Haojie MA, Cong ZHANG, Huazheng WU, Chengfei GUO, Shaowei JIANG. Developments and applications of intraoperative label-free microscopic imaging techniques (invited)[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2024, 53(9): 20240384
Search by keywords or author
- Infrared and Laser Engineering
- Vol. 53, Issue 9, 20240384 (2024)
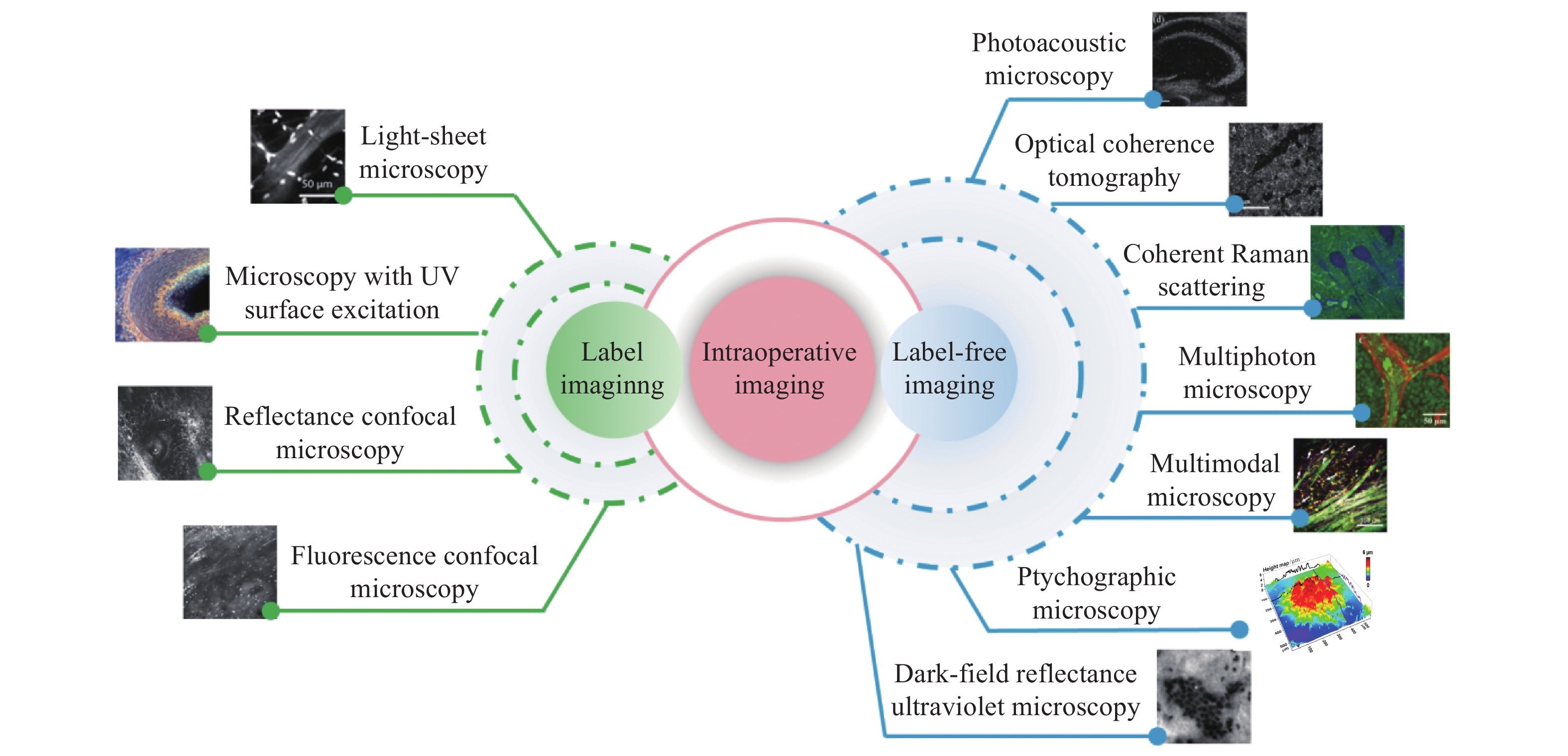
Fig. 1. Classification of intraoperative optical microscopy imaging techniques

Fig. 2. Schematic of photoacoustic microscopy
Fig. 3. Schematic of optical coherence tomography
Fig. 4. Schematic of coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering imaging
Fig. 5. Schematic of stimulated Raman scattering imaging
Fig. 6. Schematic of multiphoton fluorescence microscopy imaging
Fig. 7. (a) Schematic of Fourier ptychographic microscopy[79]; (b) Schematic of coded ptychographic microscopy[80]
Fig. 9. Stages of tumor cell invasion around connective tissue proliferation[93]
Fig. 10. Conventional microscopy, Optical coherence tomography microscopy, and dermatoscopy of (a) nodular micronodular basal cell carcinoma; (b) invasive basal cell carcinoma; (c) nodular superficial basal cell carcinoma; (d) superficial diffuse malignant melanoma; (e) basal cell carcinoma of the right eyebrow; (f) pigmented actinic keratosis on frontal LC-OCT image and RCM image, and vertical LC-OCT image and OCT image[101]
Fig. 11. Virtual H&E stained slides based on SRS imaging technology[109]
Fig. 12. TPEF, SHG, overlaid TPEF/SHG and corresponding H&E images of the normal human brain, gliomas with the deposition of collagen bundles in tumor microenvironment[110]
|
Table 1. Comparison of imaging performance for the label-free microscopy imaging techniques

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



