Suocheng Wang, Shiyun Dong, Shixing Yan, Xiaoting Liu. Fabrication of Micro/Nano Structures on Metal Surfaces by Femtosecond Laser and Its Technical Applications[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(17): 1700005
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 60, Issue 17, 1700005 (2023)
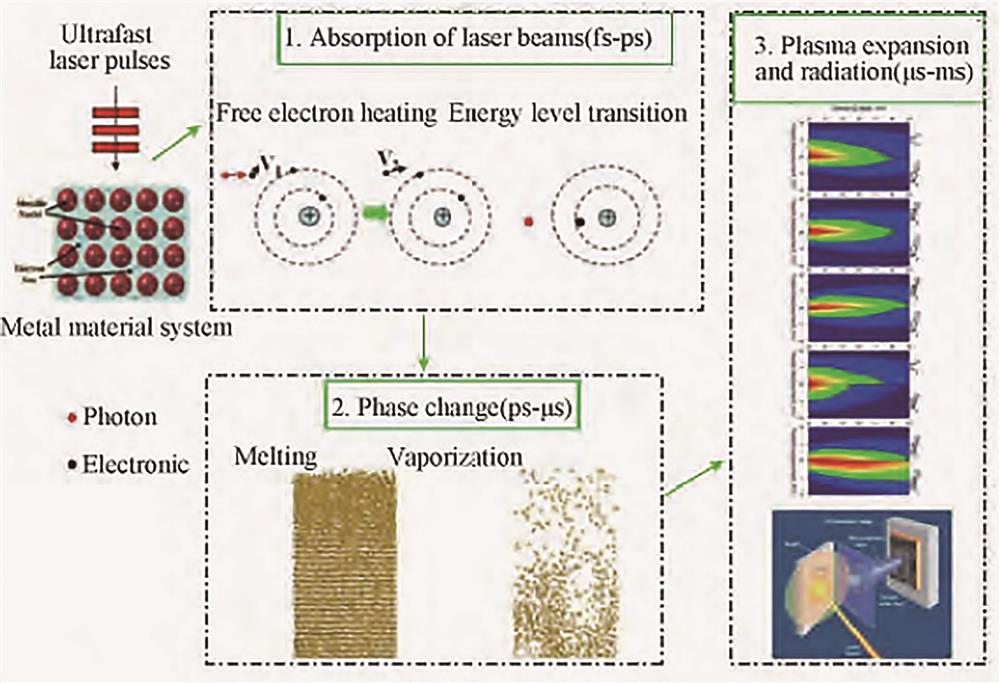
![General process of femtosecond laser interact with metal[21]](/richHtml/lop/2023/60/17/1700005/img_01.jpg)
Fig. 1. General process of femtosecond laser interact with metal[21]
![Optical absorption properties test of micro/nano flower structures constructed on copper surface[31]. (a) Reflectance of bare copper, commercial copper, and copper covered with micro/nano hierarchical structures in the 200-2000 nm wavelength band; (b) reflectance test of commercial copper and copper covered with micro/nano hierarchical structures as the incident angle changes in the 200-800 nm wavelength band](/richHtml/lop/2023/60/17/1700005/img_02.jpg)
Fig. 2. Optical absorption properties test of micro/nano flower structures constructed on copper surface[31]. (a) Reflectance of bare copper, commercial copper, and copper covered with micro/nano hierarchical structures in the 200-2000 nm wavelength band; (b) reflectance test of commercial copper and copper covered with micro/nano hierarchical structures as the incident angle changes in the 200-800 nm wavelength band
Fig. 3. Photothermal conversion performance of micro/nano flower structures constructed on copper[31]. (a) Schematic diagram of photothermal conversion test of copper sheet with micro/nano flower structures; (b) average absorbances of different samples
Fig. 4. Process flow chart of fabricating high-efficiency anti-reflection surfaces on metal surfaces by femtosecond laser pulse implantation[32]
Fig. 5. When the femtosecond laser wavelength was 400 nm, and the polarization direction was parallel to the scanning direction, the surface periodic structure was prepared on the tungsten surface[37]. (a) SEM image of the periodic structure induced by laser; (b) enlarged view of the center position of Fig.(a)
Fig. 6. When the femtosecond laser wavelength was 800 nm, and the polarization direction was parallel to the scanning direction, the surface periodic structure was prepared on the tungsten surface[37]. (a) SEM image of the periodic structure induced by laser; (b) enlarged view of the center position of Fig.(a)
Fig. 7. Preparation of copper hydroxide and copper oxide urchin like micro/nano structures with wide band antireflection properties on copper surface by femtosecond laser composite chemical oxidation[39]. (a) (b) SEM images of the urchin-like arrays; (c) (d) SEM images of nanowires and nanoflowers; (e) (f) SEM images of the nanoflowers fabricated by chemical oxidation alone
Fig. 8. Surface structure and wettability of lotus leaf[43]. (a) Appearance of lotus leaf; (b) infiltration of lotus leaf surface; (c) (d) SEM images of lotus leaf
Fig. 9. Preparation of superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic microporous structures on titanium foil surface by femtosecond laser[50]. (a)-(d) SEM images of microporous; (e)-(h) oil-water separation experiment of titanium foil contains microporous structures
Fig. 10. Preparation of microporous arrays on the surface of copper foil by femtosecond laser spatial light shaping[51]. (a) Optical image of copper sheet with microporous, the left one contains microporous and the right one was pristine copper sheet; (b) microscope picture of microporous; (c)(d) SEM images of microporous on copper sheet
