Peile Bai, Zongxin Zhang, Xinliang Wang, Jiayi Qian, Jiacheng Zhu, Fenxiang Wu, Jiabing Hu, Xiaojun Yang, Jiayan Gui, Xiaoming Lu, Yanqi Liu, Yi Xu, Xiaoyan Liang, Yuxin Leng, Ruxin Li, "Suppression of nanosecond prepulses from regenerative amplifier and multipass amplifiers in the SULF-1PW laser," Chin. Opt. Lett. 22, 051404 (2024)
Search by keywords or author
- Chinese Optics Letters
- Vol. 22, Issue 5, 051404 (2024)
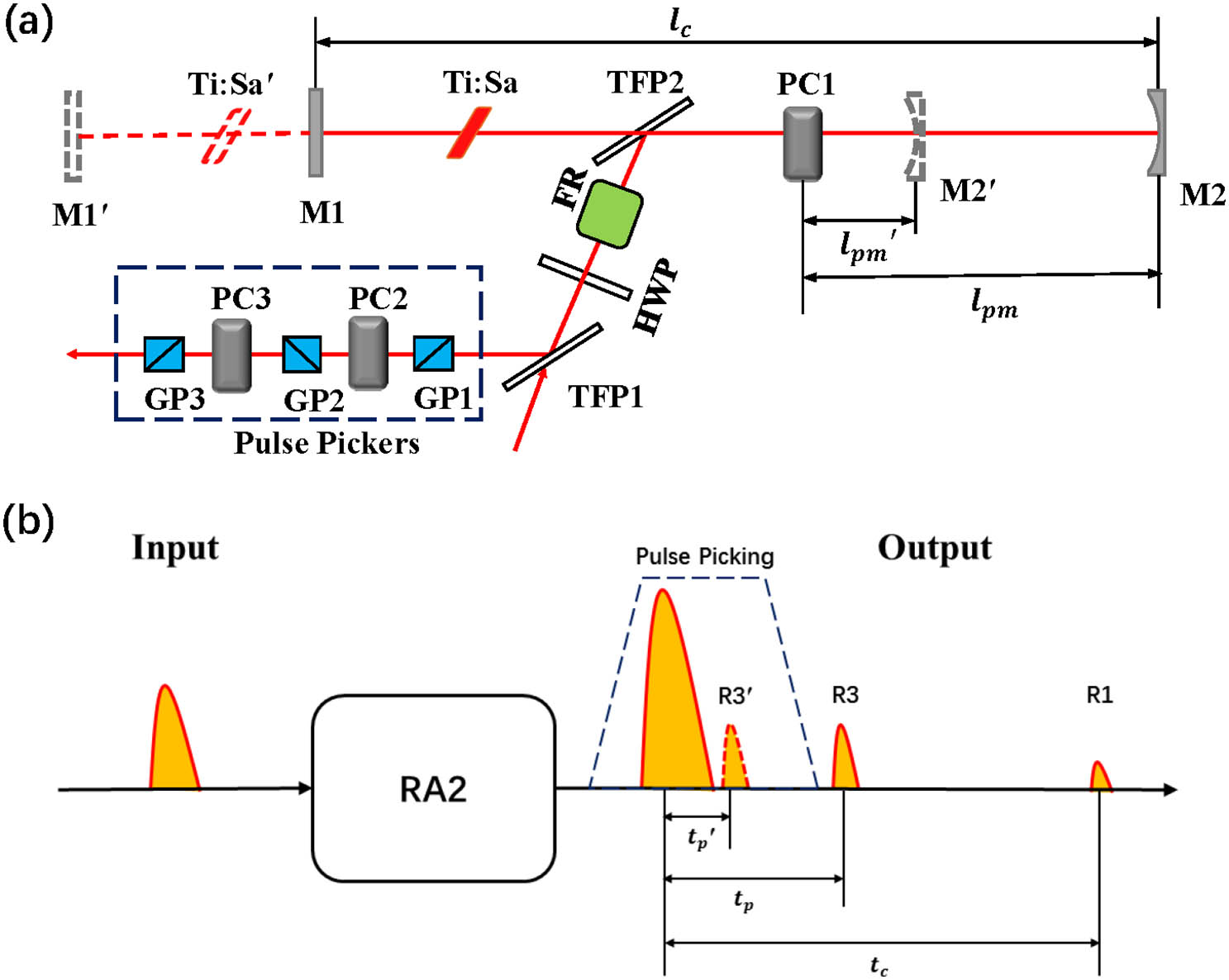
Fig. 1. (a) Scheme of the optimized RA2 in the second CPA stage. M1 and M2 are highly reflective cavity mirrors, while M1´ and M2´ represent their original positions; Ti:Sa and Ti:Sa´ represent the Ti:sapphire crystal and its original position; PC1, PC2, and PC3, Pockels cells; GP1, GP2, and GP3, Glan prisms; TFP1 and TFP2, thin-film polarizers; HWP, half-wave plate; FR, Faraday rotator. (b) Temporal shift of the third type of ns prepulse (R3) from RA2. tp and tp′ correspond to the distance lpm and lpm′, respectively. tc represents the round-trip time of RA2, corresponding to the cavity length lc. The dashed trapezium represents the picking gate of the pulse pickers.

Fig. 2. Detection of ns prepulses after the optimized RA2 and the following pulse pickers. (a) Without adjusting the switching-on time of PC2/PC3, and (b) with an adjustment on the switching-on time of PC2/PC3 for 4 ns delay. The black line represents part of the normalized main pulse, while the red line shows the corresponding ns prepulses.
Fig. 3. Optimized five-pass amplifier configurations. (a) With larger angles between the first/third/fifth passes, and (b) with larger angle between the second and fourth passes. M1 to M10 are highly reflective plane mirrors. Ti:Sa represents the Ti:sapphire crystal. The blue dashed line and the black dashed dotted line represent the paths of a backward-scattered prepulse (BS1→8) and a forward-scattered prepulse (FS1→10) generated during the first pass (from M1 to M2). The lines are drawn apart for a better view of the different paths. The intensity of the forward-scattered prepulse FS1→10 is related to the angle between the first pass and the fifth pass (∠M2-Ti:Sa-M10).
Fig. 4. Detection of ns prepulses after the second CPA stage. (a) With traditional multipass amplifier configurations, and (b) with optimized multipass amplifier configurations. The black line represents part of the normalized main pulse, while the red line shows the corresponding ns prepulses.
|
Table 1. The ns Prepulses May Be Generated in Optimized Five-pass Amplifier Configurations

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



