Xiangxia WEI, Xiaofei ZHANG, Kailong XU, Zhangwei CHEN. Current Status and Prospects of Additive Manufacturing of Flexible Piezoelectric Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 965
Search by keywords or author
- Journal of Inorganic Materials
- Vol. 39, Issue 9, 965 (2024)
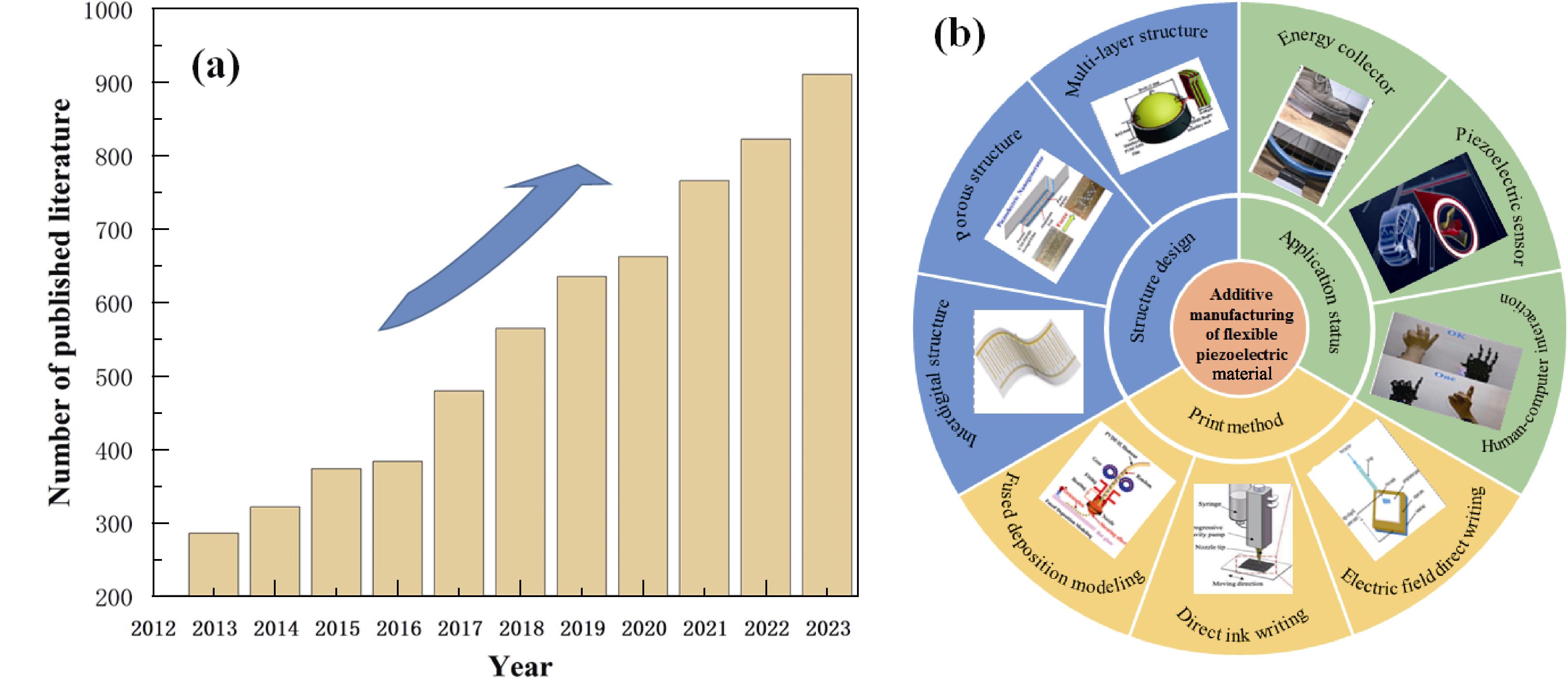
1. Overview of additive manufacturing of flexible piezoelectric materials
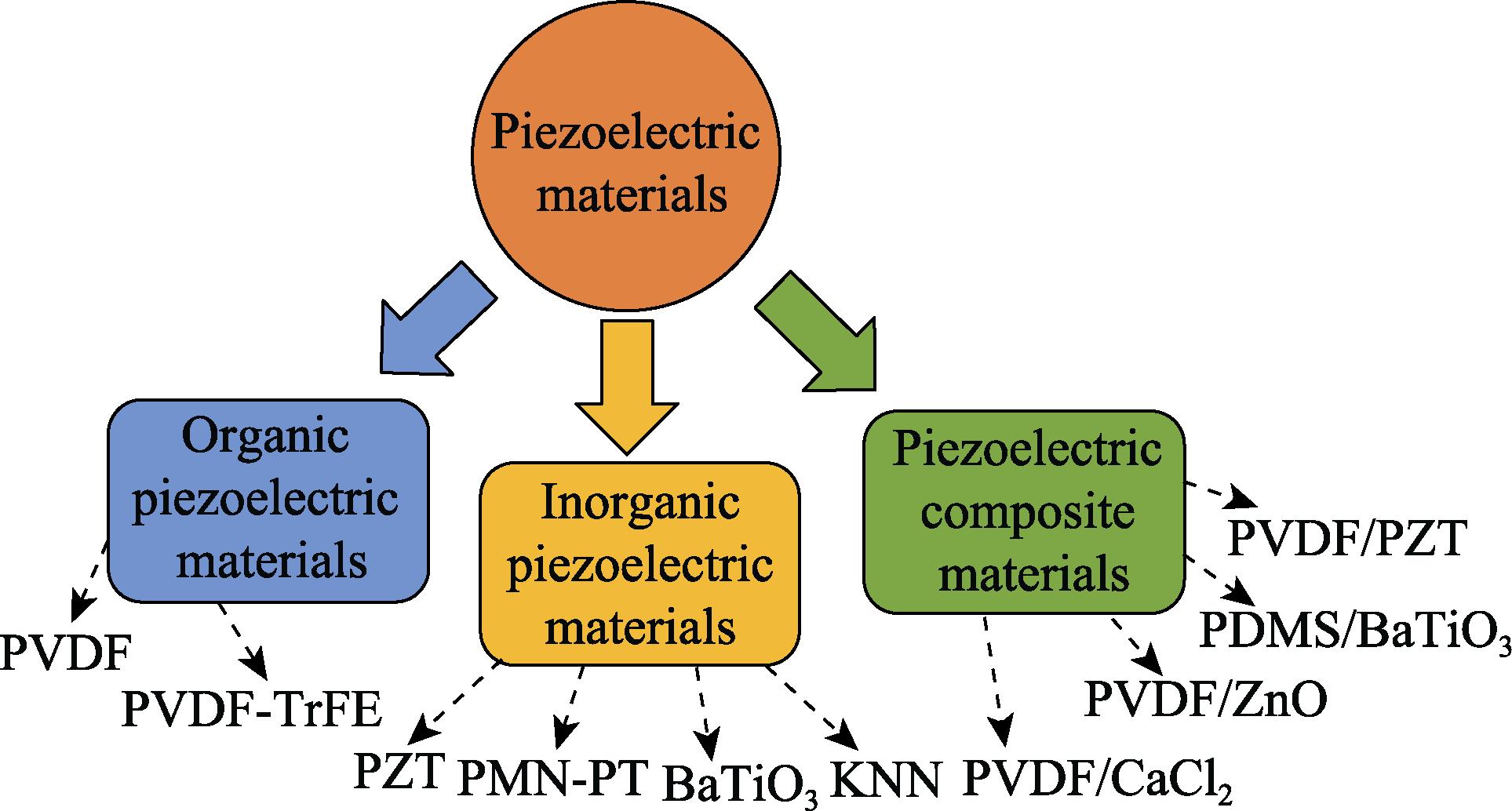
2. Summary of classification of piezoelectric materials
3. Schematic diagrams of additive manufacturing processes
4. Schematic diagrams of multi-layer structures of flexible piezoelectric materials
5. Schematic diagrams of porous structures of flexible piezoelectric materials
6. Schematic diagrams of interdigital structures of flexible piezoelectric materials
7. Application of 3D-printed flexible piezoelectric materials in energy harvesting
8. Application of 3D-printed flexible piezoelectric materials in piezoelectric sensing
9. Application of 3D-printed flexible piezoelectric materials in human-computer interaction
10. Application of 3D-printed flexible piezoelectric materials in bioengineering
|
Table 1. Performance comparison of piezoelectric energy harvesters manufactured by 3D printing technology

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



