Kaimin Zheng, Lijian Zhang. Progress on Quantum-Enhanced Time-Varying Parameter Estimation[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(11): 1106009
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 60, Issue 11, 1106009 (2023)
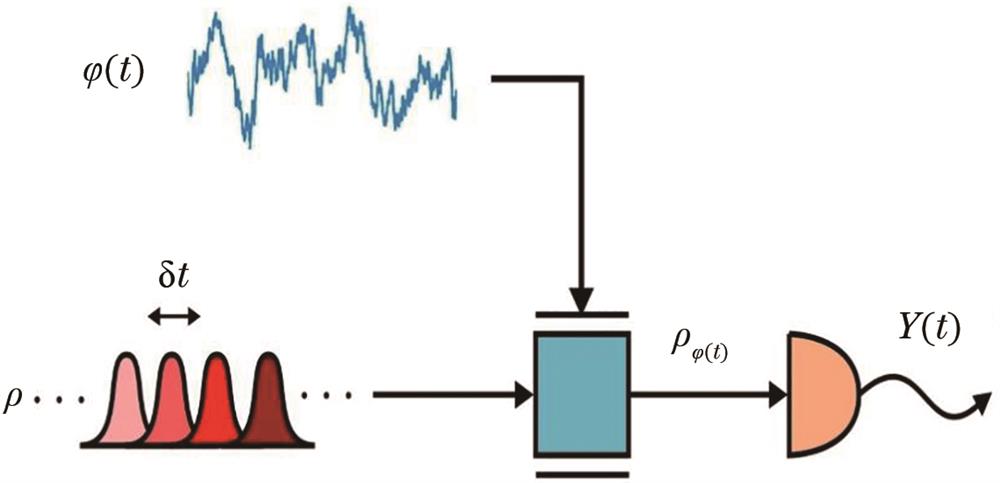
Fig. 1. Estimation of time-varying parameter
![Schematic of adaptive time-varying phase estimation method via weak measurement[49]](/richHtml/lop/2023/60/11/1106009/img_02.jpg)
Fig. 2. Schematic of adaptive time-varying phase estimation method via weak measurement[49]
Fig. 3. Adaptive optical phase estimation using time-symmetric quantum smoothing[50]. (a) Signal and local oscillator generation; (b) adaptive phase estimation; (c) no-adaptive phase estimation; (d) experimental and theoretical variance
Fig. 4. Conceptual diagram and results for waveform estimation[57]. (a) Concept of waveform estimation with n1 samplings and n2 independent or correlated quantum resources; (b) statistical error; (c) deterministic error; (d) total error
Fig. 5. Atomic sensor based on Kalman filtering[59].(a) Time-varying signal estimation based on atomic sensor; (b) applied waveform (input) along with the corresponding measured photocurrent (output) and the recovered waveform (KF estimation); (c) spectrograms of input, output, and KF estimation
Fig. 6. Schematic of magnetic field estimation[60]
Fig. 7. Real-time sensing of magnetic fields based on a NV center prepared in a CPT setting[61]

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



