Rui LUO, Yuhe ZHANG, Naqing MAO. Development of a method for measuring low energy electron beam irradiation parameters by calorimetry and step stacking[J]. Journal of Radiation Research and Radiation Processing, 2025, 43(1): 010701
Search by keywords or author
Journals >Journal of Radiation Research and Radiation Processing >Volume 43 >Issue 1 >Page 010701 > Article
- Journal of Radiation Research and Radiation Processing
- Vol. 43, Issue 1, 010701 (2025)
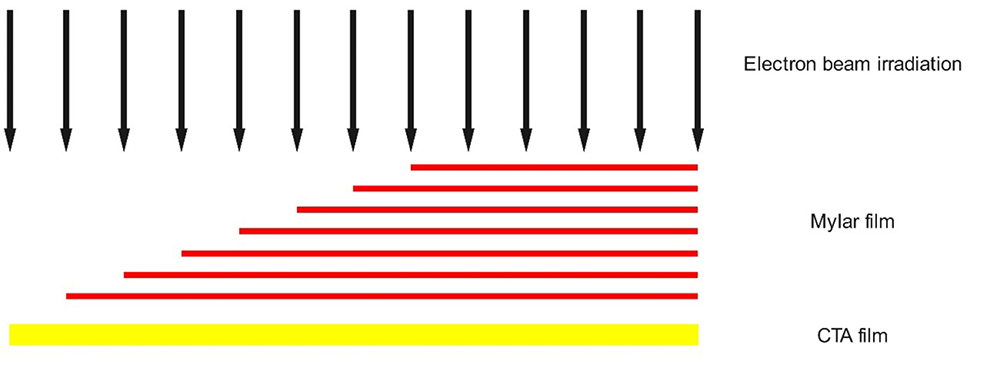
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of low energy electron energy measurement

Fig. 2. Calorimeter structure
Fig. 3. Dose distribution of CTA film measurement with length, dotted line indicates the background baseline of the film dosimeter, red line indicates the number of Mylar film layers (color online)
Fig. 4. Simulation of energy deposition of electron beam in graphite material (density is 1.77 g/cm3). The generated electrons penetrate the 10 μm titanium window, 5 cm air, and Mylar film for complete energy deposition
Fig. 5. Relationship between absorbed dose and reciprocal of the moving speed (a), and beam intensity (b)
Fig. 6. Comparison of specific heat value of graphite before and after irradiation
Fig. 7. Temperature change curve with time before and after irradiation
|
Table 1. Electron range for the energy from 100 keV to 300 keV
|
Table 2. Comparison of measurement results between calorimeter and alanine dosimeter under the same condition
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 3. Uncertainty evaluation of 140 keV electron beam irradiation absorbed dose measurement

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



