Yousi Yang, Dan Li, Encai Ji, Xiaofeng Ji, Bing Tian, Ping Yan, Mali Gong, Qirong Xiao. Thulium-Doped Fiber Laser and Its Applications in Laser Lithotripsy: Progress and Prospect[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2023, 60(15): 1500007
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 60, Issue 15, 1500007 (2023)
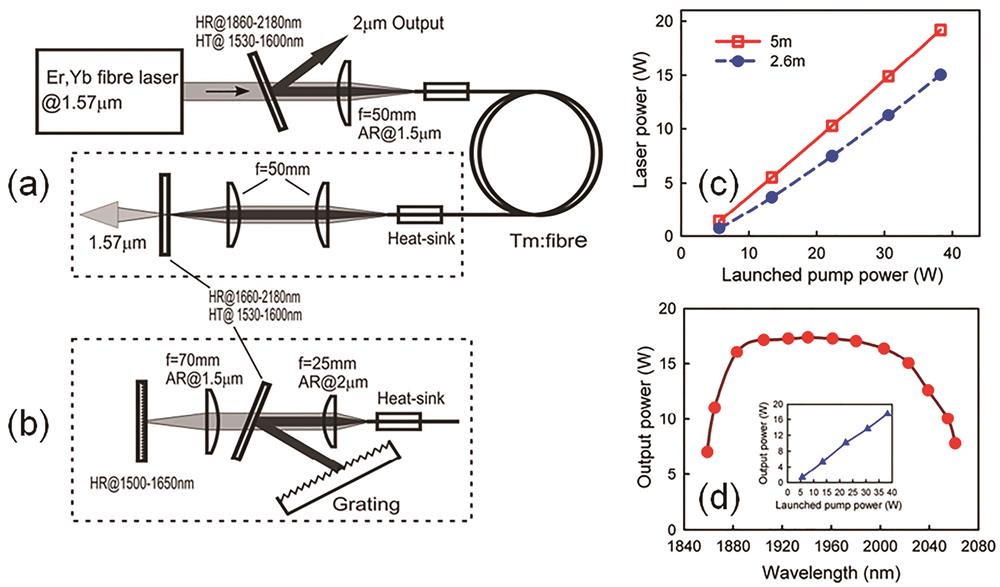
![Cladding pumped thulium-doped fiber laser. (a) Schematic of laser; (b) external cavity for tunable operation; (c) output power versus launched pump power; (d) output power versus operating wavelength for cladding pumped 2.6 m fiber (inset: output power at 1941 nm versus launched pump power)[6]](/richHtml/lop/2023/60/15/1500007/img_01.jpg)
Fig. 1. Cladding pumped thulium-doped fiber laser. (a) Schematic of laser; (b) external cavity for tunable operation; (c) output power versus launched pump power; (d) output power versus operating wavelength for cladding pumped 2.6 m fiber (inset: output power at 1941 nm versus launched pump power)[6]
![Thulium-doped fiber laser amplifier with output power of 300 W. (a) Schematic of laser; (b) output power versus pump power[8]](/richHtml/lop/2023/60/15/1500007/img_02.jpg)
Fig. 2. Thulium-doped fiber laser amplifier with output power of 300 W. (a) Schematic of laser; (b) output power versus pump power[8]
Fig. 3. 600 W single mode single frequency thulium-doped fiber laser amplifier. (a) Schematic of laser amplifier; (b) output power curve of single frequency amplifier; (c) output spectrum at 608 W (inset: OSA resolution limit of 0.05 nm)[2]
Fig. 4. 1000 W thulium-doped all-fiber laser. (a) Schematic of laser; (b) output power versus pump power[3]
Fig. 5. 530 W thulium-doped fiber laser with all-fiber structure. (a) Schematic of laser; (b) spectrum with the output power of 500 W[12]
Fig. 6. Tunable thulium-doped fiber laser at 2 µm. (a) Schematic of laser (internally marked a is the tuning structure and b is the free-running structure); (b) output power versus pump power; (c) output power of the tunable laser versus operating wavelength (inset: output power at 1930 and 1990 nm versus launched pump power); (d) spectral output of the grating-based laser and the free-running structures[15]
Fig. 7. Research scheme of high power tunable thulium fiber laser[11]
Fig. 8. 342 W narrow linewidth continuous-wave thulium-doped fiber laser with all-fiber structure. (a) Schematic setup of the seeder; (b) schematic setup of the two-stage amplifiers; (c) output power versus incident pump power[26]
Fig. 9. High-power thulium-doped superfluorescent fiber source. (a) Schematic of light source; (b) spectrum for the copropagating ASE; (c) spectrum for the counterpropagating ASE[30]
Fig. 10. Output signal in quasi-continuous-wave mode and continuous-wave mode
Fig. 11. 1940 nm quasi-continuous-wave thulium-doped fiber laser. (a) Schematic of the laser; (b) output power versus pump power at 793 nm; (c) output spectrum at the average power of 10 W[38]
Fig. 12. 564 W quasi-continuous-wave thulium-doped fiber laser. (a) Schematic of laser; (b) peak output power at 10 Hz and 5% duty cycle; (c) near-field (top) and far-field (bottom) beam profiles[39]
Fig. 13. Three quasi-continuous-wave thulium-doped fiber laser products. (a) TLM-50/500-QCW from IPG; (b) IFL QCW 650 from Futonics; (c) MIRON150/750 laser prototype from MIL MED TECH
Fig. 14. Single mode thulium fiber oscillator[42]
Fig. 15. Water absorption coefficient at different wavelengths[55]
Fig. 16. SOLTIVE™ Premium medical quasi-continuous-wave thulium-doped fiber laser system from Olympus
Fig. 17. LKSPTm120 laser treatment equipment from LAKH of China
|
Table 1. Main researches on high power thulium-doped continuous-wave fiber laser in recent 20 years
|
Table 2. Main researches on tunable thulium-doped continuous-wave fiber laser in recent 20 years.
|
Table 3. Main researches on narrow-linewidth thulium-doped continuous-wave fiber laser in recent 10 years
|
Table 4. Main researches on thulium-doped ASE continuous-wave source in recent 15 years
|
Table 5. Parameters of several typical products for quasi-continuous-wave thulium-doped fiber laser
|
Table 6. Typical research parameters of nanosecond short-pulsed thulium-doped fiber laser
|
|
Table 8. System parameters of several main medical quasi-continuous-wave thulium-doped fiber lasers
Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



