Author Affiliations
1School of Automation, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, Jiangsu , China2Key Laboratory of Measurement and Control of Complex Systems of Engineering, Ministry of Education, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, Jiangsu , China3Shenzhen Research Institute, Southeast University, Shenzhen 518063, Guangdong , Chinashow less
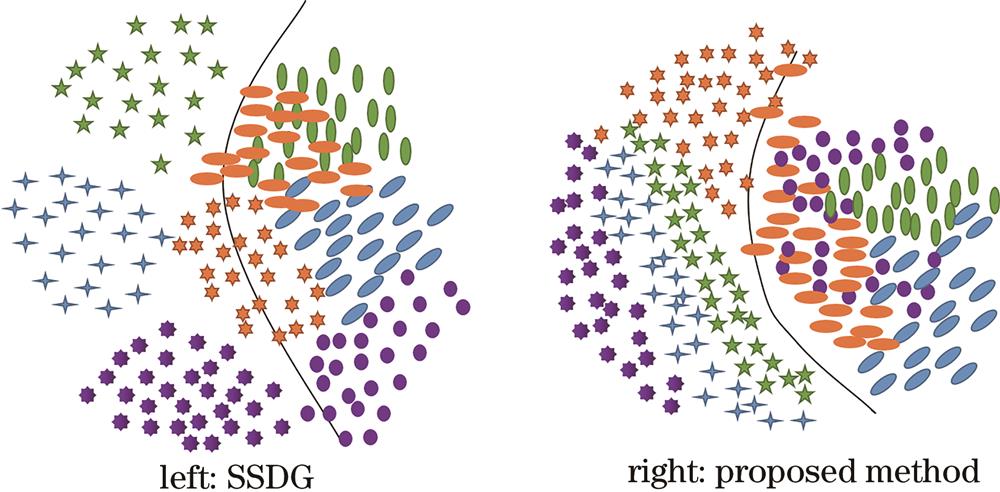
Fig. 1. Motivation of different methods
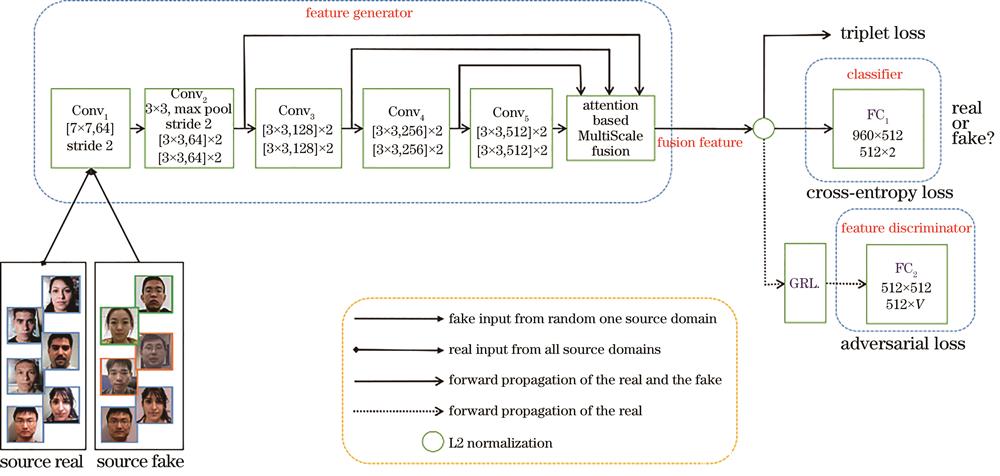
Fig. 2. Overall architecture of the proposed model
Fig. 3. Multi-scale attention fusion module
Fig. 4. Illustration of triplet loss
Fig. 5. t-SNE visualization for the classification features obtained by baseline method and proposed method under the I&C&M to O testing task
Fig. 6. Grad-CAM visualization under the I&C&M to O testing task
| Dataset | Number of identities | Number of videos | Number of real categories | Number of fake categories |
|---|
| MSU-MFSD | 35 | 280 | 2 | 6 | | CASIA-FASD | 50 | 600 | 3 | 9 | | Idiap Replay-Attack | 50 | 1200 | 4 | 20 | | OULU-NPU | 55 | 4950 | 18 | 72 |
|
Table 1. Details of four datasets
| Method | O&C&I to M | | O&M&I to C | | O&C&M to I | | I&C&M to O |
|---|
| HTER /% | AUC /% | | HTER /% | AUC /% | | HTER /% | AUC /% | | HTER /% | AUC /% |
|---|
| w /o att | 5.27 | 95.20 | | 12.11 | 94.31 | | 10.07 | 95.99 | | 13.54 | 93.22 | | w /o ad | 5.71 | 96.10 | | 10.77 | 94.51 | | 14.92 | 93.05 | | 12.30 | 94.97 | | w /o tri | 7.14 | 96.53 | | 10.66 | 95.19 | | 21.42 | 80.51 | | 22.06 | 86.37 | | all | 4.52 | 97.24 | | 9.88 | 95.46 | | 9.21 | 96.97 | | 11.45 | 95.32 |
|
Table 2. Evaluation results of different components of the proposed method
| Method | O&C&I to M | | O&M&I to C | | O&C&M to I | | I&C&M to O |
|---|
| HTER /% | AUC /% | | HTER /% | AUC /% | | HTER /% | AUC /% | | HTER /% | AUC /% |
|---|
| SSDG | 7.38 | 97.17 | | 10.44 | 95.94 | | 11.71 | 96.59 | | 15.61 | 91.54 | | Proposed method | 4.52 | 97.24 | | 9.88 | 95.46 | | 9.21 | 96.97 | | 11.45 | 95.32 |
|
Table 3. Comparison results between the proposed method and the corresponding baseline method
| Method | M&I to C | | M&I to O |
