Ning Zhang, Guozhong Hou, Yanyan Deng, Shuo Liu, Yulei Wang, Lü Zhiwei, Yuanqin Xia. Focusing Spectral CARS Microscopic Imaging in Low Fingerprint Regions[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(24): 2418001
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 59, Issue 24, 2418001 (2022)
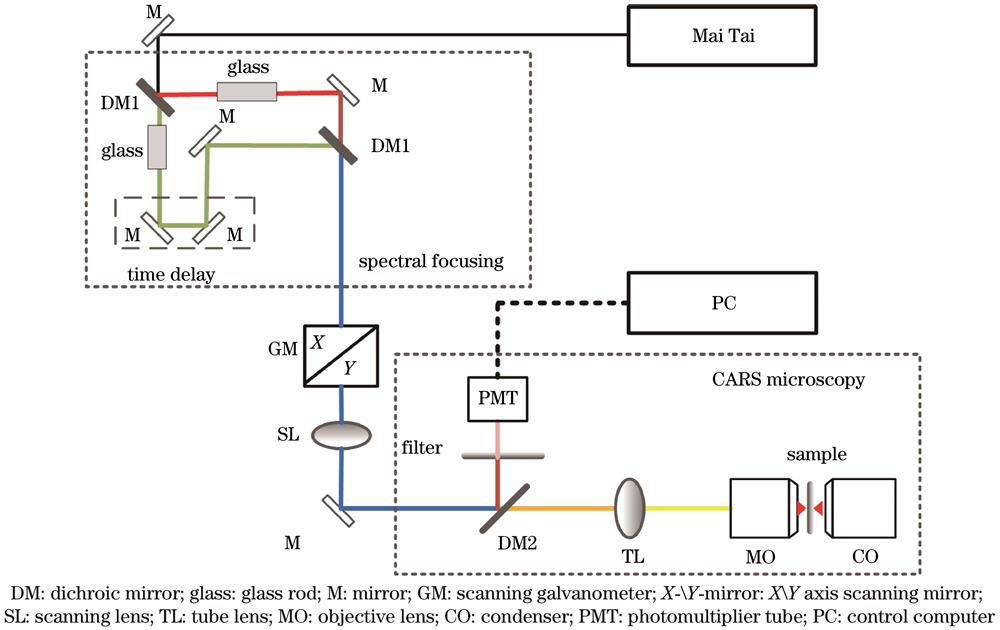
Fig. 1. Schematic of the spectral focusing CARS microscope imaging system
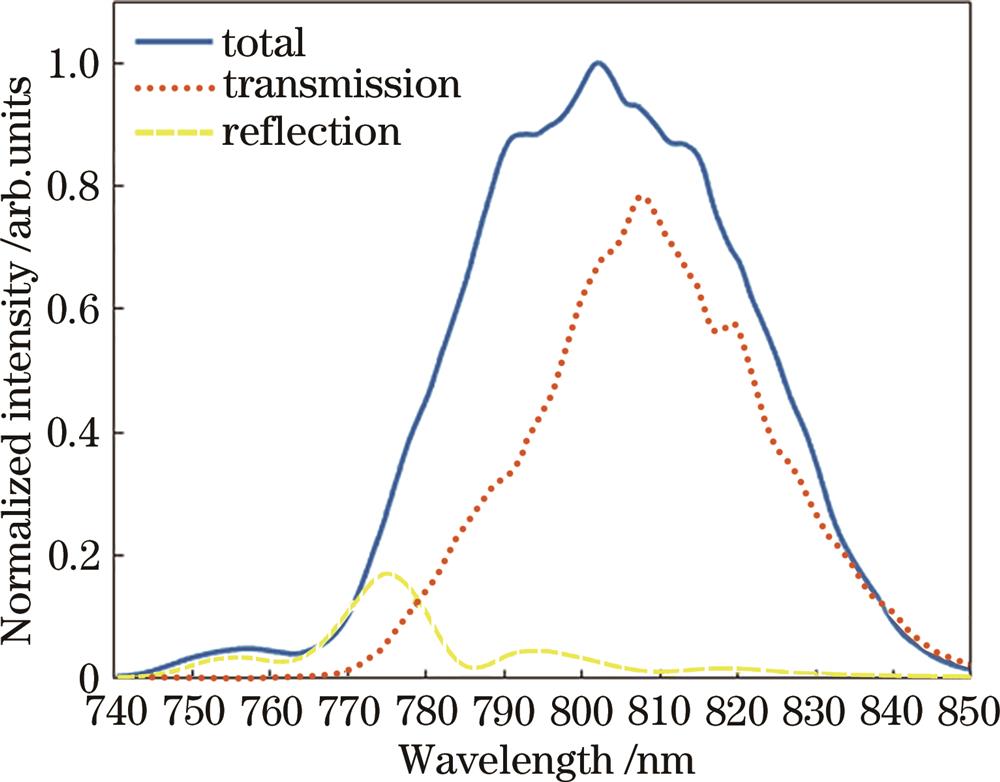
Fig. 2. Total output spectrum of femtosecond laser oscillator and reflection/transmission of DM
Fig. 3. Signal contrast diagram. (a) Multiply frequency signal; (b) sum frequency signal
Fig. 4. CARS microscopic imaging results. (a) Image of the polystyrene powder sample in the field of view of the eyepiece; (b)-(g) CARS microscopic imaging results of sample in the red frame range with pump-Stokes delays of 100, 320, 540, 660, 900, and 1200 fs
Fig. 5. Comparison results. (a) Spectral focusing CARS signal intensity spectrum of polystyrene; (b) Raman spectrum of polystyrene
Fig. 6. Gaussian fitting result. (a) CARS microscopic imaging of polystyrene; (b) Gaussian fitting curve of CARS signal in region A
Fig. 7. CARS microscopic imaging results. (a) Image of the polystyrene powder sample in the field of view of the eyepiece; (b)-(g) results of CARS microscopic imaging at the positions of 0, 4, 7, 10, 13, 16 μm obtained by Z-axis scanning
Fig. 8. Three-dimensional imaging results. (a) 3D reconstruction of nearly triangular polystyrene powder; (b) top view of 3D reconstruction

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



