Wenfeng Yang, Dehui Lin, Mian Zhong, Shaolong Li, Ziran Qian, Guochun Liu, Yu Cao, Yi Xu, Sai Zhang, Guo Li. Controllability of Laser Removal of Aircraft Skin Paint Layer Based on Response Surface Analysis[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(15): 1514004
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 60, Issue 15, 1514004 (2023)
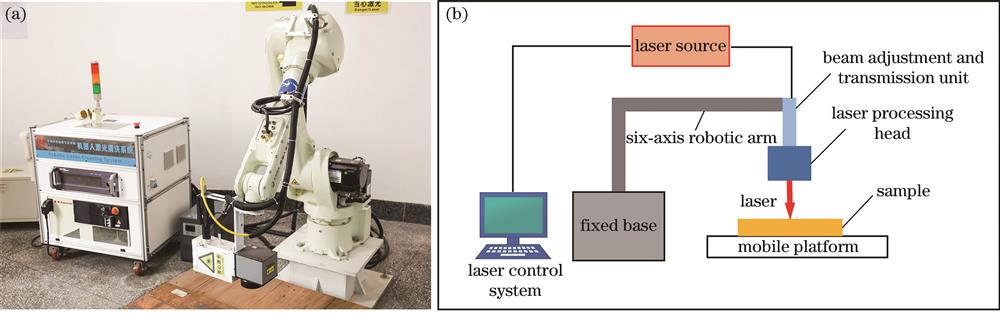
Fig. 1. Laser processing equipment diagram and process diagram. (a) Laser processing equipment; (b) schematic diagram of the process
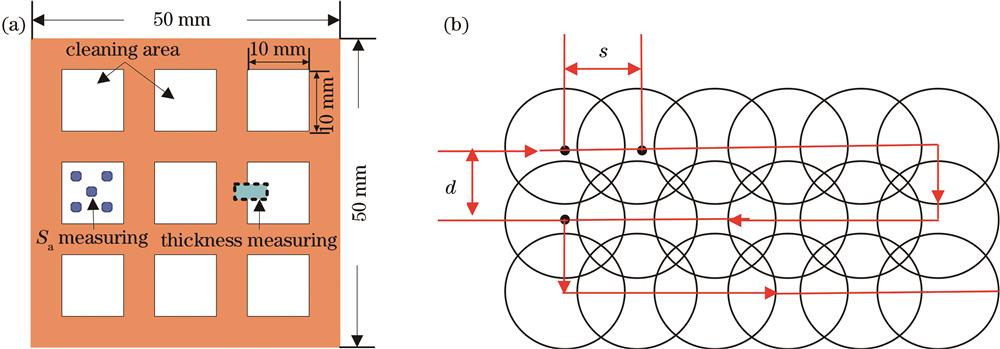
Fig. 2. Schematic of laser cleaning. (a) Cleaning area; (b) path of spot scanning
Fig. 3. Description of paint removal thickness measurement method
Fig. 4. Illustration of the Box-Behnken experimental design with three factors and three levels
Fig. 5. Effect of laser multiparameter coupling on T
Fig. 6. Interaction of laser power and number of scans on the thickness of paint removal. (a) Contour graph; (b) response graph
Fig. 7. Effect of laser multiparameter coupling on Sa
Fig. 8. Schematic diagram of the lap joint shape of the crater
Fig. 9. Interaction of laser power and number of scans on Sa. (a) Contour graph; (b) response graph
Fig. 10. Macro effect and measurements of the samples obtained in scheme 1. (a) Macro effect; (b) thickness of the paint layer removal; (c) surface roughness
Fig. 11. Macro effect and measurements of the samples obtained in scheme 2. (a) Macro effect; (b) thickness of the paint layer removal; (c) surface roughness
|
Table 1. Main parameters of the laser
| |||||||||||||||||||
Table 2. Test factor and level coding table
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 3. Response surface experimental design matrix and experimental results
|
Table 4. Analysis of variance for paint removal thickness model
|
Table 5. Analysis of variance for surface roughness model
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 6. Optimization criteria and weight
|
Table 7. Optimization results of parameter coupling and experimental verification

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



