Lujia Jin, Yang He, Luxi Qu, Chi Zhang, Meiqi Li, Peng Xi. Analysis of New Super-Resolution Microscopy Technology[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2018, 55(3): 030006
Search by keywords or author
- Laser & Optoelectronics Progress
- Vol. 55, Issue 3, 030006 (2018)
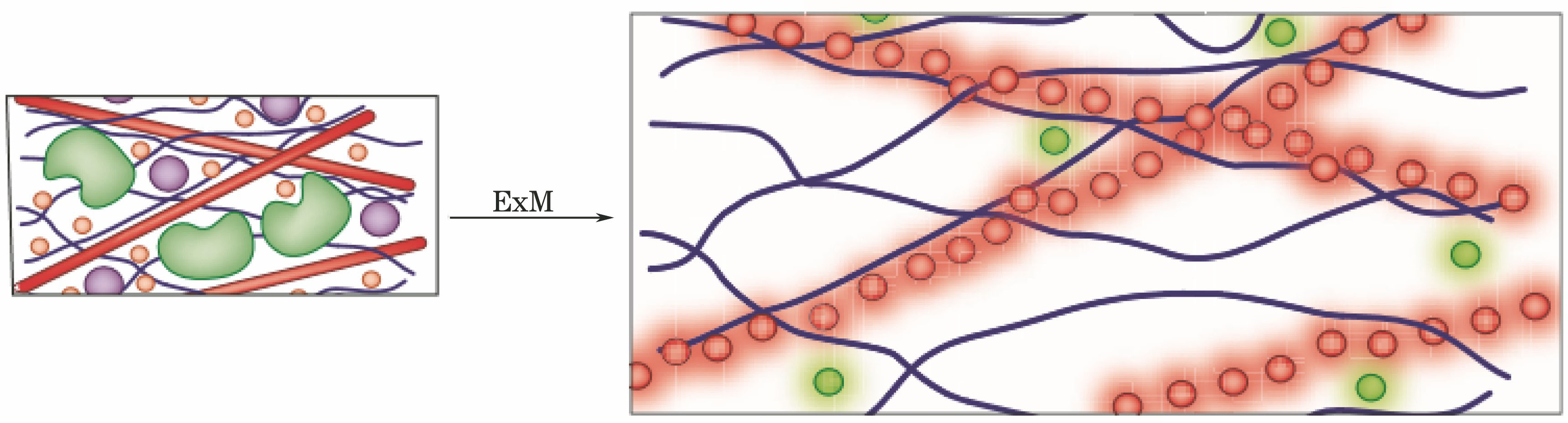
![Working principle of ExM[12]](/richHtml/lop/2018/55/3/030006/img_1.jpg)
Fig. 1. Working principle of ExM[12]
![Mammalian brain circuitry observed by proExM[14]. (a) Pre-expansion and (b) post-expansion wide field imaging pictures when virus with green fluorescent protein injected in cortex of macaque; (c) image taken with a confocal microscope and stereoscopically rendered of the boxed region in Fig. 2(b)](/richHtml/lop/2018/55/3/030006/img_2.jpg)
Fig. 2. Mammalian brain circuitry observed by proExM[14]. (a) Pre-expansion and (b) post-expansion wide field imaging pictures when virus with green fluorescent protein injected in cortex of macaque; (c) image taken with a confocal microscope and stereoscopically rendered of the boxed region in Fig. 2(b)
Fig. 3. Diagram of iExM
Fig. 4. Schematics of the PSIM system[18]
Fig. 5. Fluorescent particles with diameter of 100 nm obtained by PSIM[18]. (a) Conventional fluorescence microscopic image; (b) reconstructed PSIM image; (c) corresponding scanning electron microscope image; (d) Fourier transform of Fig. 5(a); (e) Fourier transform of Fig. 5(b); (f) fluorescence intensity distribution
Fig. 6. Waveguide chips. (a) Rib waveguide; (b) strip waveguide
|
Table 1. Main differences between chip-based ESI and dSTORM technologies
|
Table 2. Main differences between SPoD and SDOM technologies based on fluorescence polarization microscope
|
Table 3. Comparison of several new imaging methods
Set citation alerts for the article
Please enter your email address



