Meng ZHAO, Huijun XIA, Ruize CHAO, Ming SHAO, Xiangzheng CHENG, Lanshuang LU, Zheng QIU, Haimeng LIU, Yong TAN. Study on temperature inversion of deflagration spectrum of pyrotechnics[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2024, 53(6): 20240114
Search by keywords or author
- Infrared and Laser Engineering
- Vol. 53, Issue 6, 20240114 (2024)
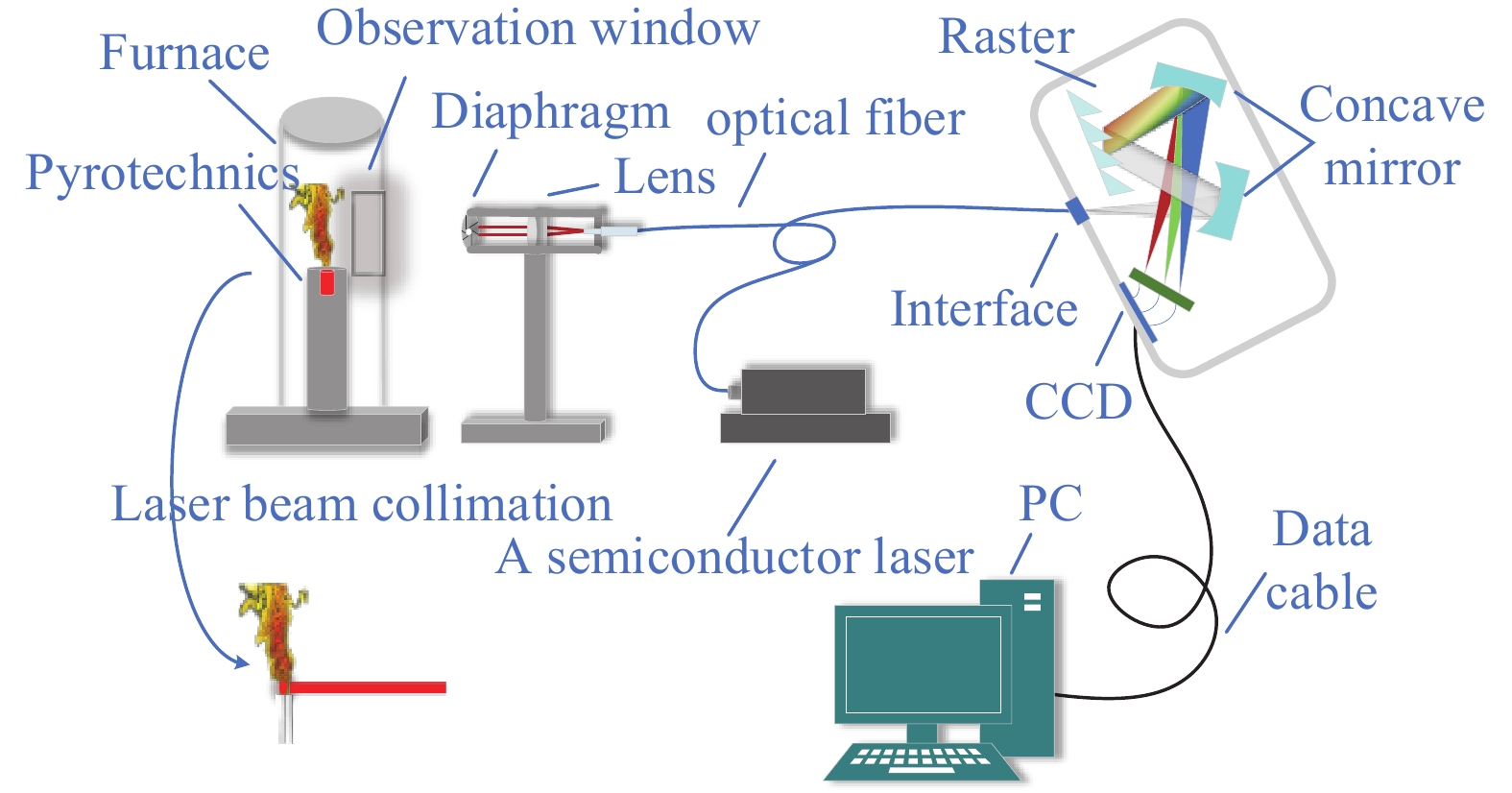
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the experimental device

Fig. 2. Improved Wien criterion spectral data processing flowchart
Fig. 3. Deflagration 1 ms to 200 ms spectral curve
Fig. 4. Wavelength response curve
Fig. 5. Spectral curve of deflagration radiation of pyrotechnic agent after correction
Fig. 6. Radiation spectrum of different deflagration stages
Fig. 7. Spectral curve after Wien transform
Fig. 8. Spectral fitting curve after Wien transform. (a) 1 ms; (b) 52 ms; (c) 60 ms; (d) 191 ms
Fig. 9. Temperature change during deflagration of pyrotechnic agent
|
Table 1. Pyrotechnic composition ratio and function
|
Table 2. Fitting temperature and fitting error of pyrotechnic agents at different detonation stages

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



