Yuxin Yang, Jiaxin Gao, Hao Wu, Zhanke Zhou, Liu Yang, Xin Guo, Pan Wang, Limin Tong, "Generating a nanoscale blade-like optical field in a coupled nanofiber pair," Photonics Res. 12, 154 (2024)
Search by keywords or author
- Photonics Research
- Vol. 12, Issue 1, 154 (2024)

Fig. 1. (a) Schematic illustration of generating a nanoscale blade-like optical field in a CNP. (b) Close-up profile of the field around the slit in (a). The inset illustrates cross-sectional distribution of the polarized charge density.
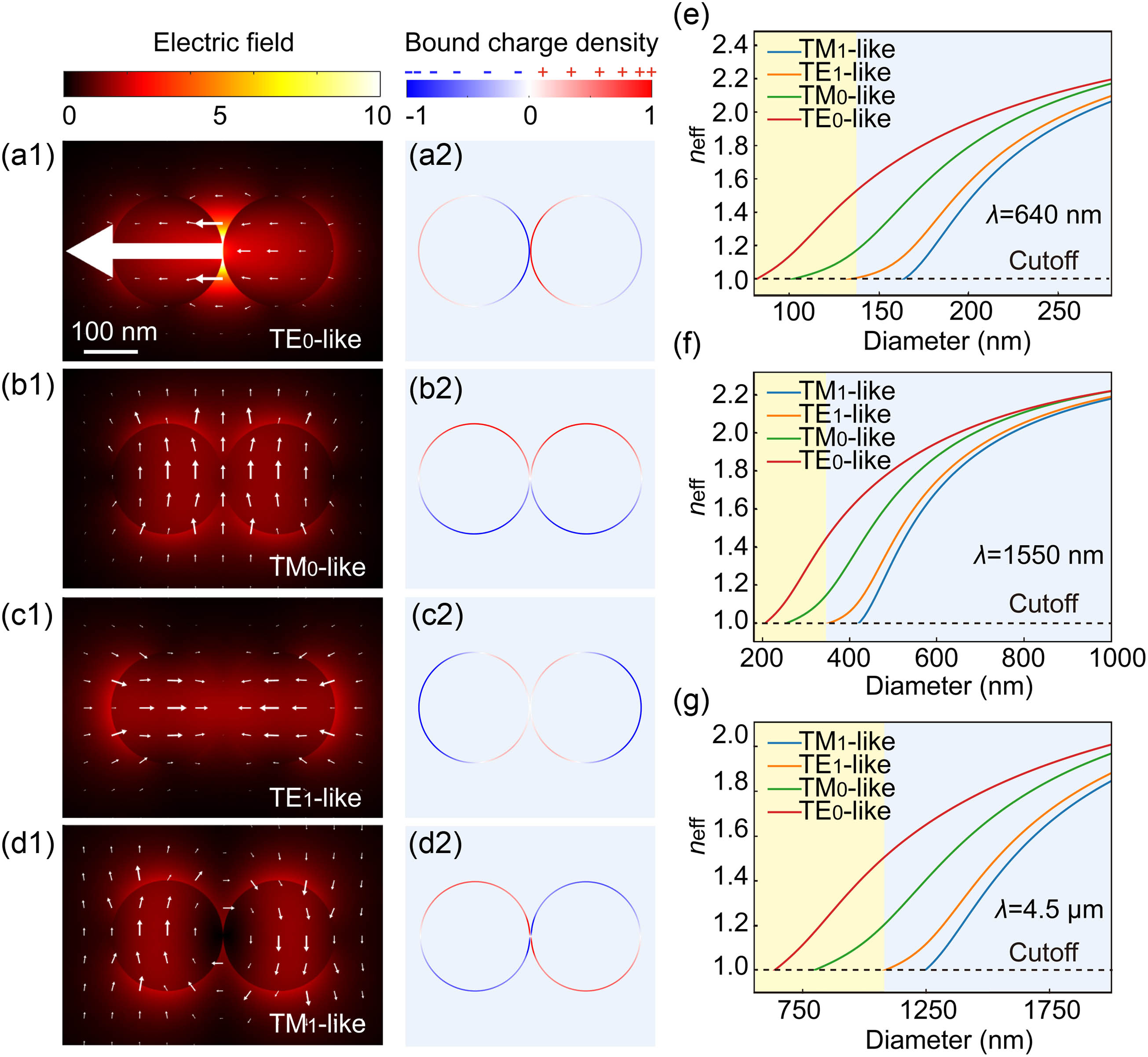
Fig. 2. Four lowest eigenmodes of the As 2 S 3 TE 0 TM 0 TE 1 TM 1 As 2 S 3 D = 200 nm n eff
Fig. 3. Sub-nm-confined optical fields in the nano-slit mode of an As 2 S 3 TE 0 As 2 S 3 D = 300 nm W = 1 nm x y = 0 y x = 0 TE 0 x y = 0 10 × z P z P z P z
Fig. 4. (a) Slit-width-dependent PBR and FWHM of the field intensity of the TE 0 As 2 S 3 D = 300 nm D / λ TE 0 W = 1 nm As 2 S 3 D = 120 nm TE 0 W = 1 nm D = 120 nm P z
Fig. 5. (a) Schematic illustration of the coupling structure. (b) Diameter-dependent effective refractive index of As 2 S 3 TE 0 As 2 S 3 D = 300 nm W = 1 nm V g As 2 S 3 D = 300 nm W = 1 nm
Fig. 7. Refractive index profiles of (a) linear and (b) step approximation in the silt of an As 2 S 3
Fig. 8. Slit-width-dependent PBR and FWHM of the TE 0 As 2 S 3 D = 200 nm x W = 1 nm
Fig. 9. Sub-nm-confined optical fields in the nano-slit mode of a SiO 2 TE 0 SiO 2 D = 50 nm W = 0.25 nm x y = 0 y x = 0 TE 0 n eff D / λ TE 0 W = 0.25 nm SiO 2 D = 50 nm TE 0 P z

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



