Cade Peters, Andrew Forbes, "Controlling the hidden parity in vectorial light with metasurfaces," Adv. Photon. 6, 040501 (2024)
Search by keywords or author
- Advanced Photonics
- Vol. 6, Issue 4, 040501 (2024)
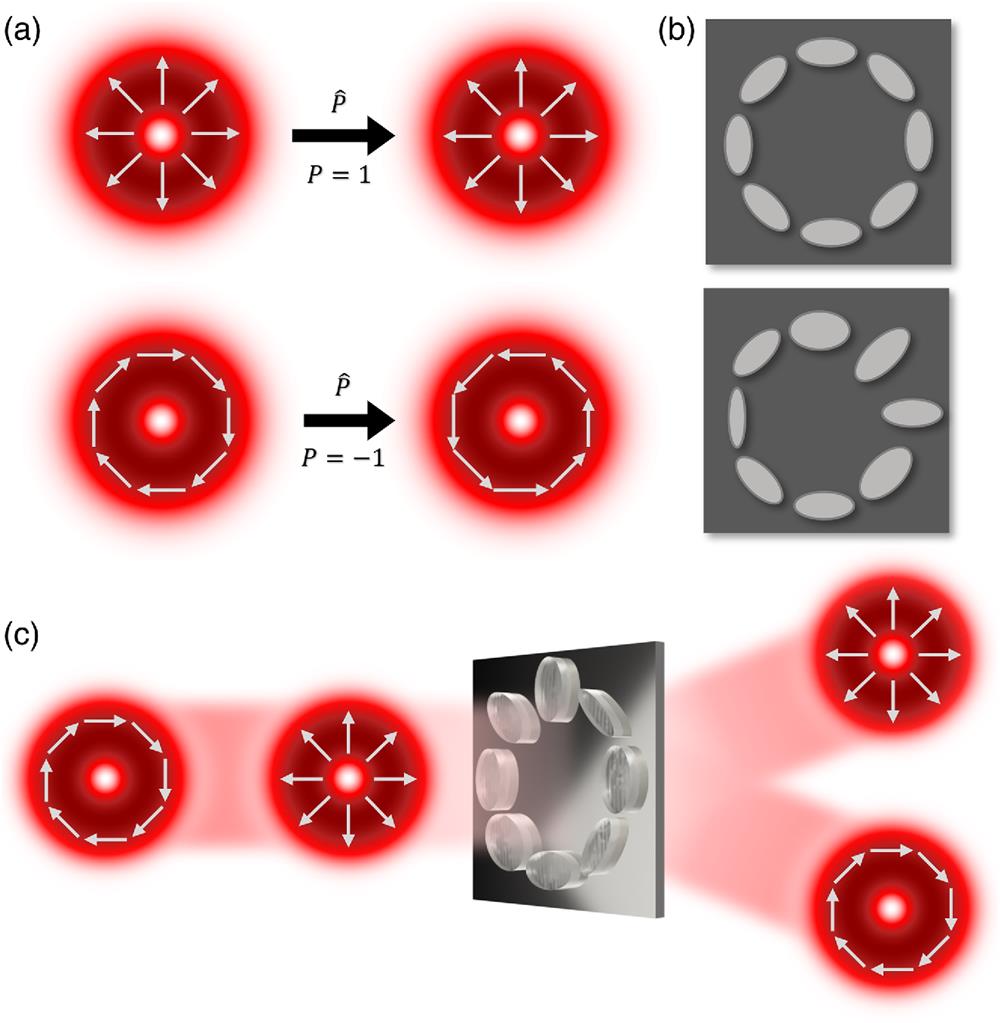
Fig. 1. Parity in vectorial light and its control. (a) If a vectorial beam is invariant under the action of the parity operator it is assigned an even parity and an odd parity if it is inverted under the action of the parity operator, shown here for radial and azimuthal vectorial light. (b) Mode parity dispersion can be induced by matching the arrangement of birefringent unit cells with the symmetry of the polarization vectors, so that each parity mode experiences a unique birefringent axis. By spatially varying the birefringence of these unit cells, one can then impart different phases onto incident beams depending on their parity. (c) This results in a vectorial version of the spin-Hall effect, coined the parity-Hall effect, where vectorial modes are separated by parity.

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



