[62] M. D. Carlo et al. Design rules of a microscale PT-symmetric optical gyroscope using group IV platform. J. Lightw. Technol., 36, 3261(2018).
Search by keywords or author
- Photonics Insights
- Vol. 4, Issue 1, R02 (2025)
References
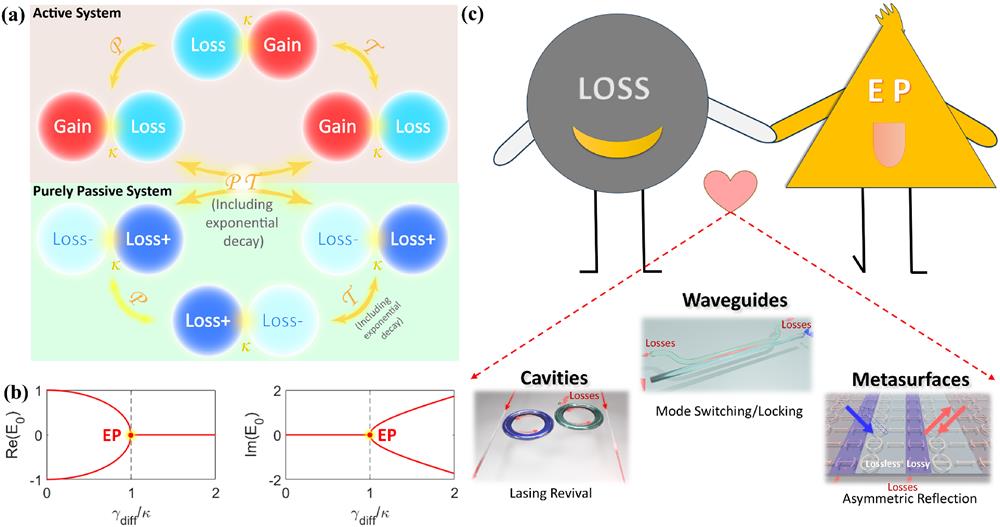
Shaohua Dong, Heng Wei, Zhipeng Li, Guangtao Cao, Kun Xue, Yang Chen, Cheng-Wei Qiu, "Exceptional-point optics with loss engineering," Photon. Insights 4, R02 (2025)
Download Citation
Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



