Tiancheng WANG, Wangtao YU, Weiyun CHEN, Zhongyi GUO. Research advances on Fourier single-pixel imaging technology (invited)[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2024, 53(9): 20240378
Search by keywords or author
- Infrared and Laser Engineering
- Vol. 53, Issue 9, 20240378 (2024)
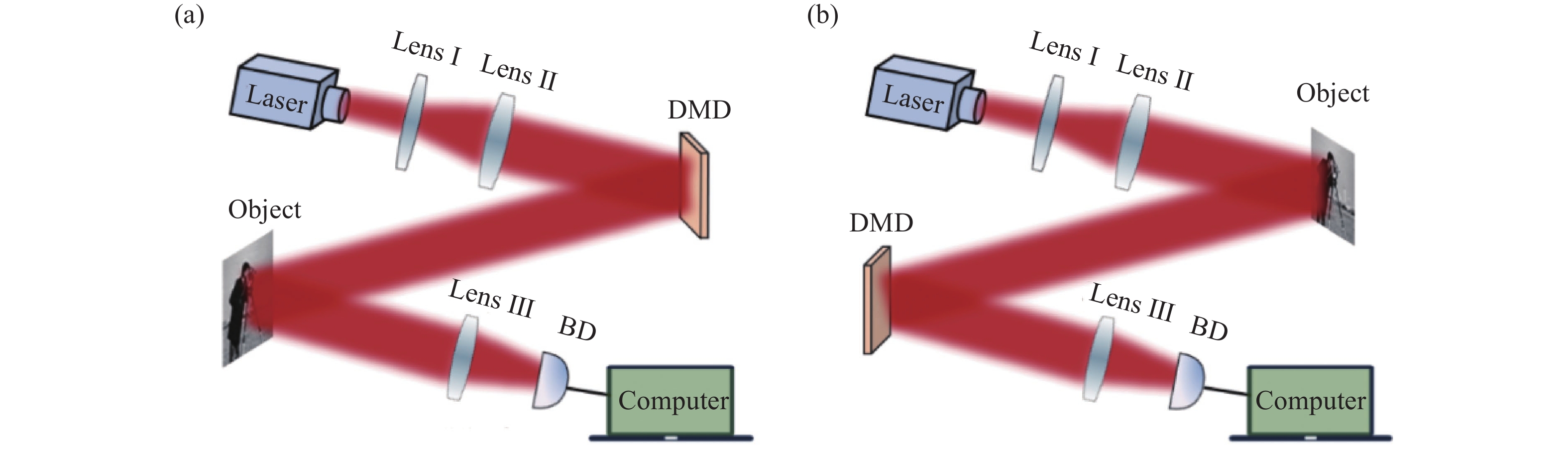
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the SPI. (a) The active SPI; (b) The passive SPI
![Schematic diagram of the synthesis and decomposition of 2D image based on Fourier forward and inverse transforms [37]](/richHtml/irla/2024/53/9/20240378/img_2.jpg)
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of the synthesis and decomposition of 2D image based on Fourier forward and inverse transforms [37]
Fig. 4. (a) The temporal dithering strategy; (b) The spatial dithering strategy; (c) The reconstructed Fourier spectra and images using different binarization methods[40]
Fig. 5. (a) The temporal dithering strategy; (b) The signal dithering strategy; (c) The reconstructed images under different spectral coverage[41]
Fig. 6. (a) Error diffusion kernels of Floyd-Steinberg and Zhang-Qi; (b) Eight different image dithering scanning strategies; (c) Different scanning methods (top row) and corresponding partial amplification (bottom row) based on Zhang-Qi dithering strategies; (d) The experimental results of 3D target scene[42]
Fig. 7. (a) Schematic diagram based on Gaussian random sampling [44]; (b) The reconstruction results at different DMD refresh rates [44]; (c) Schematic diagram based on sparse sampling [45]; (d) The reconstruction results under different sampling methods [45]
Fig. 8. (a) Flowchart of adaptive FSPI based on Fourier domain radial correlation [49]; (b) Schematic diagram of the adaptive FSPI based on DQN [50]; (c) Adaptive FSPI scheme based on the AuSamNet [51]
Fig. 9. (a) Schematic diagram of multi-block FSPI via frequency division multiplexed modulation [52]; (b) The reconstruction results of the target at a sampling rate of 1% under different signal-to-noise ratios [52]; (c) Schematic diagram of SPI for high performance based on optimized sinusoidal patterns [54]; (d) The reconstruction results of the target at a sampling rate of 20% under different signal-to-noise ratios [54]
Fig. 10. (a) Representation of nonlocal 3D sparsity in the transform domain; (b) The reconstruction results of different algorithms; (c) The experimental reconstruction results under different sampling rates[55]
Fig. 11. (a) The generative adversarial network architecture [59]; (b) Comparison of reconstruction results under different methods [59]; (c) Schematic diagram of high-resolution iterative reconstruction based on diffusion model [60]; (d) Comparison of reconstruction methods under different sampling rates [60]
Fig. 12. (a) Schematic diagram of dual-contour data processing based on the FSPI [67]; (b) Edge detection method based on the FSPI [76]
Fig. 13. [77] (a) Schematic diagram of polarized computational ghost imaging in scattering system with half-cyclic sinusoidal patterns; (b) The reconstruction results of different methods in the same scattering system
|
Table 1. Comparison of three different dithering strategies
|
Table 2. Comparison of different sampling-path strategies
|
Table 3. Comparison of different reconstruction algorithms

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



