Chonghao GAN, Wenlin FENG, Xiangzhi LIU, Xiaozhan YANG, Xiangmeng LU, Dajian CUI, Cong CHEN. Progress in analysis of large field of view achromatic function and zoom technology of metalenses (cover paper)[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2025, 54(2): 20240441
Search by keywords or author
- Infrared and Laser Engineering
- Vol. 54, Issue 2, 20240441 (2025)
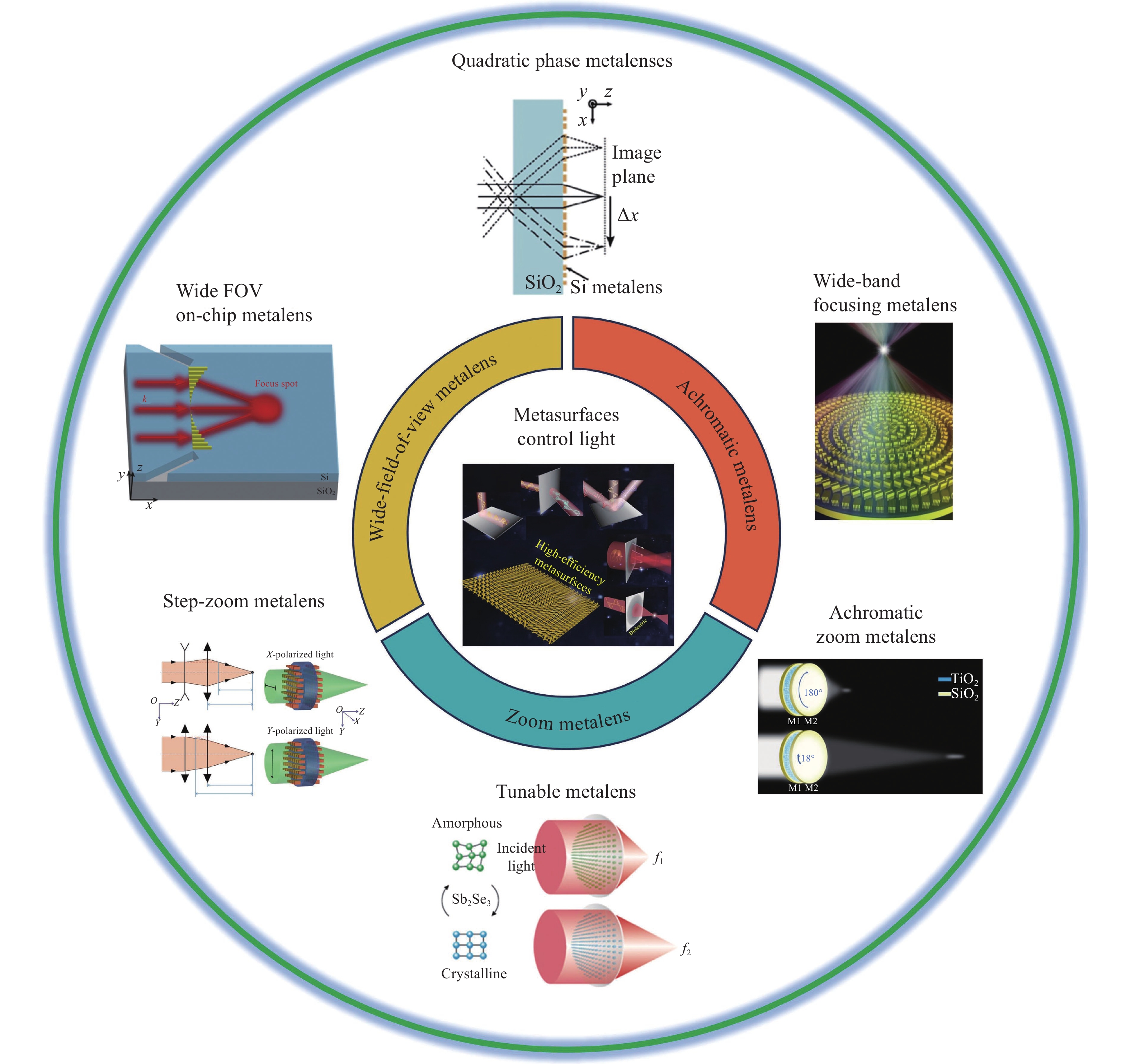
Fig. 1. Large field of view, achromatic, zoom metalenses
![Generalized Fresnel's law optical path diagram[3]](/richHtml/irla/2025/54/2/20240441/img_2.jpg)
Fig. 2. Generalized Fresnel's law optical path diagram[3]
Fig. 3. (a) The incident light is x -polarized light, and the stepping zoom metalens is focused on the pattern[14]; (b) The incident light is y -polarized light, and the step zoom metalens is focused on the lens[14]; (c) On-chip wide FOV metalenses[10]
Fig. 4. (a) Structural diagram of a perpendicular curve light field metalens[35]; (b) Focus diagram of perpendicular curve light field metalens[35]; (c) Ray trajectories through the lens[35]; (d) Focusing diagram of metalenses based on the surface of disordered media[36]; (e) Focus view of a single-layer large-field metalens in the mid-infrared band[37]; (f) Light intensity distribution of a single-layer large-field metalens in the mid-infrared band along the z -axis[37]
Fig. 5. Device architecture and metalens fabrication[38]. (a) Schematic of the optical setup for MIID; (b) Photograph of the highly compact MIID; (c) Top-view optical microscope image and side-view SEM image of the fabricated
Fig. 6. (a) Three layer metal metasurface structure [43]; (b) Metal metalenses for color imaging demonstration[43]; (c) Focus view of a metal metalens[43]; (d) Focus view of a multi-region metalens [44]; (e) Focus view of a graphene oxide metalens[45]
Fig. 7. (a) Focusing diagram of a metalens of complementary structure and its imaging[46]; (b) Focus diagram of an elliptical cylindrical metalens[48]; (c)Focus diagram of a hexagonal structure metalens[49]; (d) Focus diagram of a rectangular structure metalens[51]
Fig. 8. (a) Metalenses anisotropic nanostructured for imaging of resolution test maps of the USAF[53]; (b) Focus diagram of an anisotropic nanostructured metalens[53]; (c) Structural diagram of mid-infrared achromatic metalens[54]; (d) Mid-infrared achromatic metalens focus diagram[54]; (e) Structural diagram of Longwave infrared achromatic metalens[54]; (f) Longwave infrared achromatic metalens focus diagram[54]; (g) Schematic diagram of the odd-ring metalens and the combined metalens and their corresponding light intensity along the z -axis[56]; (h) Multi-region metalens focus diagram[56]
Fig. 9. (a) Schematic diagram of Ge2Se2Te5 metalens[64]; (b) Focusing diagram Ge2Se2Te5 metalens[64]; (c) Schematic diagram of Sb2Se3 metalens[13]; (d) Focusing diagram based on Sb2Se3 metalens[13]
Fig. 10. (a) Focusing diagram of a large chromatic aberration dispersion zoom metalens[65]; (b) Large chromatic aberration dispersion zoom metalens imaging test for USAF resolution test diagram[65]; (c) Structural diagram of a double-layer metasurface zoom lens[67]; (d) Comparison of theoretical and actual focal lengths at different rotation angles of metasurfaces[67]
|
Table 1. Review of the performance of wide FOV metalenses
|
Table 2. Review of the performance of achromatic metalenses
|
Table 3. Review of the performance of zoom metalenses

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



