Minjuan MAO, Houtong LIU, Fangping DENG, Yilei DONG. Lidar observation of pollutant transport and deposition in high impact haze weather[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2023, 18(6): 541
Search by keywords or author
- Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics
- Vol. 18, Issue 6, 541 (2023)

Fig. 1. MPL (a), TEOM 1400a (b) and URG―9000 (c) on-line monitor meters
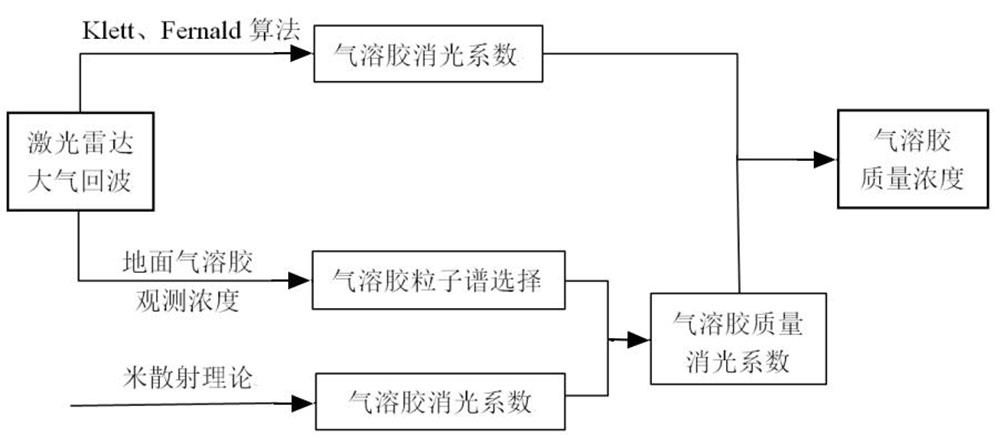
Fig. 2. Calculation steps for inversion of particulate matter mass concentration
Fig. 3. The mass concentrations of PM10 retrieved with MPL data and real time observations
Fig. 4. Depolarization ratio and radar ratio for different types of aerosols
Fig. 5. The vertical distribution of aerosol concentration detected by MPL from December 5 to 10, 2013
Fig. 6. The hourly mass concentration of PM2.5 and PM10 as well as the ratio of them in Hangzhou from December 5 to 10, 2013
Fig. 7. The depolarization ratio detected by MPL from December 5 to 10, 2013
Fig. 8. The air temperature (a) and relative humidity (b) detected by microwave radiometer from December 5 to 10, 2013
|
Table 1. Characteristics of typical heavy pollution processes in Hangzhou

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



