Xiaocui YUAN, Yongtao WANG, Baoling LIU, Dibo HOU, Zonghui JIANG. Detection method for structural defects of railway clip fastener based on 3D line laser sensor[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2024, 53(7): 20240176
Search by keywords or author
- Infrared and Laser Engineering
- Vol. 53, Issue 7, 20240176 (2024)
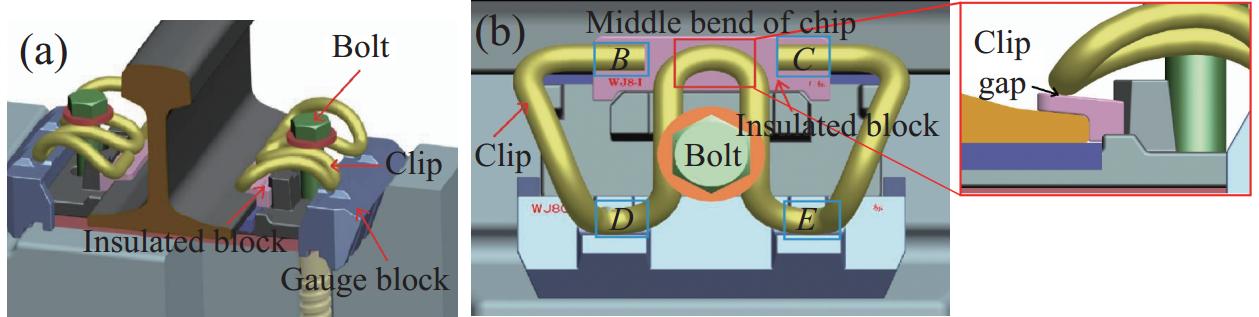
Fig. 1. (a) Fastener structure of WJ-8; (b) Structure and gap of clip

Fig. 2. (a) Diagram of railway fastener data acquisition system; (b) Physical image of railway fastener data acquisition system
Fig. 3. (a) Top view of loose fasteners; (b) Front view of loose fasteners; (c) Top view of fasteners that are too tight; (d) Front view of over tightened fasteners
Fig. 4. Point cloud of railway and fastener areas
Fig. 5. PointNet++ network architecture
Fig. 6. (a) Fastener point cloud; (b) Labeled point cloud
Fig. 7. (a) Segmentation results of fastener; (b) View of clip point cloud
Fig. 8. (a) Point cloud of clip; (b) Clip image
Fig. 9. (a) The dilated result of clip image; (b) 2D skeleton of clip
Fig. 10. (a) The center of the clip section; (b) The center of clip section after removing the error points
Fig. 11. (a) Skeleton division diagram; (b) Clip gap
Fig. 12. (a)Schematic of standard step block; (b) Schematic of step block imaging; (c) Point cloud of step block; (d) Measurement error of block
Fig. 13. PointNet++ network segmentation accuracy metric graph
Fig. 14. (a) 0.5 mm gap gauge; (b) Clip gap equaling to 9 mm
Fig. 15. Measurement results of clip gaps under different buckle pressures
Fig. 16. (a) measured clip gaps with different dx ; (b) 3D skeleton and gap of clip dy
Fig. 17. (a) dy =0.56 mm; (b) dy =0.84 mm; (c) dy =1.12 mm; (d) dy =1.68 mm; (e) dy =2.24 mm; (f) dy =2.8 mm
Fig. 18. (a) Rusted fastener; (b) Stained fastener; (c) Partial rusted fastener; (d) Clip gap of rusted fastener; (e) Clip gap of stained fastener; (f) Clip gap of partial rusted fastener
Fig. 19. (a) Fasteners measured at night; (b) Clip point cloud; (c) Skeleton and gap of clip; (d) Fasteners measured at noon; (e) Clip point cloud; (f) Skeleton and gap of clip; (g) Measuring fasteners at dusk; (h) Clip point cloud; (i) Skeleton and gap of clip
Fig. 20. (a) Over-tightening fastener scatter plot of clip gap value; (b) Histogram distribution of clip gap
Fig. 21. (a) Normal fastener scatter plot of clip gap value; (b) Histogram distribution of clip gap
Fig. 22. (a) Looseness fastener scatter plot of clip gap value; (b) Histogram distribution of clip gap
Fig. 23. (a) Field measurement of WJ-8 fastener is 14.2 mm; (b) Field measurement of WJ-8 fastener is 15.2 mm; (c) Field measurement of WJ-2 fastener is 13.32 mm; (d) Field measurement of WJ-2 fastener is 15.67 mm
|
Table 1. Hyper-parameters for PointNet++ network training
|
Table 2. Measurement results and comparison for different fasteners
|
Table 3. Accuracy of fastener detection under different allowable errors
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 4. Precision and recall of three method

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