Fig. 11. Experiment of oil-water separation with microporous structure prepared by femtosecond laser spatial light shaping[51]. (a) Oil-water mixture and separation device; (b)(c) oil-water separation process diagram
Fig. 12. Morphology of the titanium sheet processed by the combination of femtosecond laser combined chemical oxidation[53]. (a) Three-dimensional image of the micro/nano structures; (b) (c) SEM images of the micro/nano structures
Fig. 13. Preparation of TiO2 micro/nano structures by femtosecond laser combined chemical oxidation and research its photocatalytic performances[53]. (a) Test of light reflection performances of titanium sheet covered with various TiO2 micro/nano structures; (b) spectral absorption test of organic dyes after TiO2 degradation; (c) photodegradation rate test of TiO2 prepared by composite method and chemical oxidation alone; (d) cyclic performance test of photodegradation of TiO2
Fig. 14. Preparation of TiO2 nanotubes by femtosecond laser processing combined chemical oxidation[54]. (a) Original titanium sheet; (b) (c) preparation of TiO2 nanotubes by anodization alone; (d) microstructure arrays fabricated by femtosecond laser; (e) hierarchical TiO2 nanotubes; (f) amorphous layer on the surface of titanium sheet after femtosecond laser processing; (g) (h) schematic diagram of hierarchical structures
Fig. 15. Application of femtosecond laser processing metal materials in aerospace. (a) Micro-holes of engine fuel injector fabricated by femtosecond laser[55]; (b) air film holes array of turbine blade fabricated by femtosecond laser[56]; (c) heat sink fabricated on metal surface by femtosecond laser[57]
Fig. 16. Preparation of micro/nano structures on titanium alloy by femtosecond laser processing and test its anti-icing performance[63]. (a1)-(a4) Freezing process of droplets when the scanning speed was 600 mm/s; (b1)-(b4) freezing process of droplets when the scanning speed was 2000 mm/s; (c1)-(c4) freezing process of droplets when the scanning speed was 5000 mm/s
Fig. 17. Femtosecond laser fabricates micro/nano structures with different morphologies on copper surface and tests its anti-icing[64]. (a) (b) SEM images of copper surface morphologies when the laser scanning speed was 20 mm/s; (c) (d) SEM images of copper surface morphologies when the laser scanning speed was 60 mm/s; (e) (f) SEM images of copper surface morphologies when the laser scanning speed was 100 mm/s; (g) freezing delay test of copper sheets at low temperatures
Fig. 18. Principle of making corneal flap with femtosecond laser[66]
Fig. 19. Preparation of micro/nano structures of zirconium-based materials by femtosecond laser processing[71]. (a) SEM image of the materials processed by femtosecond laser; (b) (c) magnification images of material surface
Fig. 20. Preparation of anticoagulant and antibacterial micro/nano structures on nitinol alloy by temporally shaped femtosecond laser[72]. (a) Single-pulse laser shaping into double-pulse; (b) preparation of porous structures; (c) anticoagulant and antibacterial performance test of porous structure; (d) anticoagulant and antibacterial performance test of nitinol alloy bare sheet
|
Table 1. Femtosecond laser preparation of micro/nano structures with different morphologies on common metal materials
|
Table 2. Application of femtosecond laser fabrication of metal surface micro/nano structures in environmental engineering
|
Table 3. Application of femtosecond laser fabrication of metal surface micro/nano structures in aerospace
|
Table 4. Application of femtosecond laser fabrication of metal surface micro/nano structures in biomedicine
Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



