Dan-Dan Liu, Yin-Bo Huang, Yu-Song Sun, Xing-Ji Lu, Zhen-Song Cao. Influence of tropopause height on inversion of greenhouse gas column concentration in Lhasa, China [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2020, 69(13): 130201-1
Search by keywords or author
- Acta Physica Sinica
- Vol. 69, Issue 13, 130201-1 (2020)

Fig. 1. (a) Observing site (Lhasa meteorological bureau); (b) FTIR spectrometer (EM27/SUN).
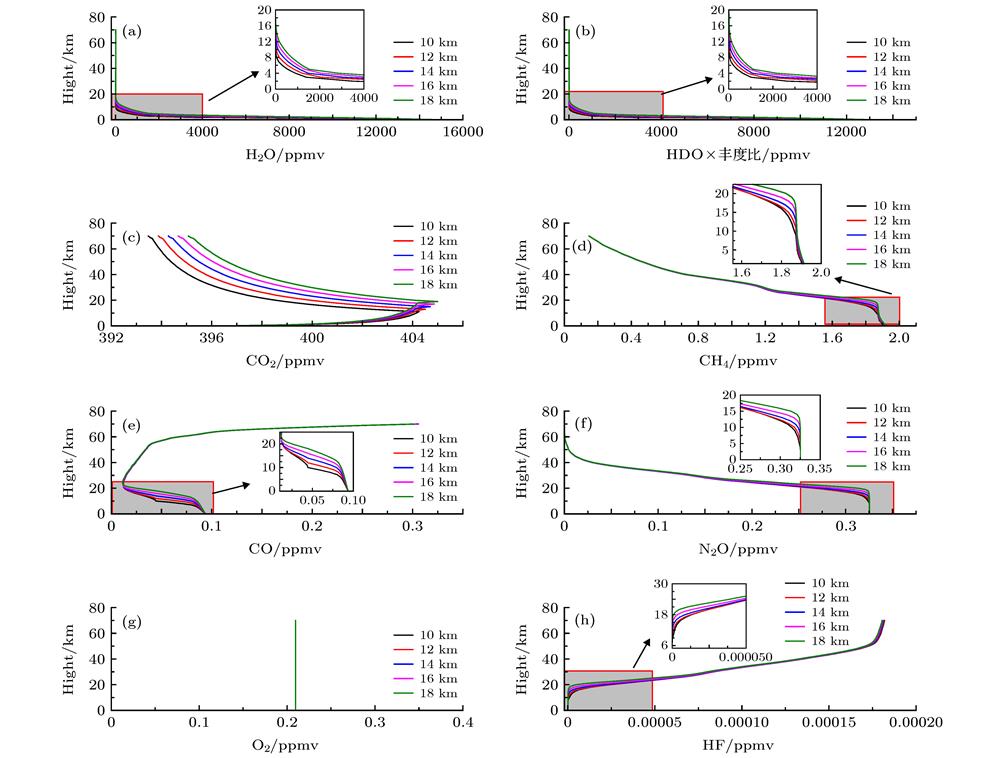
Fig. 2. The profiles of H2O (a), HDO (b), CO2 (c), CH4 (d), CO (e), N2O (f), HF (g) and O2 (h) at different heights of top troposphere
Fig. 3. The diurnal variation of X H2O (a), (e), X CO2 (b), (f), X CH4 (c), (g) and X CO (d), (h) with tropopause height.
Fig. 4. Linear fit of the average mole fraction of CO2 (a), CH4 (b) and CO (c) to the top of the troposphere.
Fig. 5. Time series of X H2O (a), X CO2 (b), X CH4 (c)and X CO (d).
Fig. 6. Time series of X CO2 (a), (b)and X CH4 (c), (d)at August 7, 8, 2018.
Fig. 7. The correlation between X CO2 and X CH4: (a) August 6, 2018; (b) August 7, 2018; (c) August 8, 2018; (d) August 10, 2018
Fig. 8. 72-hour back trajectories of Lhasa during August 6—16, 2018: (a) August 4-6, 2018; (b) August 7-9, 2018; (c) August 10-12, 2018; (d) August 14-16, 2018
Fig. 9. Comparison of X CO2 (a) and X CH4 (b) based on ground-based observations and WACCM data.
|
Table 1. [in Chinese]
Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