|---|
| HTER /% | AUC /% | | HTER /% | AUC /% |
|---|
| MS-LBP[23] | 51.16 | 52.09 | | 43.63 | 58.07 | | IDA[4] | 45.16 | 58.80 | | 54.52 | 42.17 | | LBP-TOP[24] | 45.27 | 54.88 | | 47.26 | 50.21 | | MADDG[10] | 41.02 | 64.33 | | 39.35 | 65.10 | | SSDG-M[9] | 31.89 | 71.29 | | 36.01 | 66.88 | | DRDG[11] | 31.28 | 71.50 | | 33.35 | 69.14 | | DASN[12] | 21.48 | 83.41 | | 21.74 | 80.87 | | Proposed method | 17.88 | 89.91 | | 22.70 | 86.17 |
|
Table 4. Comparison result of different domain generalization methods in the case of limited source domains
| Backbone | FLOPs /109 | Params /106 | Speed /(frame·s-1) | Avg HTER /% | Avg AUC /% |
|---|
| Resnet50 | 5.37 | 25.60 | 46.57 | 12.05 | 93.51 | | Resnet34 | 4.79 | 21.81 | 52.65 | 12.31 | 93.87 | | Resnet18 | 2.37 | 11.70 | 100.75 | 8.76 | 96.29 |
|
Table 5. Comparison result of different backbone networks
| Method | O&C&I to M | | O&M&I to C | | O&C&M to I | | I&C&M to O |
|---|
| HTER /% | AUC /% | | HTER /% | AUC /% | | HTER /% | AUC /% | | HTER /% | AUC /% |
|---|
| MS-LBP[23] | 29.76 | 78.50 | | 54.28 | 44.98 | | 50.30 | 51.64 | | 50.29 | 49.31 | | Binary CNN[25] | 29.25 | 82.87 | | 34.88 | 71.94 | | 34.47 | 65.88 | | 29.61 | 77.54 | | IDA[4] | 66.67 | 27.86 | | 55.17 | 39.05 | | 28.35 | 78.25 | | 54.20 | 44.59 | | Color Texture[26] | 28.09 | 78.47 | | 30.58 | 76.89 | | 40.40 | 62.78 | | 63.59 | 32.71 | | LBP-TOP[24] | 36.90 | 70.80 | | 33.52 | 73.15 | | 29.14 | 71.69 | | 30.17 | 77.61 | | Auxiliary(Depth) | 22.72 | 85.88 | | 33.52 | 73.15 | | 29.14 | 71.69 | | 30.17 | 77.61 | | Auxiliary[27] | — | — | | 28.40 | — | | 27.60 | — | | — | — | | MADDG[10] | 17.69 | 88.06 | | 24.50 | 84.51 | | 22.19 | 84.99 | | 27.89 | 80.02 | | SSDG[9] | 7.38 | 97.17 | | 10.44 | 95.94 | | 11.71 | 96.59 | | 15.61 | 91.54 | | DRDG[11] | 12.43 | 95.81 | | 19.05 | 88.79 | | 15.56 | 91.79 | | 15.63 | 91.75 | | DASN[12] | 8.33 | 96.31 | | 12.04 | 95.33 | | 13.38 | 86.63 | | 11.77 | 94.65 | | Proposed method | 4.52 | 97.24 | | 9.88 | 95.46 | | 9.21 | 96.97 | | 11.45 | 95.32 |
|
Table 6. Comparison result between the proposed method and other methods for domain generalization on face anti-spoofing