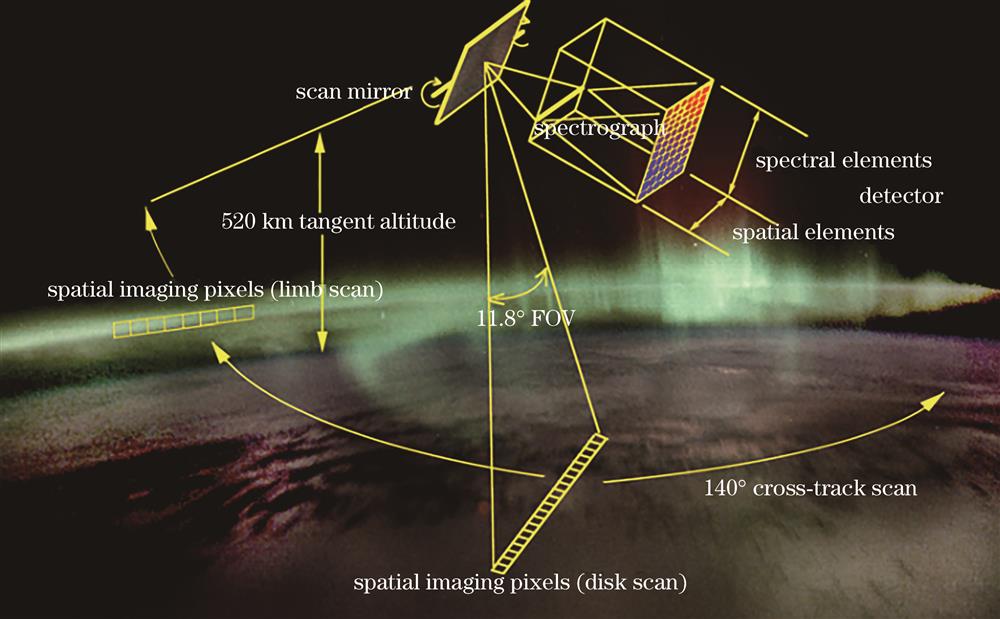
Fig. 1. Observation diagram
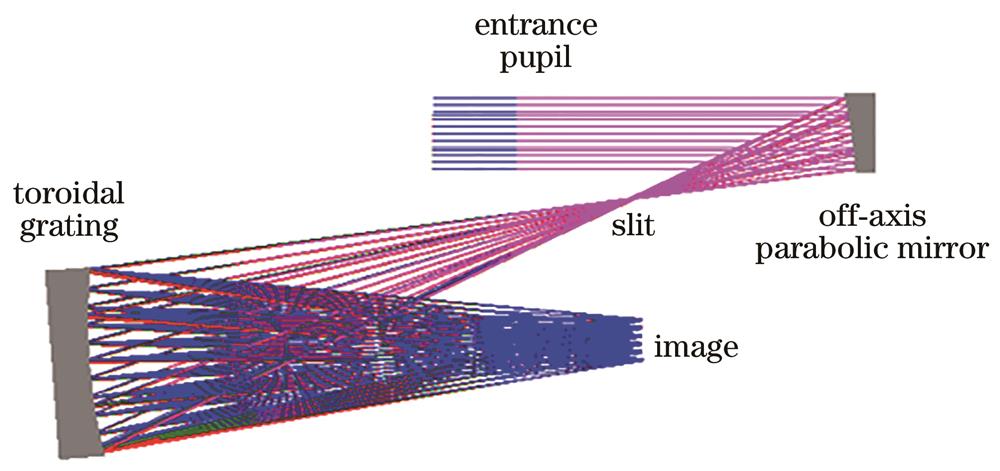
Fig. 2. Optical system structure diagram
Fig. 3. Schematic of mechanical structure
Fig. 4. Three-dimensional model of the system
Fig. 5. Geometric diagram of bidirectional scattering distribution function
Fig. 6. Schematic of energy transmission between micro panels
Fig. 7. Light source spectral weight
Fig. 8. Ray tracing diagram (before inhibition)
Fig. 9. Ray tracing diagram (after inhibition)
Fig. 10. Energy distribution diagram (before inhibition)
Fig. 11. Energy distribution diagram (after inhibition)
Fig. 12. Image plane energy of each field of view
Fig. 13. Diffraction order energy of the grating
Fig. 14. Noncentral wavelength energy distribution
Fig. 15. Full band energy distribution
|
Table 1. Technical indicators
|
Table 2. Structural parameters
|
Table 3. Optical mechanical model parameters
|
Table 4. Central wavelength stray light level

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



