An-ran JIN, He LI. Hybrid Continuous-discrete Variable Quantum Key Distribution[J]. Study On Optical Communications, 2023, 49(3): 24
Search by keywords or author
- Study On Optical Communications
- Vol. 49, Issue 3, 24 (2023)
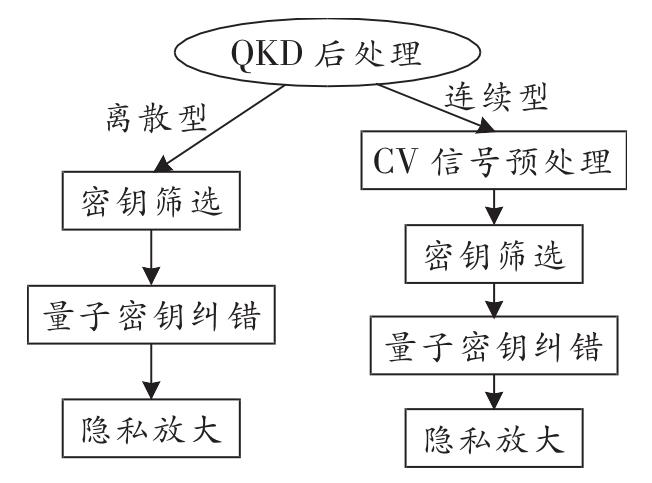
Fig. 1. A diagram of QKD post-processing
![An architecture of coherent-state discrete-modulated CVQKD protocol[19]](/richHtml/gtxyj/2023/49/3/24/2303005-F002.jpg)
Fig. 2. An architecture of coherent-state discrete-modulated CVQKD protocol[19]
Fig. 3. Qubit extraction in the squashing model[19]
Fig. 4. Key generation rate of the coherent-state discrete-modulated CVQKD protocol against channel attenuation[19]
Fig. 5. The receiver setup of the coherent-detection polarization-encoding CVQKD protocol[20]
Fig. 6. Key generation rate of the coherent-detection polarization-encoding CVQKD protocol, compared with the key rate under perfect SPD[20]
Fig. 7. An architecture of coherent-detection time-bin encoding protocol[21]
Fig. 8. Key generation rates of the coherent-detection time-bin encoded protocol[21]

Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



