Mingna ZHANG, Xiaoqi LÜ, Yu GU. Image registration based on residual mixed attention and multi-resolution constraints[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(10): 1203
Search by keywords or author
- Optics and Precision Engineering
- Vol. 30, Issue 10, 1203 (2022)
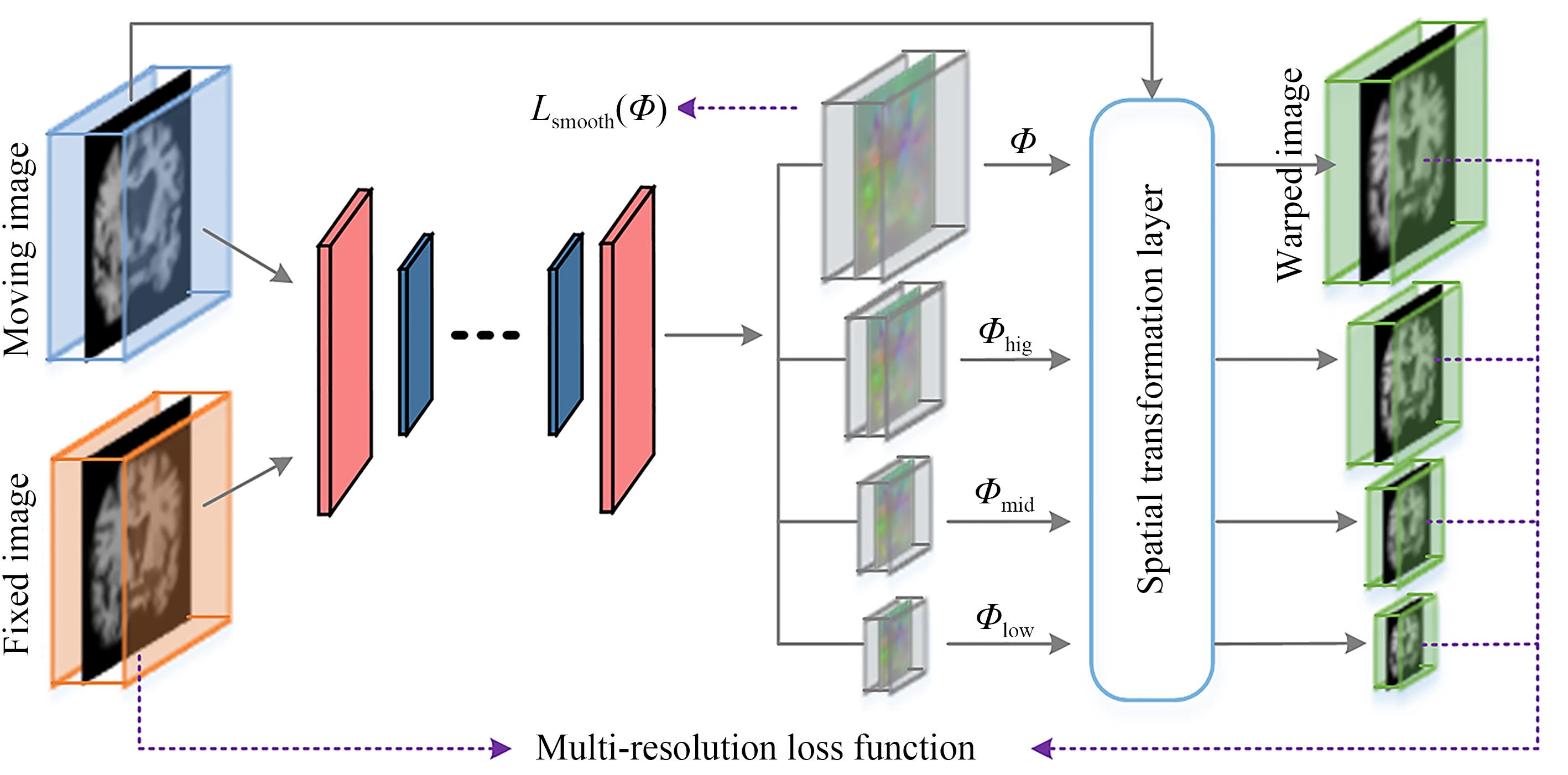
Fig. 1. Diagram of registration network model

Fig. 2. Architecture of MAMReg-Net network
Fig. 3. Diagram of residual mixed attention
Fig. 4. Structure of Mask branching
Fig. 5. Non-Local module
Fig. 6. Images before and after preprocessing
Fig. 7. Image of 12 examples of anatomical structures
Fig. 8. Samples registration result from test images
Fig. 9. Color overlay images before and after registration
Fig. 10. Registration results using different methods
Fig. 11. Histogram of the average Dice score of the 12 anatomical structures on the test images
Fig. 12. Histogram of the average ASD score of the 12 anatomical structures on the test images
Fig. 13. Dice score boxplot of 12 anatomical structures in ablation experiment
Fig. 14. ASD score boxplot of 12 anatomical structures in ablation experiment
|
Table 1. Registration accuracy of different methods
|
Table 2. Comparison of registration time between different methods
|
Table 3. Comparison of registration accuracy of ABIDE dataset
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 4. Comparison of registration accuracy of ablation experiments

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



